Environmental health is a multifaceted discipline focused on the interactions between humans and their environment and how these interactions impact human health and well-being. It encompasses a wide range of scientific fields, including toxicology, epidemiology, exposure assessment, and risk management. Understanding environmental health is crucial for safeguarding public health and promoting sustainable development.
Defining Environmental Health
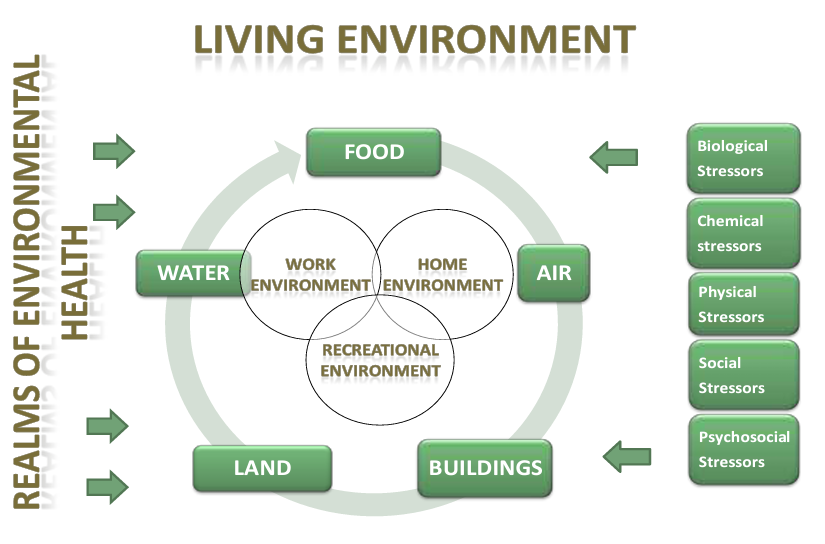
At its core, environmental health seeks to prevent disease and promote health by reducing exposure to adverse environmental factors. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines environmental health as "those aspects of human health, including quality of life, that are determined by physical, chemical, biological, social, psychosocial and aesthetic factors in our environment." It also refers to the theory and practice of assessing, correcting, controlling, and preventing those factors in the environment that can potentially affect adversely the health of present and future generations.
This definition underscores the broad scope of environmental health, extending beyond purely physical or chemical hazards to include social, psychological, and aesthetic elements. This holistic approach acknowledges the complex interplay of factors that contribute to human health.
Key Components of Environmental Health
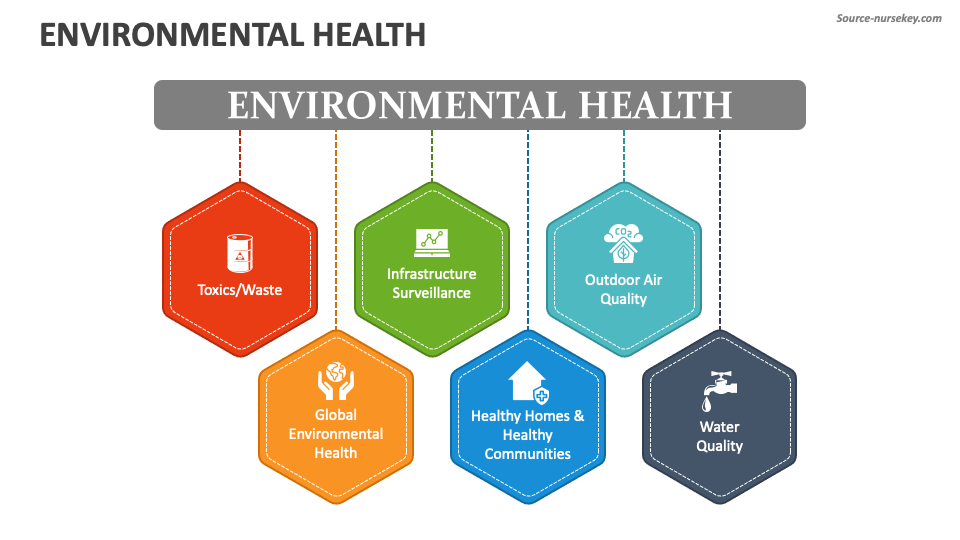
Environmental health can be broadly categorized into several key areas, each addressing specific environmental hazards and their impact on human health.
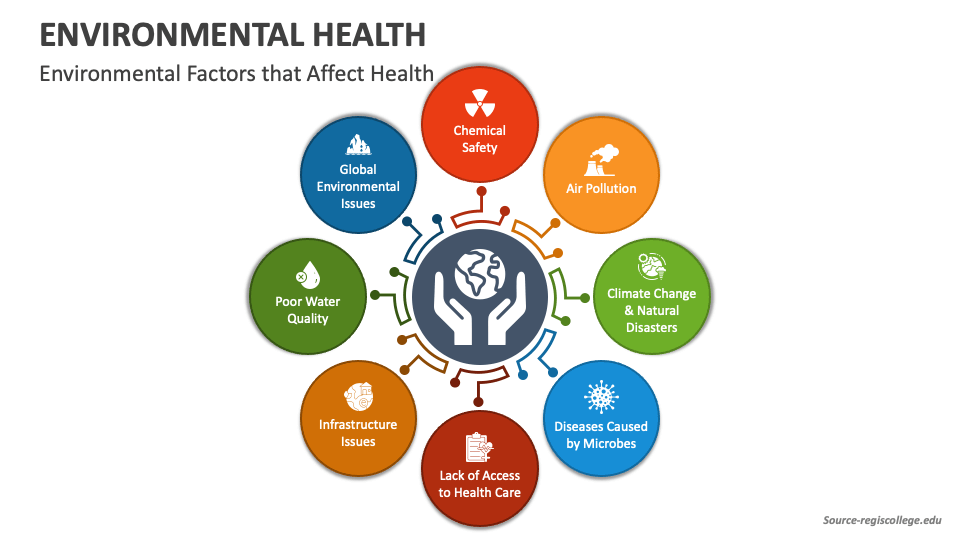
1. Air Quality
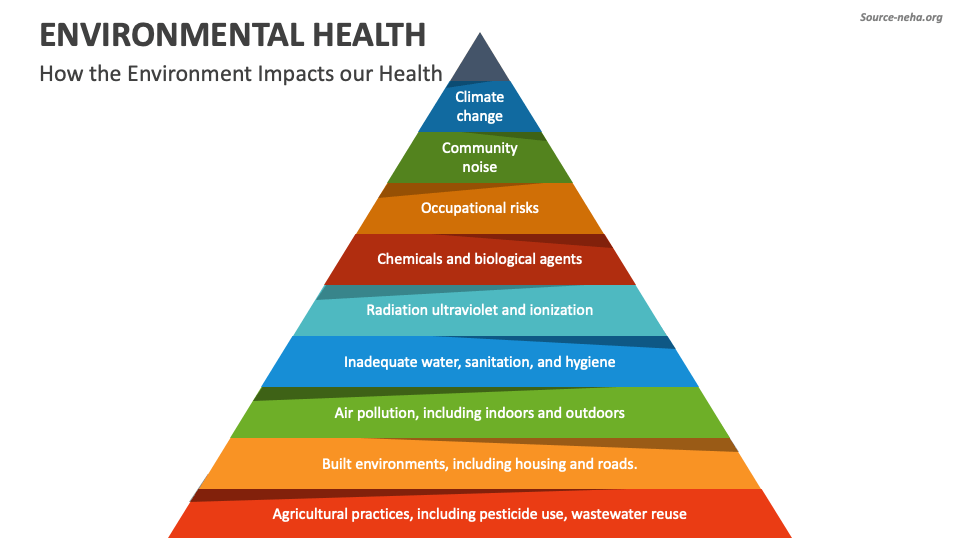
Air quality encompasses both outdoor and indoor air pollution. Outdoor air pollution stems from sources like vehicle emissions, industrial processes, and burning fossil fuels. Common pollutants include particulate matter (PM), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), and sulfur dioxide (SO2). These pollutants can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and even cancer.
Indoor air pollution, often overlooked, can be equally harmful. Sources include combustion appliances (like gas stoves), building materials (like asbestos and lead paint), mold, cleaning products, and tobacco smoke. Poor ventilation exacerbates these issues. Exposure to indoor air pollutants can lead to respiratory illnesses, allergies, and other health problems.
2. Water Quality
Access to clean and safe drinking water is fundamental to human health. Water quality concerns arise from both natural and human-induced sources. Natural contaminants include arsenic and fluoride, which can occur in groundwater. Human-induced contaminants include sewage, industrial waste, agricultural runoff (containing pesticides and fertilizers), and pharmaceuticals.
Contaminated water can transmit infectious diseases like cholera, typhoid fever, and dysentery. It can also cause chronic health problems due to exposure to toxic chemicals. Ensuring access to safe drinking water requires effective water treatment and distribution systems, as well as proper management of wastewater and pollution sources.
3. Food Safety
Food safety focuses on preventing foodborne illnesses and ensuring that food is safe for consumption. Hazards in the food supply can be biological (bacteria, viruses, parasites), chemical (pesticides, heavy metals), or physical (foreign objects). Foodborne illnesses can cause a range of symptoms, from mild gastrointestinal upset to severe, life-threatening complications.
Maintaining food safety requires a comprehensive approach, from farm to fork. This includes proper food handling and storage practices, effective sanitation in food processing facilities, and robust regulatory oversight.
4. Waste Management
Proper waste management is essential for protecting environmental health. Improper disposal of solid waste can lead to soil and water contamination, as well as the spread of disease. Hazardous waste, such as medical waste and industrial chemicals, poses even greater risks.
Effective waste management strategies include reducing waste generation, promoting recycling and composting, and implementing safe disposal methods like landfills and incineration. Sustainable waste management aims to minimize environmental impacts and conserve resources.
5. Occupational Health
Occupational health focuses on protecting the health and safety of workers in the workplace. Workers can be exposed to a variety of hazards, including chemical exposures, physical hazards (noise, radiation, extreme temperatures), ergonomic stressors, and psychosocial stressors.
Occupational health programs aim to prevent work-related injuries and illnesses through hazard identification, risk assessment, and implementation of control measures. These programs also promote worker well-being and productivity.
6. Built Environment
The built environment encompasses all the human-made surroundings that provide the setting for human activity, ranging in scale from buildings and parks or green space to neighborhoods and cities, and that include the infrastructure to support human activity. The built environment can significantly impact human health. Factors such as access to green spaces, availability of healthy food options, walkability, and housing quality can all influence physical and mental health.
Poorly designed built environments can contribute to sedentary lifestyles, social isolation, and exposure to environmental hazards. Creating healthy built environments requires careful planning and design that prioritizes public health and sustainability.
Environmental Health and Climate Change
Climate change is increasingly recognized as a major threat to environmental health. Rising temperatures, extreme weather events, and changes in precipitation patterns can exacerbate existing environmental health problems and create new ones. For example, heat waves can increase the risk of heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses. Flooding can contaminate water supplies and spread disease. Changes in vector ecology can expand the range of vector-borne diseases like malaria and dengue fever.
Addressing climate change requires a multifaceted approach, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions, adapting to the impacts of climate change, and promoting climate resilience in communities.
Practical Advice for Everyday Life
Individuals can take several steps to protect their own environmental health and contribute to a healthier environment for everyone.
- Reduce your exposure to air pollution: Monitor air quality reports and avoid outdoor activities during periods of high pollution. Use air purifiers in your home. Ensure proper ventilation.
- Conserve water: Fix leaks, take shorter showers, and use water-efficient appliances.
- Choose safe foods: Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly, cook food to the proper temperature, and avoid cross-contamination.
- Reduce waste: Recycle, compost, and reduce your consumption of single-use plastics.
- Choose safer products: Opt for cleaning products, personal care products, and building materials that are low in volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful chemicals.
- Support sustainable transportation: Walk, bike, or use public transportation whenever possible.
- Advocate for environmental policies: Support policies that protect air and water quality, promote sustainable development, and address climate change.
By understanding the principles of environmental health and taking action to reduce our environmental footprint, we can create a healthier and more sustainable future for ourselves and future generations.