Assurance services are a vital component of the modern business landscape, offering stakeholders a degree of confidence and reliability regarding information. These services, typically provided by independent professionals, involve a systematic and objective evaluation of evidence to provide an opinion or conclusion about the reliability of the information being assessed. Understanding the core elements that constitute assurance services is crucial for anyone interacting with financial or operational data, whether as an investor, manager, or auditor.
Defining Assurance Services
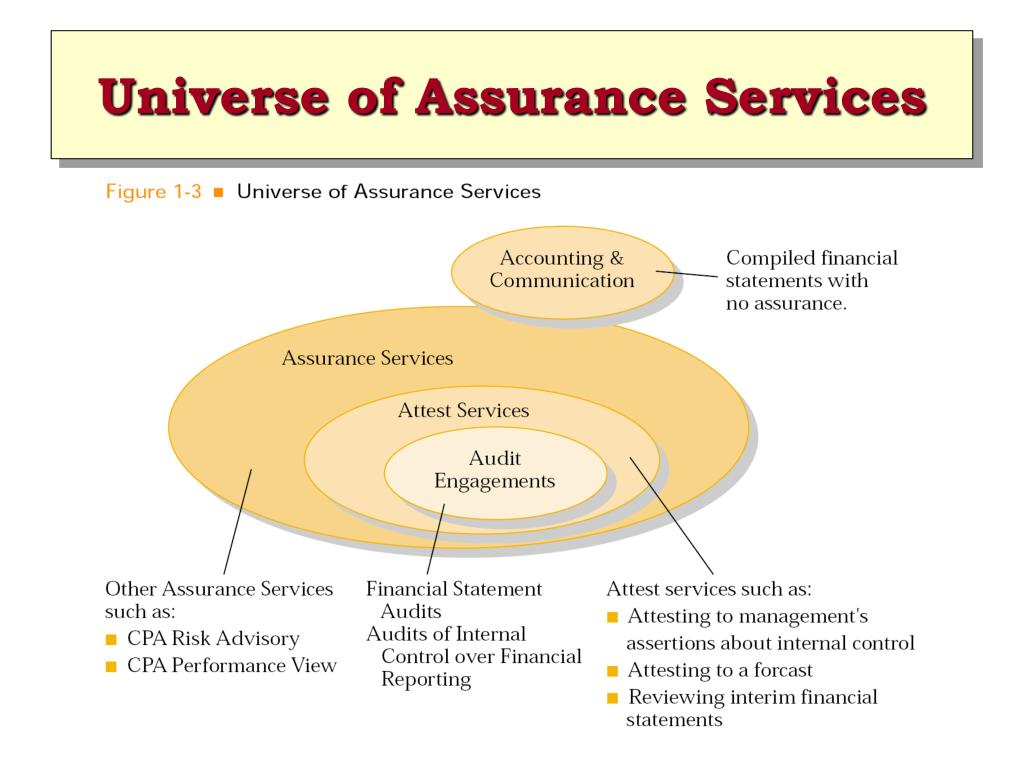
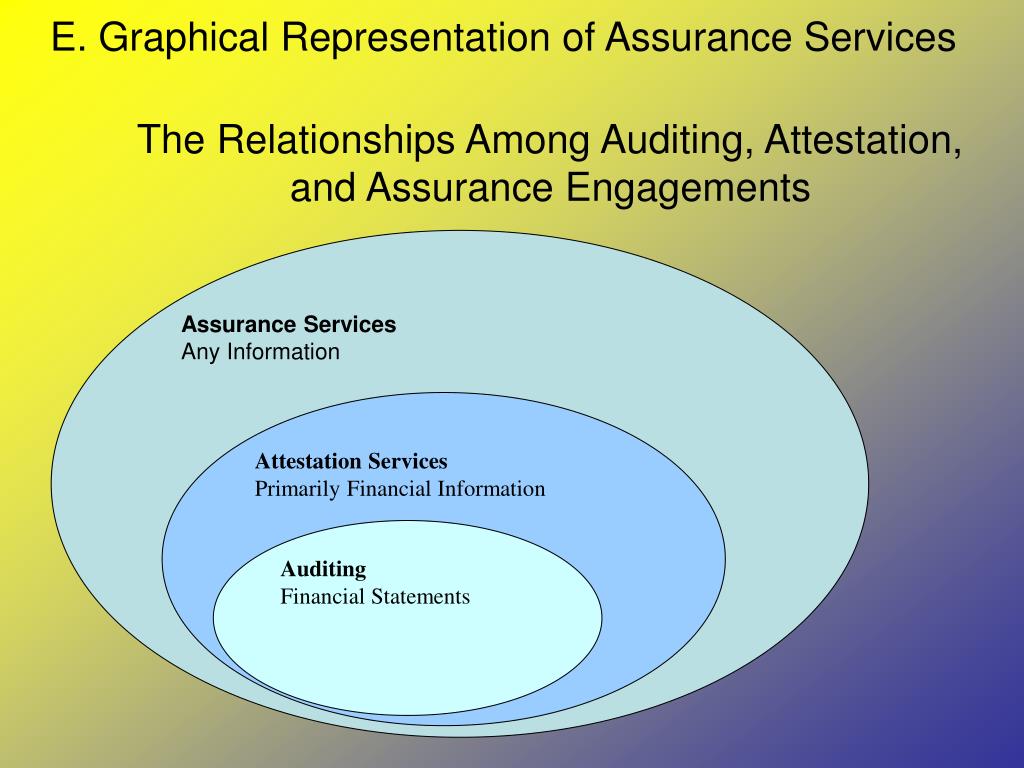
At its core, an assurance service is an independent professional service that improves the quality of information, or its context, for decision makers. This encompasses a wide range of engagements designed to enhance the credibility and trustworthiness of data. The goal is to reduce information risk, which is the risk that information used for decision-making is inaccurate or misleading. Assurance engagements are governed by professional standards and ethical guidelines to ensure objectivity and competence.
Key Components of Assurance Services
Several key components define assurance services:
- Independence: The assurance provider must be independent of the party whose information is being assessed. This independence is crucial to ensure objectivity and unbiased opinions. Conflicts of interest must be avoided.
- Objectivity: Assurance services require an objective and impartial evaluation of evidence. The assurance provider must approach the engagement with a neutral perspective and avoid any preconceived notions.
- Competence: The assurance provider must possess the necessary skills, knowledge, and experience to perform the engagement effectively. This includes a thorough understanding of the subject matter and relevant standards.
- Systematic Process: Assurance engagements follow a structured and systematic process, typically involving planning, evidence gathering, evaluation, and reporting. This systematic approach ensures consistency and reliability.
- Evidence-Based: The opinion or conclusion expressed by the assurance provider must be supported by sufficient appropriate evidence. This evidence is gathered through various procedures, such as inspection, observation, inquiry, and analysis.
- Reporting: The results of the assurance engagement are communicated to the intended users in a clear and concise report. This report typically includes the scope of the engagement, the procedures performed, the evidence gathered, and the opinion or conclusion reached.
These components collectively ensure the integrity and reliability of the assurance service, providing stakeholders with confidence in the information being assessed.
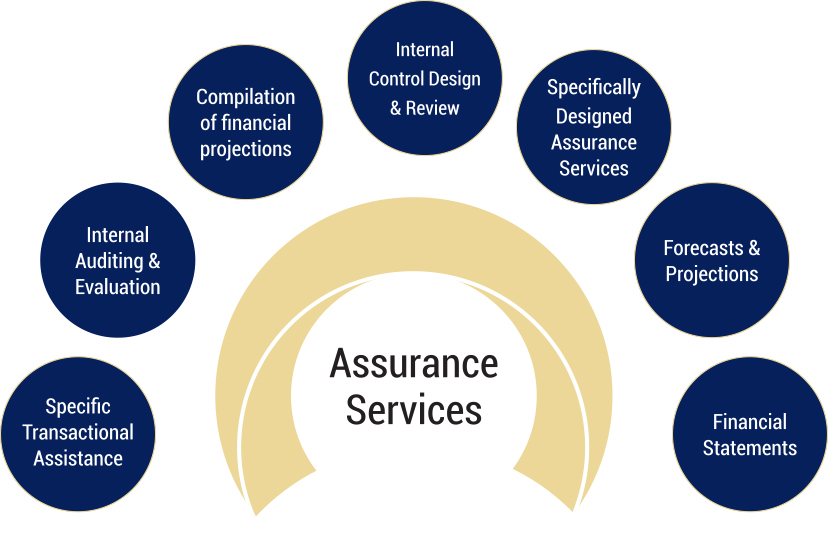
Examples of Assurance Services
To further illustrate the nature of assurance services, consider the following examples:
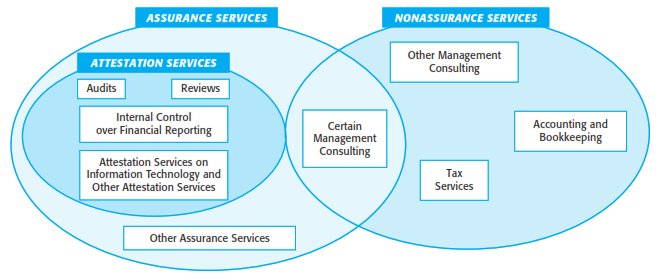
- Financial Statement Audits: This is perhaps the most well-known type of assurance service. Independent auditors examine a company's financial statements to provide an opinion on whether they are presented fairly in accordance with applicable accounting standards (e.g., GAAP or IFRS).
- Internal Control Audits: These audits evaluate the effectiveness of a company's internal control system. This helps to ensure that assets are protected, financial information is reliable, and operations are efficient.
- Compliance Audits: Compliance audits assess whether an organization is adhering to specific laws, regulations, policies, or contracts. For example, a company might undergo a compliance audit to ensure it is meeting environmental regulations.
- Performance Audits: These audits evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of an organization's operations or programs. The goal is to identify areas for improvement and to help the organization achieve its objectives.
- IT Audits: IT audits focus on the security and reliability of an organization's information technology systems. They assess whether the systems are adequately protected from unauthorized access and whether data is accurate and complete.
- Sustainability Reporting Assurance: With increasing emphasis on environmental and social responsibility, assurance services are now often used to verify the accuracy and completeness of a company’s sustainability reports.
What Assurance Services Do NOT Involve
While assurance services encompass a broad range of activities, it is equally important to understand what they do not include. Assurance services do not typically involve activities that lack independence, objectivity, or a systematic process. Here are some key exclusions:
- Management Consulting that Directly Implements Changes: While assurance professionals might provide recommendations for improvement, directly implementing these changes themselves often compromises their independence for future assurance engagements. Consulting engagements where the advisor is heavily involved in design and execution fall outside the realm of pure assurance.
- Tax Preparation: While tax professionals provide valuable services related to tax compliance, these services typically do not involve an independent assessment of information provided by the client. The focus is on accurately preparing and filing tax returns based on the information provided.
- Advocacy: Assurance professionals must maintain objectivity and cannot act as advocates for their clients. Their role is to provide an unbiased assessment of information, not to represent the client's interests.
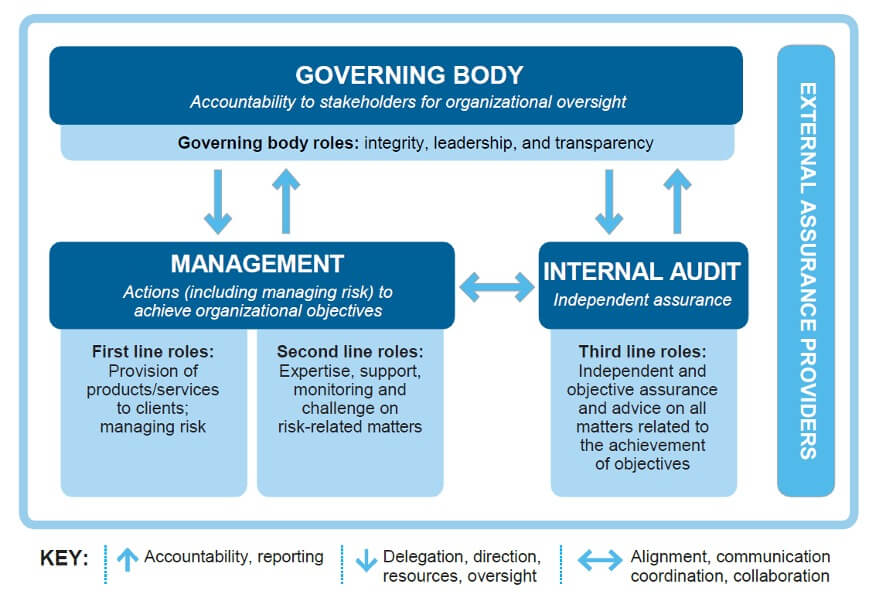
- Internal Activities Without Independent Verification: While internal audits are a component of good governance, without independent external verification, they do not constitute assurance services in the same way. The key difference is the external validation.
- Predictions without a Basis in Reliable Data: While assurance services may involve reviewing forecasts or projections, the focus is on the reasonableness of the assumptions and the reliability of the underlying data, not on guaranteeing the accuracy of the predictions themselves.
- Simple Data Entry or Clerical Tasks: These tasks do not involve the professional judgment and evaluation of evidence required for assurance services.
- Unstructured Advice: Ad-hoc advice or suggestions without a structured assessment or underlying evidence base would not qualify as an assurance service. The systematic approach is a defining characteristic.
For example, a company's internal team generating sales forecasts for the next quarter is not an assurance service. However, if an independent third party were to review the methodology, data, and assumptions used to generate those forecasts and issue a report on the reasonableness of those forecasts, that would be an assurance service.
Practical Insights for Everyday Life
The principles of assurance services can be applied to various aspects of everyday life to improve decision-making:
- Seek Independent Opinions: When making important decisions, such as buying a car or investing money, seek advice from independent experts who have no vested interest in the outcome.
- Verify Information: Don't blindly trust information you receive. Verify it through reliable sources and cross-check it with other information.
- Maintain Objectivity: Be aware of your own biases and strive to approach decisions with an open mind.
- Follow a Systematic Approach: When tackling complex tasks or projects, break them down into smaller steps and follow a structured process.
- Gather Evidence: Base your decisions on evidence rather than assumptions or emotions.
By applying these principles, you can improve the quality of your decisions and reduce the risk of making mistakes. The critical takeaway is the importance of verifying information, seeking independent opinions, and maintaining objectivity.
In conclusion, assurance services are essential for fostering trust and confidence in information. By understanding the core elements of these services and what they do not encompass, stakeholders can better evaluate the reliability of information and make informed decisions.