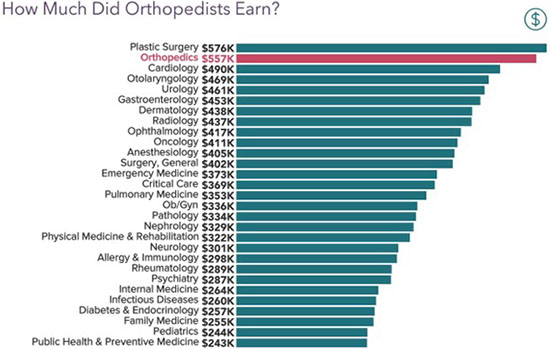
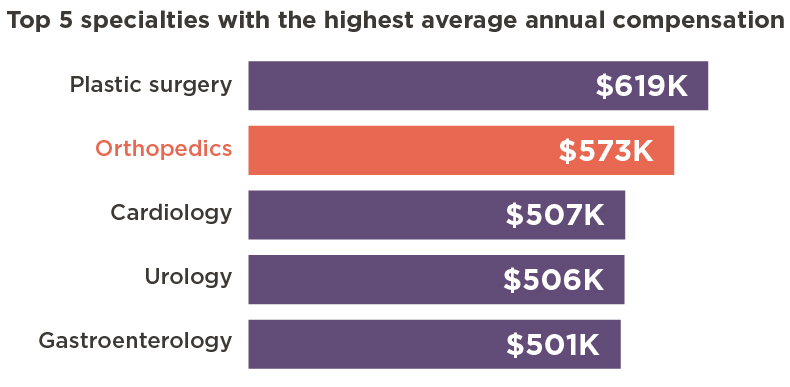
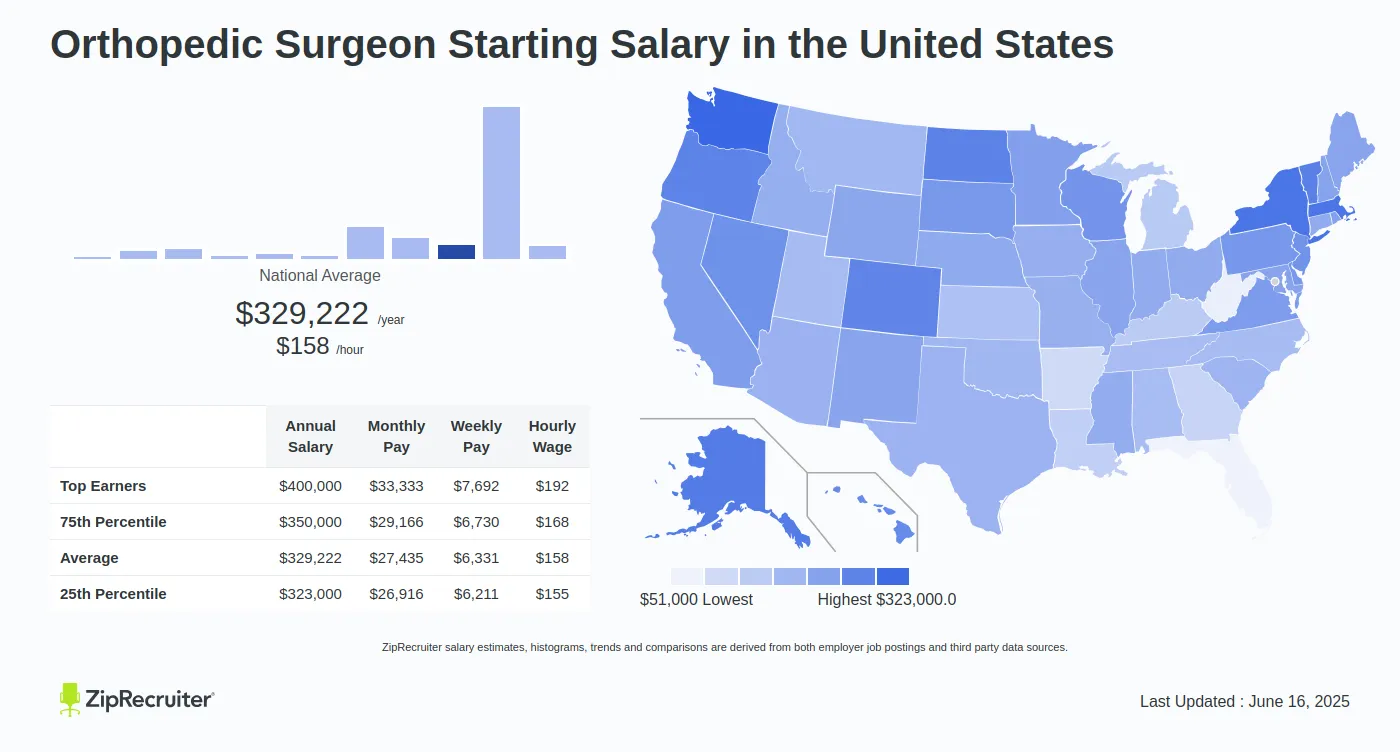
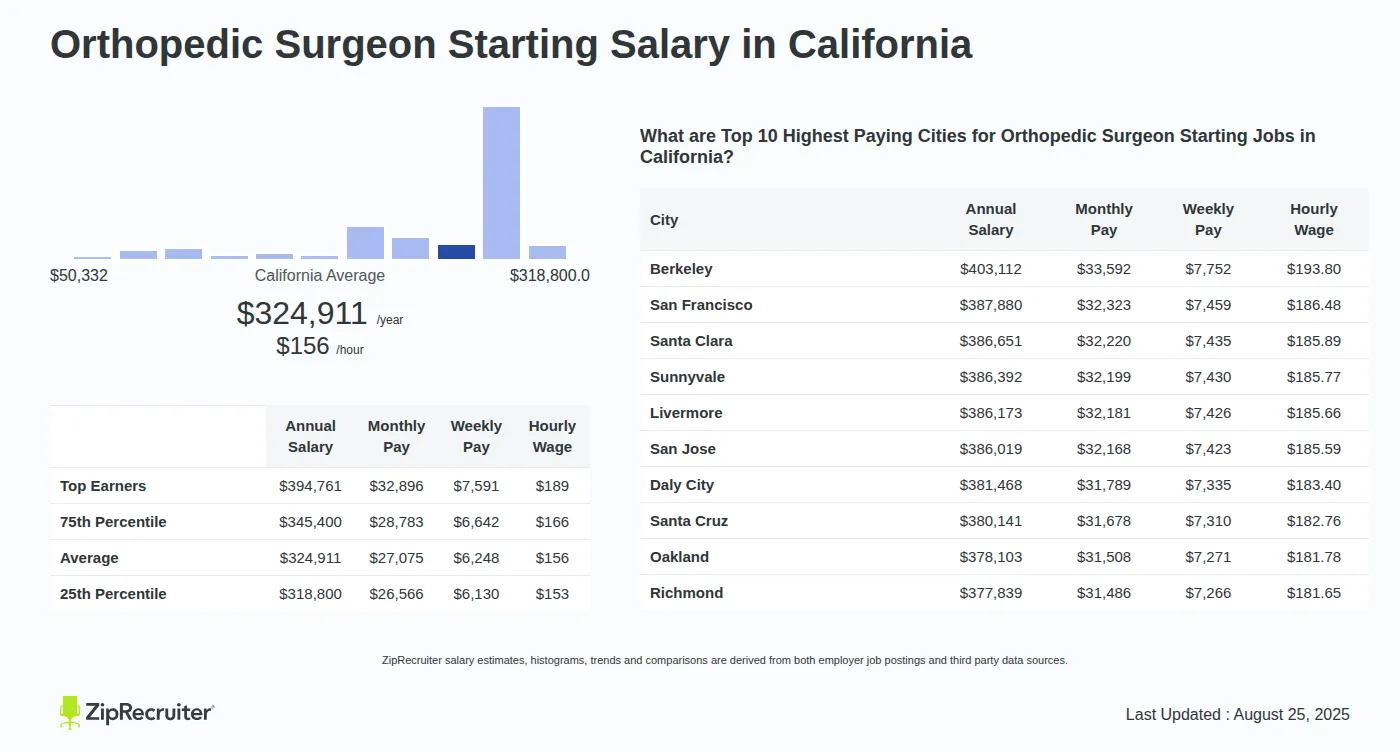
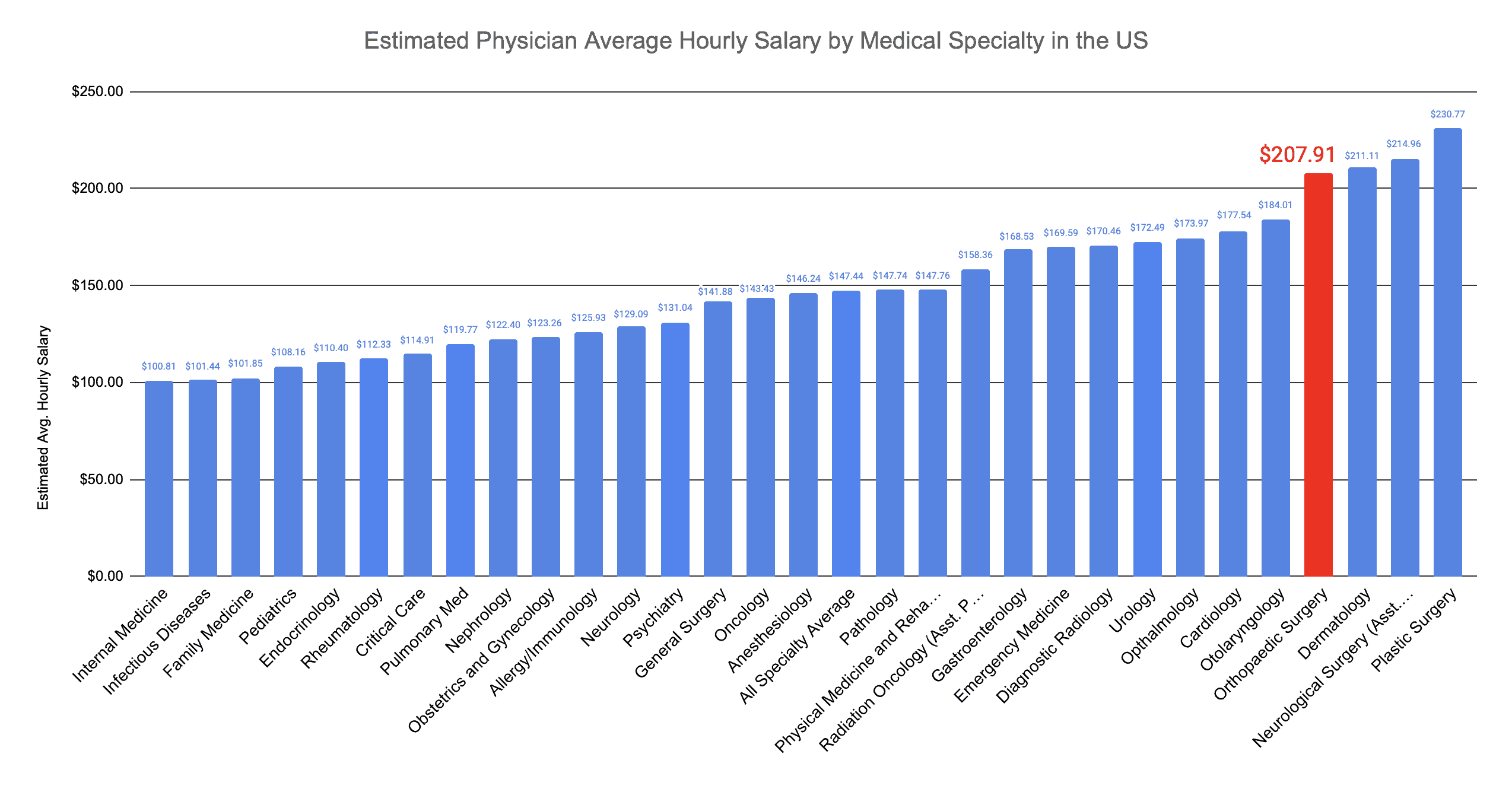
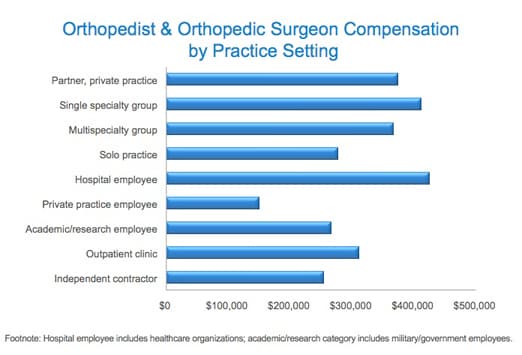
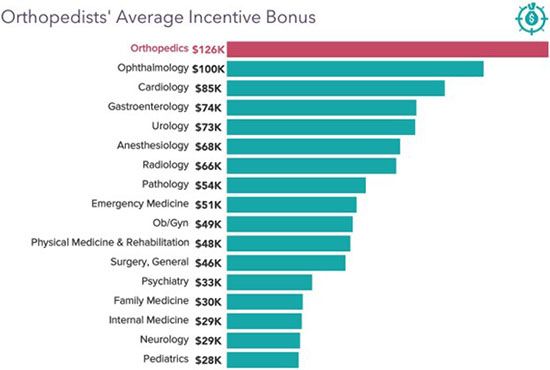
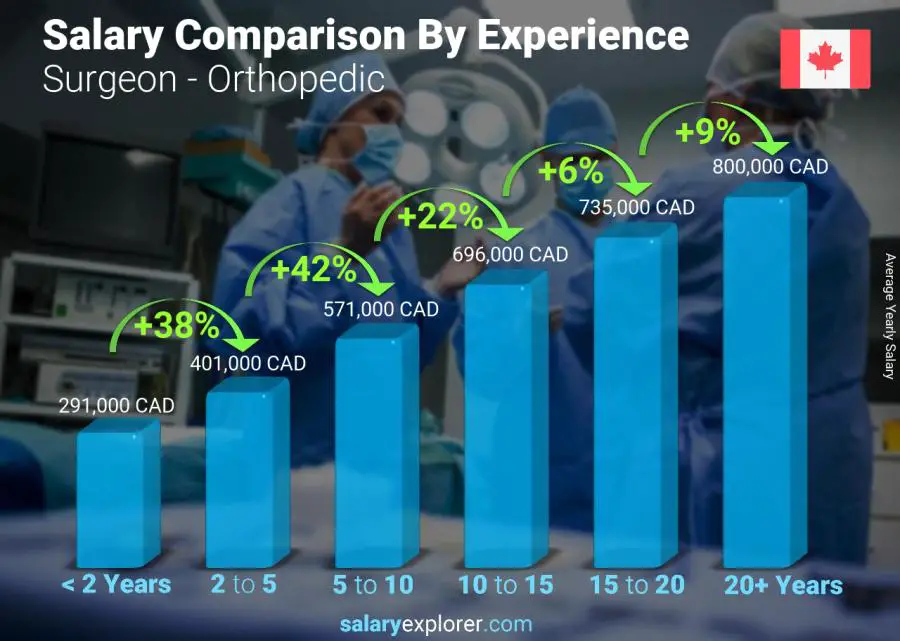
The compensation of orthopedic surgeons is a subject of considerable interest within the medical community and beyond. It reflects not only the demanding nature of the specialty but also broader trends in healthcare economics. Understanding the average salary requires examining the factors that contribute to its determination, the effects of this income level on individual practitioners and the healthcare system, and the wider implications for patient care and access.
Orthopedic surgery focuses on the musculoskeletal system, addressing injuries, diseases, and congenital conditions affecting bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. This specialty requires extensive training, including a four-year undergraduate degree, four years of medical school, and a five-year residency program. Many orthopedic surgeons pursue additional fellowship training for specialization in areas such as sports medicine, joint replacement, spine surgery, or hand surgery. This lengthy and rigorous education contributes significantly to the high earning potential.
Causes of High Orthopedic Surgeon Salaries
Several factors contribute to the substantial salaries earned by orthopedic surgeons.
Extensive Education and Training
As mentioned previously, the pathway to becoming an orthopedic surgeon is long and arduous. The significant investment of time and resources in education justifies a higher earning potential. The specialized knowledge and skills acquired during this training are critical for performing complex surgical procedures and managing challenging orthopedic conditions.
High Demand for Services
The demand for orthopedic services is consistently high due to several reasons. The aging population is experiencing increased rates of arthritis and other degenerative joint conditions, leading to a greater need for joint replacement surgeries and other orthopedic interventions. Furthermore, the prevalence of sports-related injuries, particularly among younger individuals, sustains a demand for sports medicine specialists within orthopedics. Accidents and trauma also necessitate orthopedic care, contributing to the overall demand.
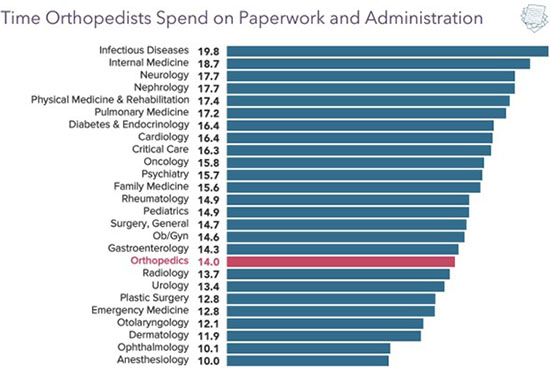
Complexity and Risk of Procedures
Orthopedic surgeries are often complex and carry inherent risks. These procedures require a high degree of precision and skill to ensure successful outcomes and minimize complications. The potential for complications, such as infections, nerve damage, or implant failure, adds to the responsibility and stress associated with the profession. The high stakes involved in these procedures justify higher compensation.
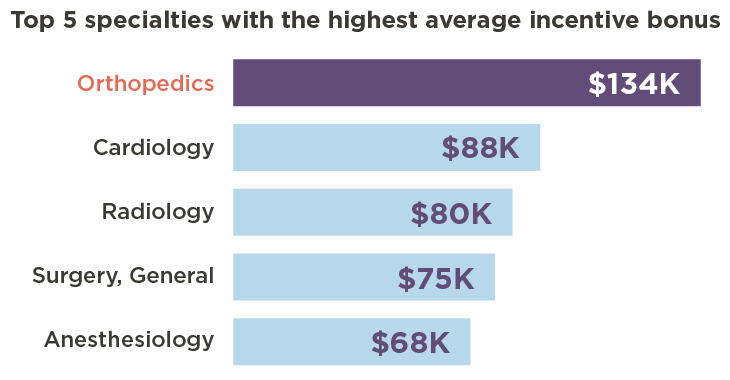
Reimbursement Rates
Reimbursement rates from insurance companies and government healthcare programs significantly influence physician salaries. Orthopedic procedures often involve expensive implants and require significant resources, leading to higher reimbursement rates compared to other medical specialties. However, it is important to note that reimbursement models are constantly evolving and can impact income stability.
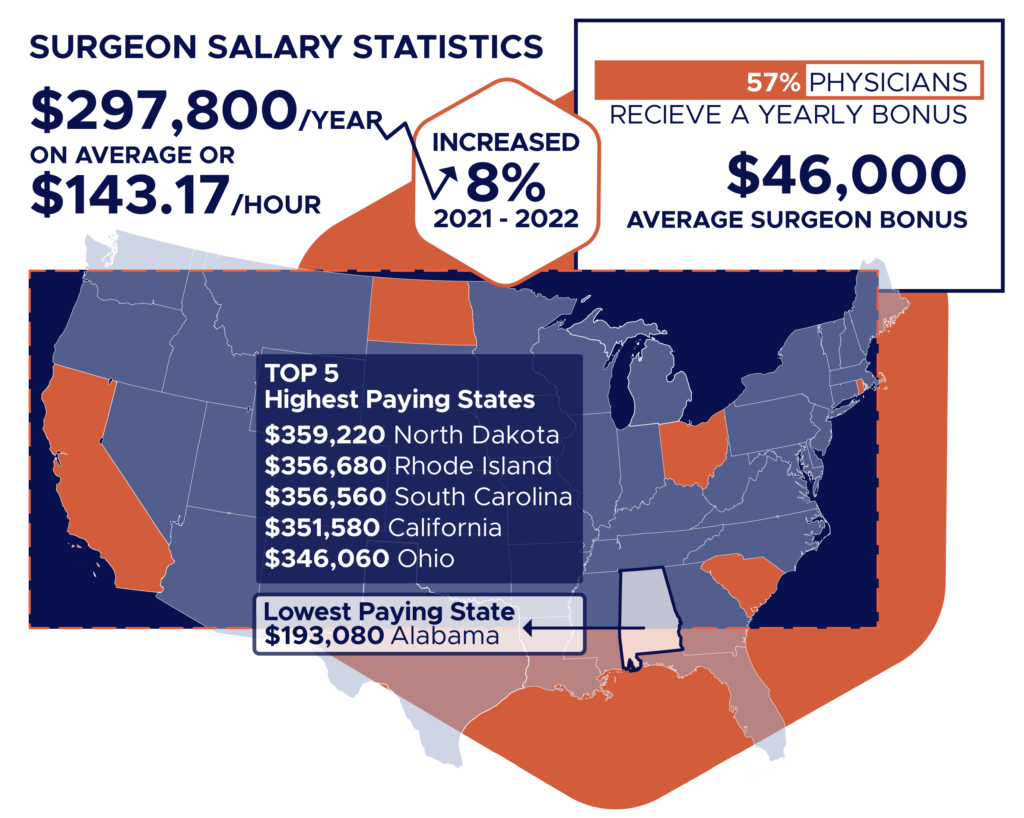
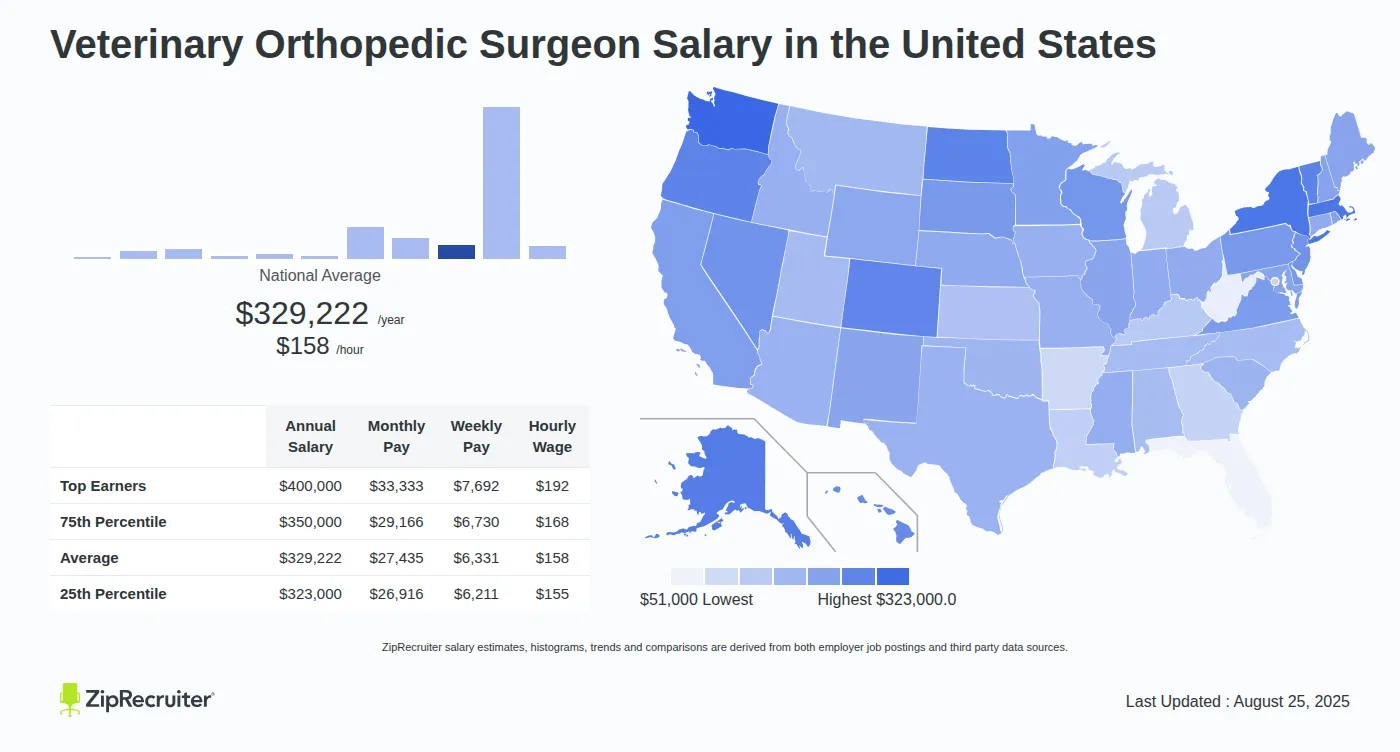
Geographic Location
Geographic location can also play a crucial role in determining salary. Metropolitan areas with a higher cost of living typically offer higher salaries to compensate for the increased expenses. Rural areas, while potentially offering lower base salaries, may provide loan repayment programs or other incentives to attract orthopedic surgeons to underserved communities.
Effects of High Orthopedic Surgeon Salaries
The high earning potential of orthopedic surgeons has several effects, both positive and negative, on individuals and the healthcare system.
Attracting Talent
The lucrative nature of orthopedic surgery attracts talented and dedicated individuals to the field. This ensures that the specialty remains competitive and that patients have access to highly skilled surgeons. The ability to earn a substantial income can be a strong motivator for pursuing the demanding training required to become an orthopedic surgeon.
Increased Healthcare Costs
High physician salaries, including those of orthopedic surgeons, contribute to the overall rising costs of healthcare. While not the sole driver of increased costs, physician compensation is a significant factor. This can lead to higher insurance premiums and out-of-pocket expenses for patients.
Geographic Disparities in Access to Care
The concentration of orthopedic surgeons in affluent urban areas can exacerbate disparities in access to care. Rural and underserved communities may struggle to attract and retain orthopedic surgeons, leading to longer wait times and limited access to specialized care. This geographic imbalance can negatively impact patient outcomes in these areas.
Impact on Career Choices within Medicine
The high earning potential of certain specialties, such as orthopedic surgery, can influence medical students' career choices. Some students may be drawn to these specialties primarily for financial reasons, potentially diverting talent away from other crucial areas of medicine, such as primary care.
Implications for Patient Care and the Healthcare System
The salary structure for orthopedic surgeons has significant implications for patient care and the broader healthcare system.
Focus on High-Reimbursement Procedures
The financial incentives associated with certain orthopedic procedures can potentially influence treatment decisions. While most orthopedic surgeons prioritize patient well-being, the economic realities of the healthcare system may incentivize a focus on high-reimbursement procedures, even when less invasive or non-surgical options might be appropriate.
Research and Innovation
The financial resources available to orthopedic surgeons, particularly those in academic settings, can support research and innovation in the field. This can lead to the development of new surgical techniques, improved implants, and more effective treatments for orthopedic conditions. However, the focus on profitability can also influence the direction of research, potentially favoring commercially viable projects over those with a greater public health impact.
Access to Care for Underserved Populations
Addressing the geographic disparities in access to orthopedic care requires creative solutions. Loan repayment programs, tax incentives, and the development of telemedicine technologies can help attract orthopedic surgeons to underserved communities. Furthermore, efforts to increase the diversity of the physician workforce can ensure that healthcare providers are culturally competent and able to effectively serve diverse patient populations.
Ethical Considerations
Orthopedic surgeons, like all physicians, must adhere to a strong ethical code. This includes prioritizing patient well-being, avoiding conflicts of interest, and ensuring that treatment decisions are based on sound medical evidence. Maintaining ethical standards is crucial for preserving public trust in the medical profession and ensuring that patients receive the best possible care.
The average salary of an orthopedic surgeon is a complex issue with multifaceted causes, effects, and implications. While high compensation can attract talented individuals to the field and support research and innovation, it also contributes to rising healthcare costs and can exacerbate disparities in access to care. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort from policymakers, healthcare providers, and insurance companies to create a more equitable and sustainable healthcare system that prioritizes patient well-being and access to high-quality orthopedic care for all.