Pregnancy is a transformative period marked by significant physiological changes. During this time, ensuring optimal health and well-being for both the mother and developing fetus is paramount. Consequently, pregnant women are often advised to carefully consider their diet and supplement intake. Magnesium, an essential mineral involved in numerous bodily functions, is often discussed in this context. This article delves into the safety and potential benefits of taking Calm Magnesium, a popular magnesium supplement, during pregnancy.
Understanding Magnesium and Its Role in Pregnancy
Magnesium plays a crucial role in a wide array of bodily processes. These include muscle and nerve function, blood sugar control, blood pressure regulation, and bone health. Furthermore, it's involved in protein synthesis, energy production, and DNA replication. During pregnancy, the demand for magnesium increases due to the growing needs of the fetus and the mother's changing physiology.
Adequate magnesium intake during pregnancy can contribute to several positive outcomes, such as:
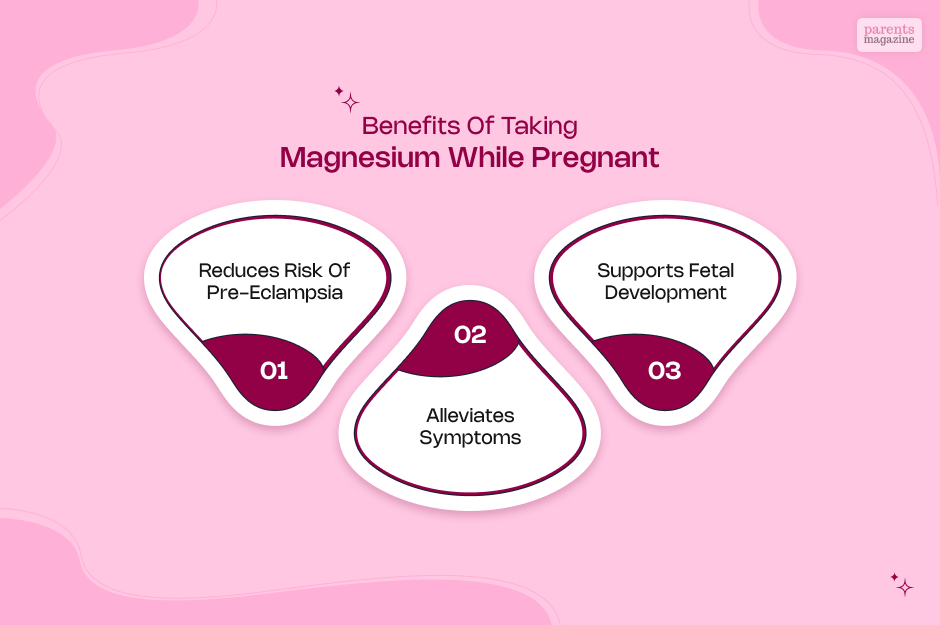
- Reducing the risk of preeclampsia: A serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and protein in the urine.
- Preventing preterm labor: Magnesium sulfate is sometimes used intravenously to delay preterm labor, although oral magnesium supplements are not typically used for this purpose.
- Alleviating leg cramps: A common complaint during pregnancy.
- Improving sleep quality: Magnesium can promote relaxation and improve sleep.
- Supporting fetal development: Magnesium is essential for the healthy development of the fetus's bones, muscles, and nervous system.
Calm Magnesium: What Is It?
Calm Magnesium is a popular brand of magnesium supplement known for its effervescent form and purported calming effects. The active ingredient is typically magnesium carbonate, which, when mixed with water, converts to magnesium citrate. Magnesium citrate is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium, meaning it's readily absorbed by the body. Calm Magnesium often includes flavorings and other additives.
Can You Take Calm Magnesium While Pregnant? Considerations and Cautions
While magnesium is generally considered safe during pregnancy, it's crucial to approach supplementation with informed awareness. Here are key considerations before taking Calm Magnesium during pregnancy:
Consultation with a Healthcare Provider
The most important step is to consult with your doctor, midwife, or a registered dietitian before starting any new supplement, including Calm Magnesium. They can assess your individual needs, considering your medical history, current medications, and overall health status. They can also determine if you have any underlying conditions that might be affected by magnesium supplementation.
Dosage
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) of magnesium for pregnant women is typically higher than for non-pregnant women. The exact amount varies based on age and individual circumstances. Exceeding the recommended dosage can lead to adverse effects, such as diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. Your healthcare provider can advise you on the appropriate dosage for your specific needs.
Form of Magnesium
Calm Magnesium typically contains magnesium citrate, which is generally well-absorbed. However, magnesium citrate can have a laxative effect, especially at higher doses. If you are prone to diarrhea or have irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), you may want to consider alternative forms of magnesium, such as magnesium glycinate, which is less likely to cause digestive upset. Discuss different forms with your doctor to determine the best option for you.
Potential Interactions
Magnesium can interact with certain medications, including some antibiotics and diuretics. It can also interfere with the absorption of iron and calcium. If you are taking any medications or supplements, inform your healthcare provider to avoid potential interactions. They may recommend adjusting the timing of your doses to minimize any interference.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, can affect magnesium levels in the body and alter the safety of magnesium supplementation. If you have any pre-existing health conditions, your healthcare provider will need to carefully assess your situation before recommending Calm Magnesium or any other magnesium supplement.
Source and Quality
It is essential to choose a high-quality magnesium supplement from a reputable brand. Look for products that have been third-party tested for purity and potency. This ensures that you are getting a product that contains the stated amount of magnesium and is free from contaminants.
Potential Benefits of Calm Magnesium During Pregnancy
If deemed appropriate by your healthcare provider, Calm Magnesium may offer several potential benefits during pregnancy, including:
- Improved Sleep: Magnesium can promote relaxation and improve sleep quality, which is particularly beneficial during pregnancy when sleep disturbances are common.
- Reduced Leg Cramps: Magnesium deficiency can contribute to leg cramps, a frequent complaint during pregnancy. Supplementation may help alleviate these cramps.
- Stress Reduction: Magnesium plays a role in regulating the nervous system and may help reduce stress and anxiety.
- Prevention of Constipation: Magnesium citrate, the form typically found in Calm Magnesium, can have a mild laxative effect, which can help prevent constipation, another common issue during pregnancy.
Alternatives to Calm Magnesium
If Calm Magnesium is not suitable for you due to its laxative effect or other concerns, there are alternative ways to increase your magnesium intake during pregnancy:
- Dietary Sources: Incorporate magnesium-rich foods into your diet, such as leafy green vegetables (spinach, kale), nuts and seeds (almonds, pumpkin seeds), whole grains, beans, and avocados.
- Other Magnesium Supplements: Consider alternative forms of magnesium, such as magnesium glycinate, magnesium oxide, or magnesium chloride. Each form has different bioavailability and potential side effects. Discuss the best option with your healthcare provider.
Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency During Pregnancy
Recognizing the symptoms of magnesium deficiency can help prompt timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Muscle cramps and spasms
- Fatigue and weakness
- Irritability and anxiety
- Sleep disturbances
- Headaches
- Nausea and vomiting
- High blood pressure
If you experience any of these symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider to determine if magnesium deficiency is a contributing factor.
When to Avoid Calm Magnesium During Pregnancy
There are certain situations where Calm Magnesium should be avoided during pregnancy:
- Kidney Disease: Individuals with kidney disease should avoid magnesium supplementation unless specifically directed by their doctor.
- Certain Medications: As mentioned earlier, magnesium can interact with some medications. Consult with your doctor to rule out any potential interactions.
- Diarrhea: Due to its laxative effect, Calm Magnesium should be avoided if you are already experiencing diarrhea.
- Allergic Reactions: If you have a known allergy to magnesium or any of the other ingredients in Calm Magnesium, avoid using the product.
The Importance of a Holistic Approach
While magnesium supplementation may be beneficial, it's essential to adopt a holistic approach to health during pregnancy. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, managing stress, and attending all scheduled prenatal appointments. Focusing on these factors will contribute to a healthier pregnancy and a better outcome for both you and your baby.
Disclaimer: This information is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Calm Magnesium can be a beneficial supplement during pregnancy for some women, provided it's taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional, it's not a universally suitable option. Careful consideration of individual needs, potential risks, and alternative options is crucial. The ultimate decision should be made in consultation with your doctor or midwife to ensure the safety and well-being of both you and your developing baby. Remember, prioritising prenatal care and open communication with your healthcare provider is paramount for a healthy pregnancy.








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-GettyImages-MagnesiumWhilePregnant-d6440f40c1944a26a5b37cff838903d8.jpg)