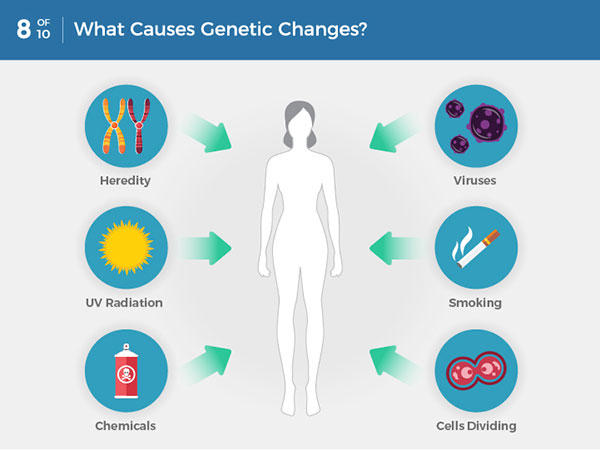
Total Body Enhancement (TBE), often found in gyms and tanning salons, involves short bursts of ultraviolet (UV) light exposure across the entire body. These booths, sometimes marketed as a way to obtain Vitamin D or improve skin appearance, raise concerns about the potential for increased cancer risk. This article will explore the science behind TBE and its connection to cancer, examining the types of UV radiation involved, the known risks, and recommendations for minimizing exposure.
Understanding Total Body Enhancement and UV Radiation
TBE devices primarily emit UVA radiation, although some also emit UVB radiation. It's crucial to understand the differences between these types of UV radiation to grasp their potential health effects.
UVA Radiation
UVA radiation has a longer wavelength than UVB radiation. It penetrates deeper into the skin, reaching the dermis. While it's less likely to cause sunburn than UVB, UVA is a major contributor to skin aging, causing wrinkles, sunspots, and loss of elasticity. Critically, UVA also damages DNA in skin cells, which can lead to skin cancer over time.
UVB Radiation
UVB radiation has a shorter wavelength and primarily affects the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. It is the primary cause of sunburn. UVB radiation is also a potent carcinogen, directly damaging DNA and increasing the risk of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma. The intensity of UVB radiation varies depending on the time of day, season, and geographical location, being highest during midday in the summer.
While some TBE systems claim to filter out harmful UVB rays, the vast majority still emit UVA radiation, and the long-term effects of repeated UVA exposure should not be underestimated.
The Link Between UV Radiation and Cancer
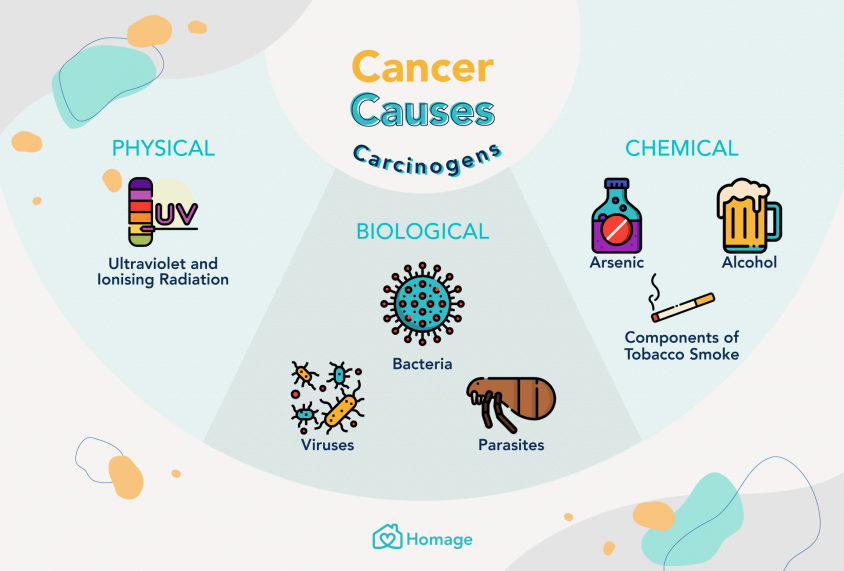
The primary concern with TBE lies in its use of UV radiation, a well-established carcinogen. Extensive research has demonstrated a clear association between UV exposure and an increased risk of skin cancer.
Skin Cancer Types
The three main types of skin cancer are:
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): The most common type, BCCs are slow-growing and rarely metastasize (spread to other parts of the body). They often appear as pearly or waxy bumps or flat, flesh-colored lesions. UV exposure is a significant risk factor.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): The second most common type, SCCs can grow more quickly than BCCs and have a higher risk of metastasis. They often appear as firm, red nodules or flat lesions with a scaly, crusted surface. UV exposure is a major cause.
- Melanoma: The most dangerous type of skin cancer, melanoma can metastasize rapidly and be fatal if not detected and treated early. Melanoma often appears as a mole-like growth that is asymmetrical, has irregular borders, uneven color, and a diameter greater than 6 millimeters (the "ABCDEs" of melanoma). UV exposure, particularly intermittent, high-intensity exposure (like that from tanning beds or sunburns), is a significant risk factor.
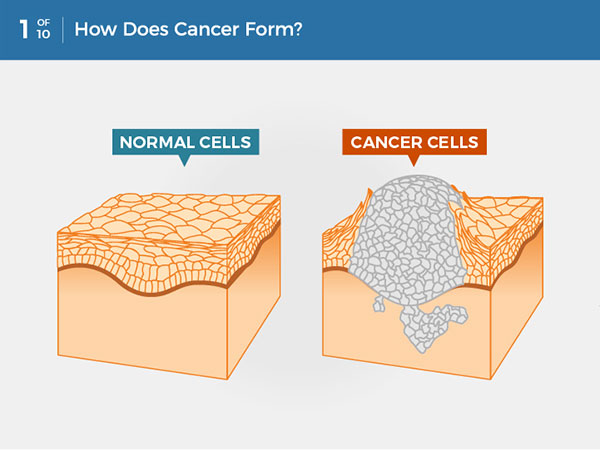
Each type of skin cancer is directly linked to UV exposure. TBE, by intentionally exposing the entire body to UV radiation, increases the overall risk of developing these cancers.
How UV Radiation Causes Cancer
UV radiation damages the DNA within skin cells. This damage can disrupt normal cell growth and division, leading to mutations that can cause cells to become cancerous. The body has mechanisms to repair some of this DNA damage, but repeated or excessive exposure to UV radiation can overwhelm these repair mechanisms, increasing the likelihood of mutations and cancer development.
Furthermore, UV radiation can suppress the immune system in the skin, making it less effective at detecting and destroying precancerous cells. This allows damaged cells to proliferate and potentially develop into skin cancer.
Addressing Misconceptions About Total Body Enhancement
Despite the scientific consensus on the dangers of UV radiation, some misconceptions persist regarding TBE. It's crucial to address these claims with accurate information.
Vitamin D Production
One common argument for TBE is that it promotes Vitamin D production. While UVB radiation does stimulate Vitamin D synthesis in the skin, TBE is not a safe or effective way to obtain adequate levels. Safe and effective alternatives include Vitamin D-rich foods, Vitamin D supplements, and limited, responsible sun exposure (with appropriate sun protection).
"Safer" Tanning Beds
Some TBE providers may claim that their systems are "safer" than traditional tanning beds due to filtered UVB rays. However, as mentioned earlier, UVA radiation is still a significant risk factor for skin cancer and premature aging. There is no such thing as a "safe" tanning bed or TBE system.
"There is no safe level of exposure to UV radiation from tanning beds," - The American Academy of Dermatology.
Minimizing Risk and Protecting Your Skin
Given the established risks of UV radiation exposure, it is essential to take steps to protect your skin.
Avoid Total Body Enhancement
The most effective way to eliminate the risk associated with TBE is to avoid it altogether. There is no scientifically sound reason to intentionally expose yourself to UV radiation for cosmetic purposes or perceived health benefits.
Sun Protection Measures
When outdoors, particularly during peak sunlight hours (10 AM to 4 PM), it's important to practice sun-safe behaviors:
- Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher. Apply generously and reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Protective Clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, pants, and wide-brimmed hats to shield your skin from the sun.
- Sunglasses: Protect your eyes from UV damage with sunglasses that block 100% of UVA and UVB rays.
- Seek Shade: Limit your time in direct sunlight, especially during peak hours.
Regular Skin Exams
Perform self-exams regularly to check for any new or changing moles or lesions. Consult a dermatologist for professional skin exams, especially if you have a family history of skin cancer or have had significant sun exposure. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment of skin cancer.
Conclusion: The Importance of Informed Choices
The scientific evidence overwhelmingly demonstrates a link between UV radiation exposure, including that from Total Body Enhancement devices, and an increased risk of skin cancer. While TBE may be marketed as a quick or convenient way to improve appearance or boost Vitamin D levels, the potential health consequences far outweigh any perceived benefits. Choosing to avoid TBE and prioritizing sun-safe behaviors are essential steps in protecting your skin and reducing your risk of developing skin cancer. Making informed decisions based on credible scientific evidence is paramount when it comes to your health.