Argentina, a vast country stretching from subtropical regions in the north to subantarctic zones in the south, experiences a diverse range of climates. Understanding these variations is crucial for planning your daily life, whether you're a resident, a tourist, or conducting business here. This guide provides practical insights into Argentina's climate and offers tips on adapting to its seasonal changes.
Understanding Argentina's Climate Zones
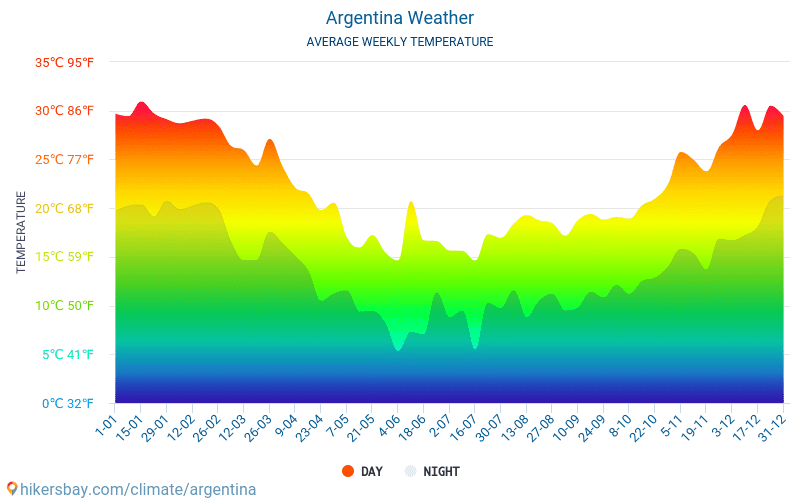
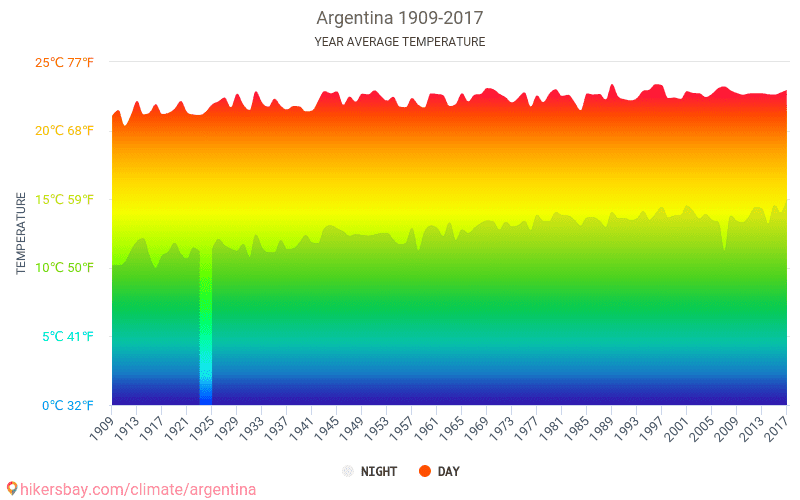
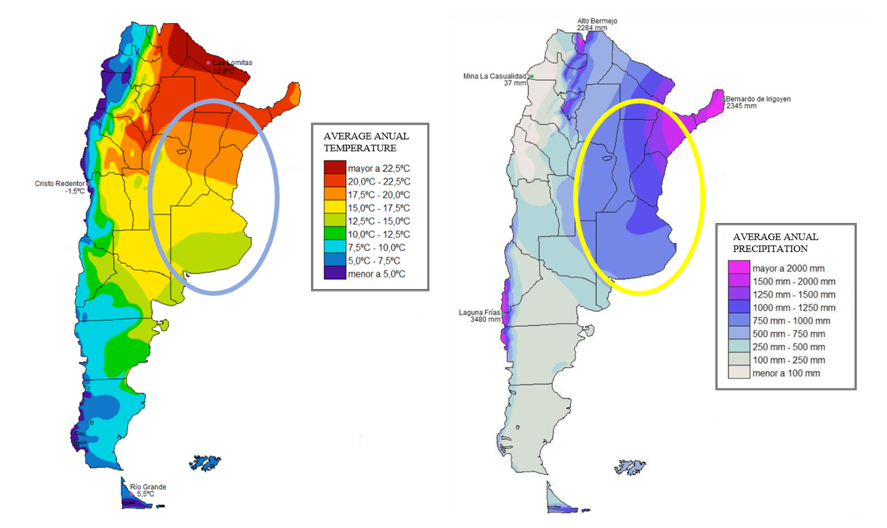
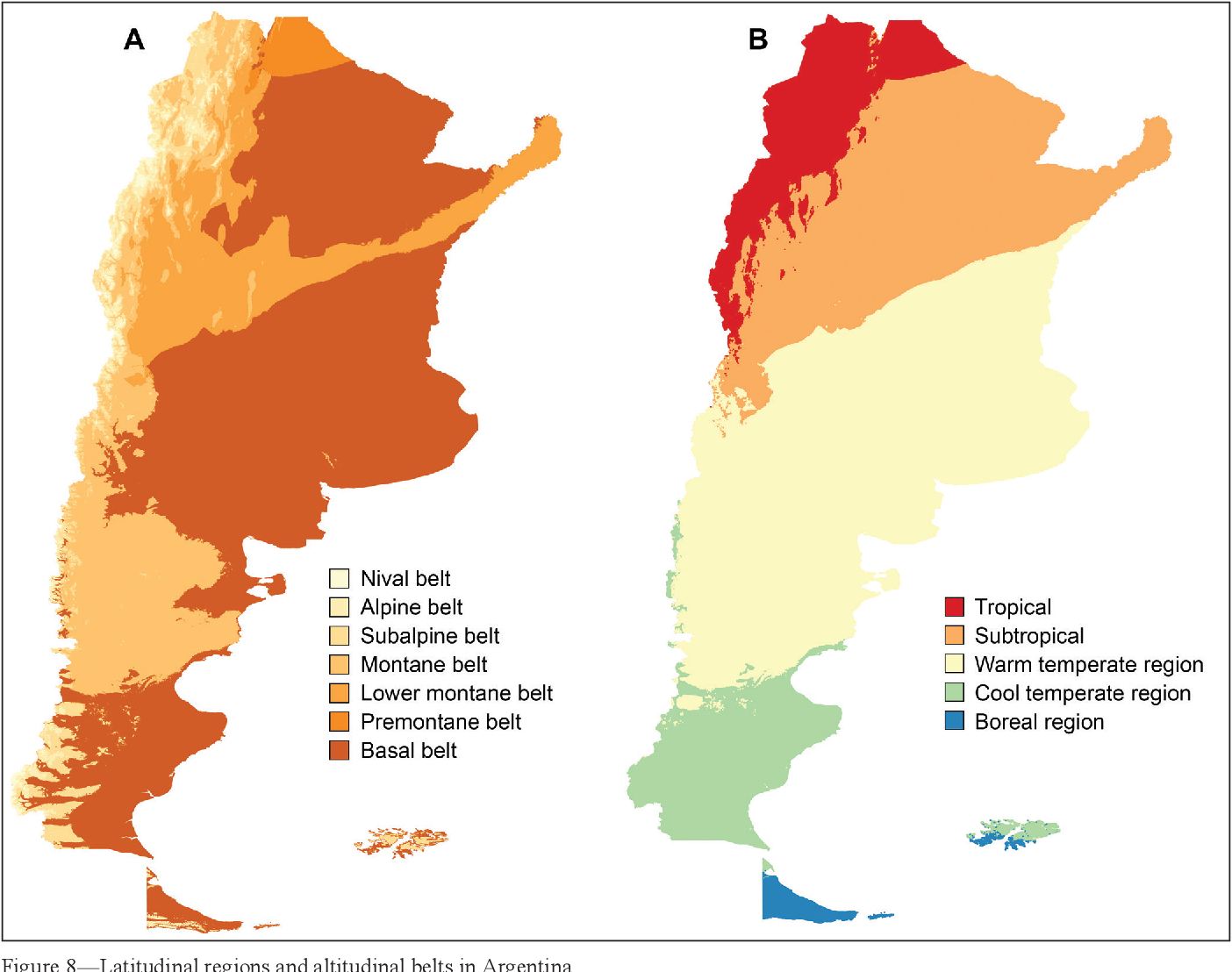
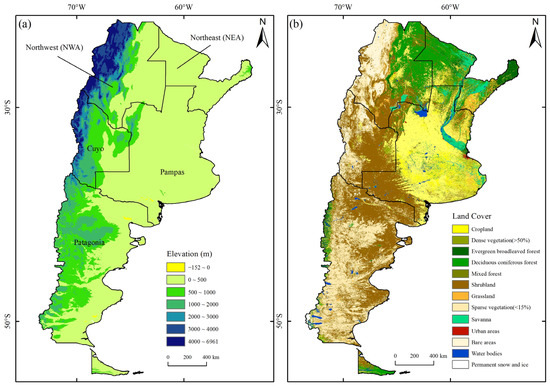
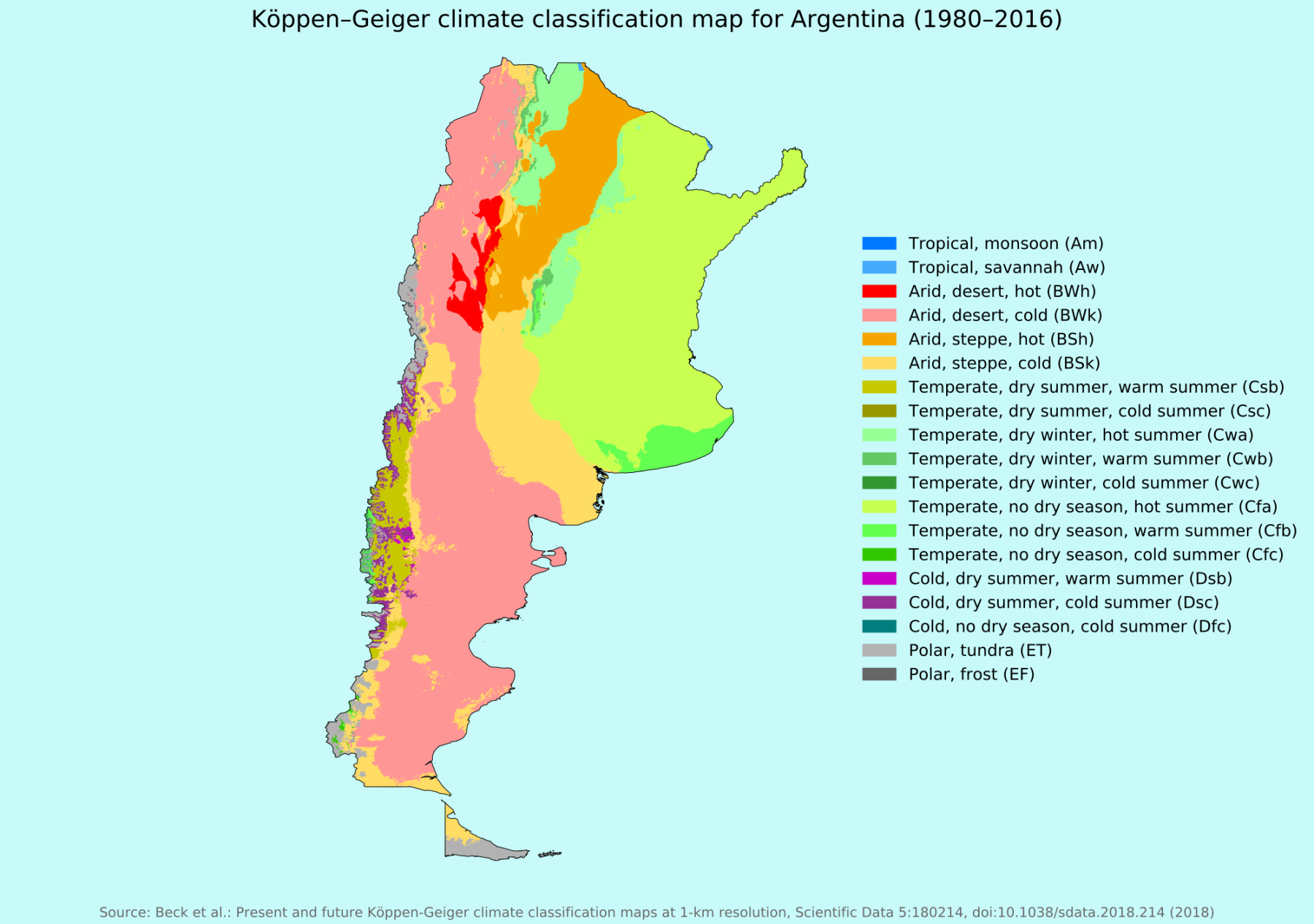
Argentina can be broadly divided into several climate zones:
- Northwest (Subtropical): Hot and humid summers, mild and dry winters. Includes provinces like Salta, Jujuy, and Tucumán.
- Northeast (Humid Subtropical): Characterized by high humidity and rainfall throughout the year. Corrientes, Misiones, and Formosa fall into this zone.
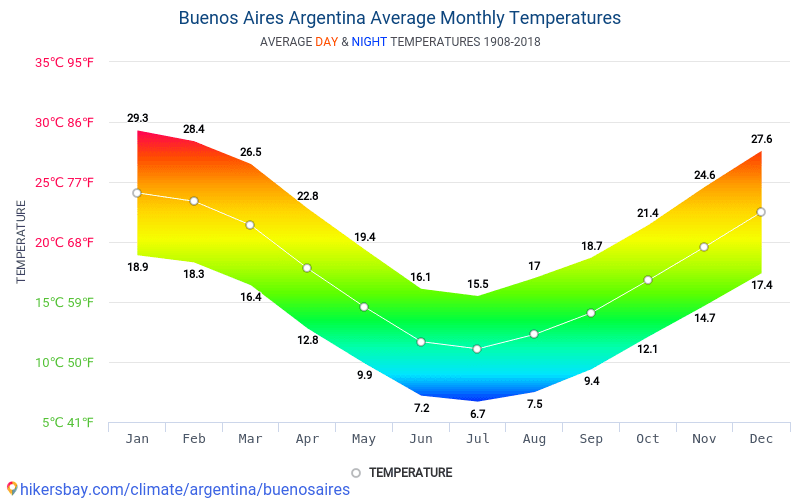
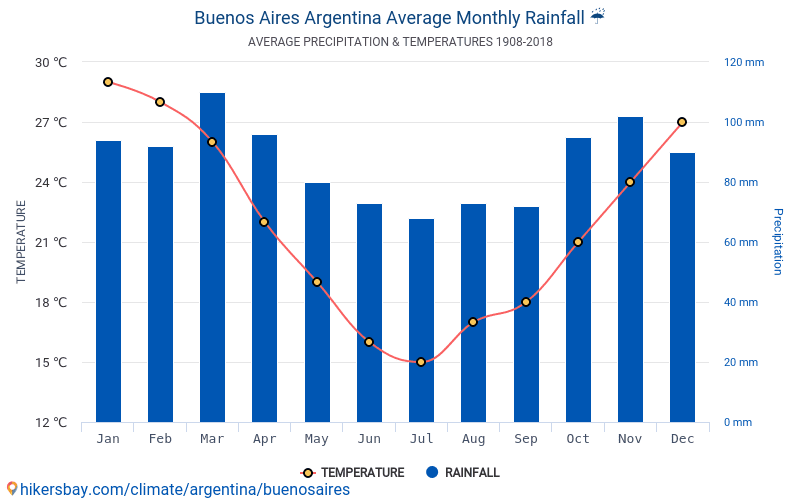
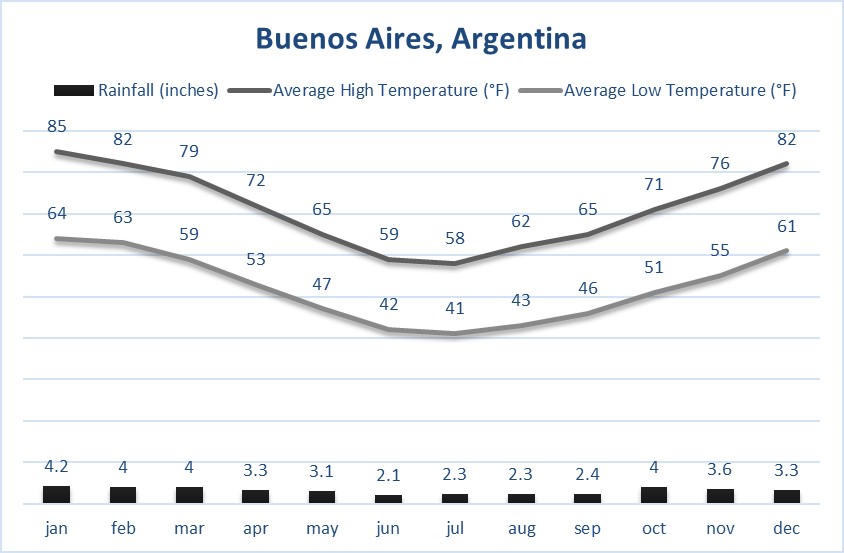
- Central Pampas (Humid Temperate): Experiences four distinct seasons: hot summers, cool winters, and transitional spring and autumn periods. Buenos Aires, Córdoba, and Santa Fe are in this region.
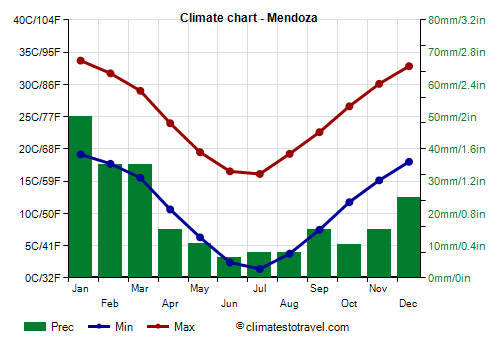
- Cuyo (Arid): Known for its dry climate, with hot summers and cold winters. Mendoza and San Juan are part of this arid region.
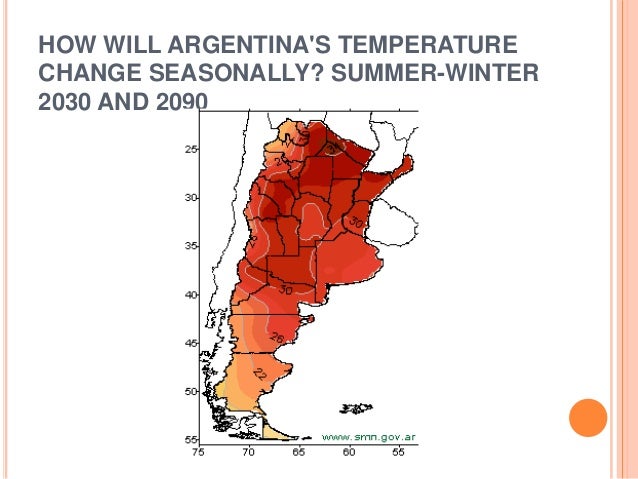
- Patagonia (Cold Semi-Arid/Tundra): Features cool summers and cold, snowy winters. Includes provinces like Río Negro, Chubut, Santa Cruz, and Tierra del Fuego.
Seasonal Climate Breakdown and Practical Applications
Spring (September - November)
Spring brings warmer temperatures and increasing rainfall across most of Argentina. However, regional differences are significant:
- Northwest: Temperatures rise significantly, reaching pleasant levels. This is an ideal time for outdoor activities like hiking and exploring. Practical Tip: Be prepared for occasional showers, especially in the afternoons. Pack light, breathable clothing and a rain jacket.
- Northeast: High humidity continues, but temperatures become more comfortable. This is a good time to visit the Iguazu Falls as water levels are generally high. Practical Tip: Insect repellent is essential due to the warm, humid conditions.
- Central Pampas: A transition period with fluctuating temperatures. Expect mild days and cooler nights. Practical Tip: Layering clothing is key. A light jacket or sweater will be useful for cooler evenings. Agriculture is active during this time; be aware of potential agricultural activities when traveling in rural areas.
- Cuyo: Temperatures start to rise, and the landscape begins to bloom. This is a great time for wine tourism in Mendoza. Practical Tip: Protect yourself from the sun with sunscreen and a hat, as the UV index can be high even in spring.
- Patagonia: The snow begins to melt, and the landscape awakens. This is the start of the trekking season. Practical Tip: Be prepared for unpredictable weather conditions. Pack waterproof gear and sturdy hiking boots.
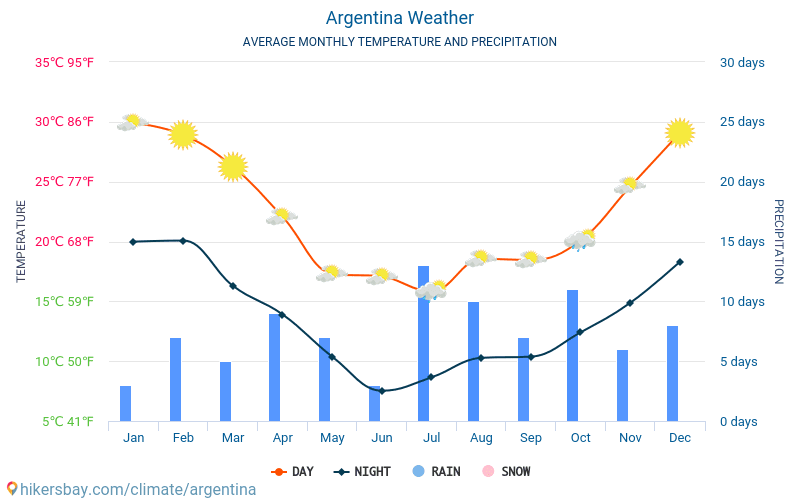
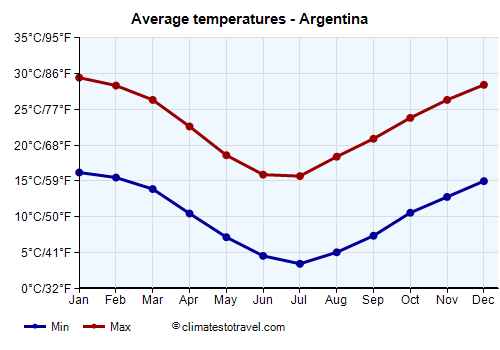
Summer (December - February)
Summer is the warmest season across Argentina, with varying levels of humidity and rainfall:
- Northwest: Hot and humid, with frequent afternoon thunderstorms. Practical Tip: Seek shelter during thunderstorms and stay hydrated. Lightweight, loose-fitting clothing is recommended.
- Northeast: High temperatures and humidity levels make this the most uncomfortable time of year for some. Practical Tip: Air conditioning is essential. Consider visiting attractions early in the morning or late in the afternoon to avoid the peak heat.
- Central Pampas: Hot and humid, with occasional heat waves. Practical Tip: Stay indoors during the hottest part of the day. Beaches along the Atlantic coast are popular destinations.
- Cuyo: Hot and dry, with intense sunshine. Practical Tip: Sun protection is crucial. Drink plenty of water to avoid dehydration. This is harvest season for many vineyards.
- Patagonia: Mild temperatures and longer daylight hours make this the best time to visit Patagonia. Practical Tip: Book accommodations and tours well in advance, as this is the peak tourist season.
Autumn (March - May)
Autumn brings cooler temperatures and vibrant foliage across much of Argentina:
- Northwest: Temperatures become milder, and the humidity decreases. This is a pleasant time to visit. Practical Tip: Enjoy outdoor activities like hiking and exploring the scenic landscapes.
- Northeast: A transition period with decreasing temperatures and humidity. Practical Tip: This is a good time to visit the Iguazu Falls as the crowds thin out.
- Central Pampas: Mild temperatures and colorful foliage make this a beautiful time of year. Practical Tip: Ideal for outdoor activities like cycling and picnics.
- Cuyo: Temperatures cool down, and the vineyards are awash in autumnal colors. Practical Tip: Wine tourism is still popular during this season.
- Patagonia: The landscape transforms into a tapestry of autumn colors. This is a great time for photography. Practical Tip: Be prepared for cooler temperatures and possible snowfall in higher elevations.
Winter (June - August)
Winter brings cooler temperatures, with snow in the Andes Mountains and Patagonia:
- Northwest: Mild and dry, with sunny days. Practical Tip: A good time to escape the cold of other regions. Pack light layers for variable temperatures.
- Northeast: Temperatures are cooler, but still relatively mild. Practical Tip: A pleasant time to visit without the oppressive humidity of summer.
- Central Pampas: Cool and damp, with occasional frosts. Practical Tip: Dress warmly and be prepared for rain. Indoor activities like visiting museums and art galleries are popular.
- Cuyo: Cold and dry, with snowfall in the Andes Mountains. Practical Tip: Skiing and snowboarding are popular activities in the Andes.
- Patagonia: Cold and snowy, with limited daylight hours. Practical Tip: Prepare for extreme weather conditions. Some tourist attractions may be closed. Winter sports are popular in certain areas.
Applying Climate Knowledge in Your Daily Life or Work
Understanding Argentina's climate can benefit you in numerous ways:
- Travel Planning: Choose the best time to visit specific regions based on your preferred weather conditions and activities.
- Agriculture: Farmers can optimize planting and harvesting schedules based on seasonal rainfall and temperature patterns.
- Business: Businesses can adjust their operations and marketing strategies to align with seasonal demand and consumer behavior. For example, retailers can stock up on winter clothing in Patagonia and swimwear in Buenos Aires during the appropriate seasons.
- Daily Activities: Plan your outdoor activities, clothing choices, and home maintenance based on the current and expected weather conditions.
- Health: Be aware of potential health risks associated with certain climates, such as heatstroke in the summer or respiratory illnesses in the winter. Take appropriate precautions to protect your health.
"Knowing the climate patterns of Argentina helps in anticipating challenges and opportunities across different sectors."
Essential Considerations
- Altitude: Remember that altitude can significantly affect temperature and weather conditions, especially in the Andes Mountains.
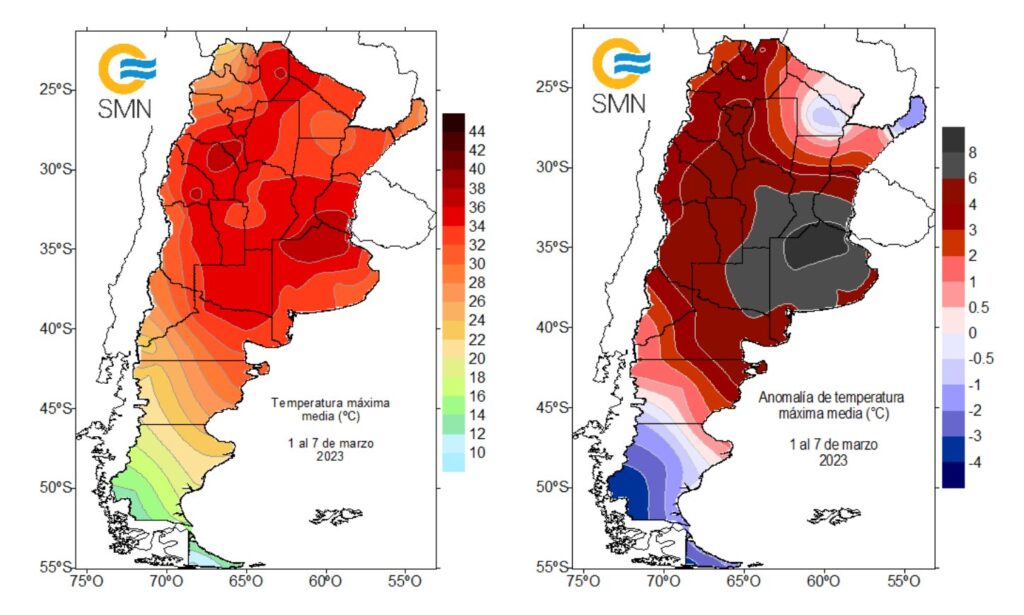
- El Niño/La Niña: Be aware of the potential impacts of El Niño and La Niña on Argentina's climate. These phenomena can cause significant variations in rainfall and temperature patterns.
- Local Variations: Keep in mind that climate can vary significantly even within the same region due to factors such as topography and proximity to water bodies.
Checklist for Climate-Aware Living in Argentina
- Research the climate zone of your destination or region.
- Check the weather forecast regularly.
- Pack appropriate clothing for the season and potential weather changes.
- Stay hydrated, especially in hot and dry climates.
- Protect yourself from the sun with sunscreen, a hat, and sunglasses.
- Be aware of potential health risks associated with the climate, such as heatstroke or hypothermia.
- Adjust your activities based on the weather conditions.
- Consider the impact of El Niño/La Niña on the climate in your region.
By understanding and adapting to Argentina's diverse climate, you can enhance your experiences and make informed decisions in your daily life and work.