The effectiveness of surge protectors, specifically when used without a proper ground connection, is a critical concern for electronic device protection. This article explores the functionality of surge protectors in the absence of grounding, addressing potential limitations and offering insights into ensuring adequate protection against voltage surges.
Surge Protector Functionality: A Grounded Perspective
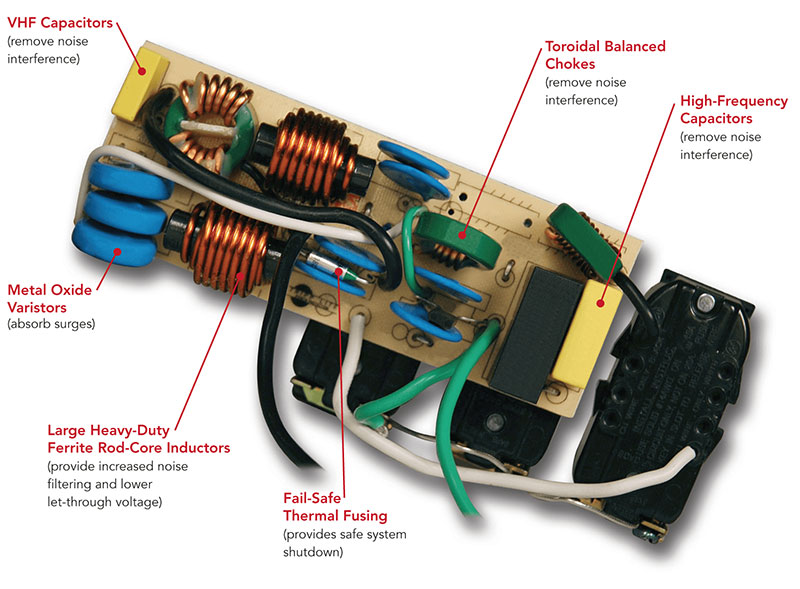
A surge protector's primary function is to divert excess voltage, known as a surge or transient voltage, away from connected electronic devices. This diversion is typically achieved through components called Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs). MOVs act as voltage-controlled resistors; they exhibit high resistance at normal operating voltages, preventing current flow. However, when a surge occurs and the voltage exceeds a certain threshold, the MOV's resistance drops dramatically, allowing the excess current to flow through it.
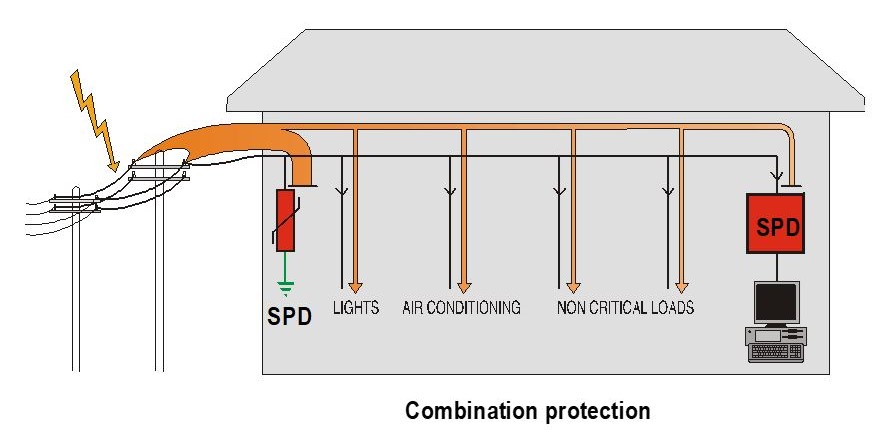
In a standard, properly grounded surge protector, this diverted current is directed to the grounding wire. The grounding wire then provides a low-impedance path back to the electrical panel and ultimately to the earth. This effectively neutralizes the surge, preventing it from reaching and potentially damaging connected equipment. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) provides standards and guidelines that emphasize the importance of grounding for effective surge protection.
Operating Without Ground: Limitations and Risks
The absence of a proper ground connection significantly compromises the surge protector's ability to function as intended. When a surge protector is plugged into an ungrounded outlet, the diverted surge current has no designated path to safely dissipate. This leads to several potential problems:
Incomplete Surge Diversion
Without a ground, the MOVs may still attempt to divert the surge. However, the current will be forced to find alternative paths, which may involve:
Elevated Voltage: The voltage on the neutral wire may increase, potentially exceeding safe levels for connected devices.
Reduced Effectiveness: The surge protector's capacity to absorb and divert the surge is significantly reduced, increasing the likelihood of damage to connected equipment.
Floating Ground and Voltage Instability
An ungrounded surge protector can contribute to a "floating ground" situation. This means that the voltage of the supposedly grounded parts of the connected equipment may fluctuate unpredictably relative to the true earth ground. This instability can:
Introduce Noise: Create electrical noise that interferes with sensitive electronic equipment, potentially causing malfunctions or data corruption.
Increase Shock Risk: Present a shock hazard if a person comes into contact with the equipment and another grounded object. Although the risk might be low, it's a real possibility.
Premature Surge Protector Failure
Repeated surges without a proper grounding path can stress the MOVs beyond their design limits, leading to:
Degradation: Gradual degradation of the MOVs' performance, reducing their ability to protect against subsequent surges.
Complete Failure: Ultimately, the MOVs can fail completely, rendering the surge protector ineffective. Some surge protectors have indicator lights that are supposed to warn about this, but they aren't always reliable.
Circumstances and Alternatives
While a grounded outlet is the ideal scenario, there are situations where it may not be readily available. Older homes, for example, may have ungrounded two-prong outlets. In such cases, several alternatives can be considered, although none provide the same level of protection as a properly grounded surge protector:
Professional Electrical Upgrade
The most effective solution is to have a qualified electrician upgrade the electrical system to include grounded outlets. This involves running a grounding wire to each outlet, ensuring a proper path for surge current. While this is the most expensive option, it provides the most comprehensive and reliable protection.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) Outlets
Replacing ungrounded outlets with GFCI outlets offers a degree of safety, primarily against electrical shock. GFCIs monitor the current flowing to and from an appliance. If there's a difference, indicating a leakage current (which could happen when a person is shocked), the GFCI trips, cutting off the power. However, GFCI outlets do not provide surge protection. They protect people from electric shock, not equipment from voltage surges.
"Cheater" Adapters (Not Recommended)
Using a "cheater" adapter, which converts a three-prong plug to a two-prong plug, is generally not recommended. These adapters often have a grounding tab intended to be connected to the outlet's screw. However, if the outlet box itself is not grounded (which is common in older homes), the adapter provides no effective grounding. In fact, it can create a false sense of security while offering no real protection and potentially increasing the risk of electrical problems.
Line Conditioners (Limited Benefit)
Line conditioners offer a different approach to power quality. While they may provide some degree of surge suppression, their primary function is to regulate voltage fluctuations and filter out electrical noise. Line conditioners are not a substitute for a properly grounded surge protector, particularly for dealing with large voltage surges caused by lightning or grid switching. However, a high-quality line conditioner may offer supplementary protection. The key is to check the Joule rating and response time.
Understanding Joule Ratings
The Joule rating of a surge protector indicates its ability to absorb energy from a surge. A higher Joule rating generally signifies greater protection. When selecting a surge protector, especially for valuable electronic equipment, choose one with a sufficiently high Joule rating. The appropriate rating depends on the type of equipment being protected and the potential severity of surges in the area. Devices that draw a large amount of power, like refrigerators, benefit from surge protection as well, but are likely to be more robust to power fluctuations. It's important to remember that the Joule rating reflects the total amount of energy the surge protector can absorb over its lifetime, not the maximum energy it can handle in a single surge.
Key Takeaways and Recommendations
Based on the information presented, the following conclusions can be drawn:
- Surge protectors are most effective when properly grounded. Without a ground connection, their ability to divert surge current is significantly compromised.
- Ungrounded surge protectors offer limited protection. They may provide some degree of surge suppression, but they are not a substitute for a grounded outlet.
- Consider professional electrical upgrades. Upgrading to grounded outlets is the most reliable way to ensure effective surge protection.
- GFCI outlets protect against electric shock, not surges. While they enhance safety, they do not replace the need for surge protection.
- Avoid "cheater" adapters. These adapters are often ineffective and can create a false sense of security.
- Understand Joule ratings. Choose surge protectors with appropriate Joule ratings based on the equipment being protected.
Ultimately, prioritizing a properly grounded electrical system is the most reliable approach to protecting valuable electronic equipment from voltage surges. While alternative solutions may offer some degree of protection in the absence of grounding, they are not equivalent to a properly grounded surge protector.