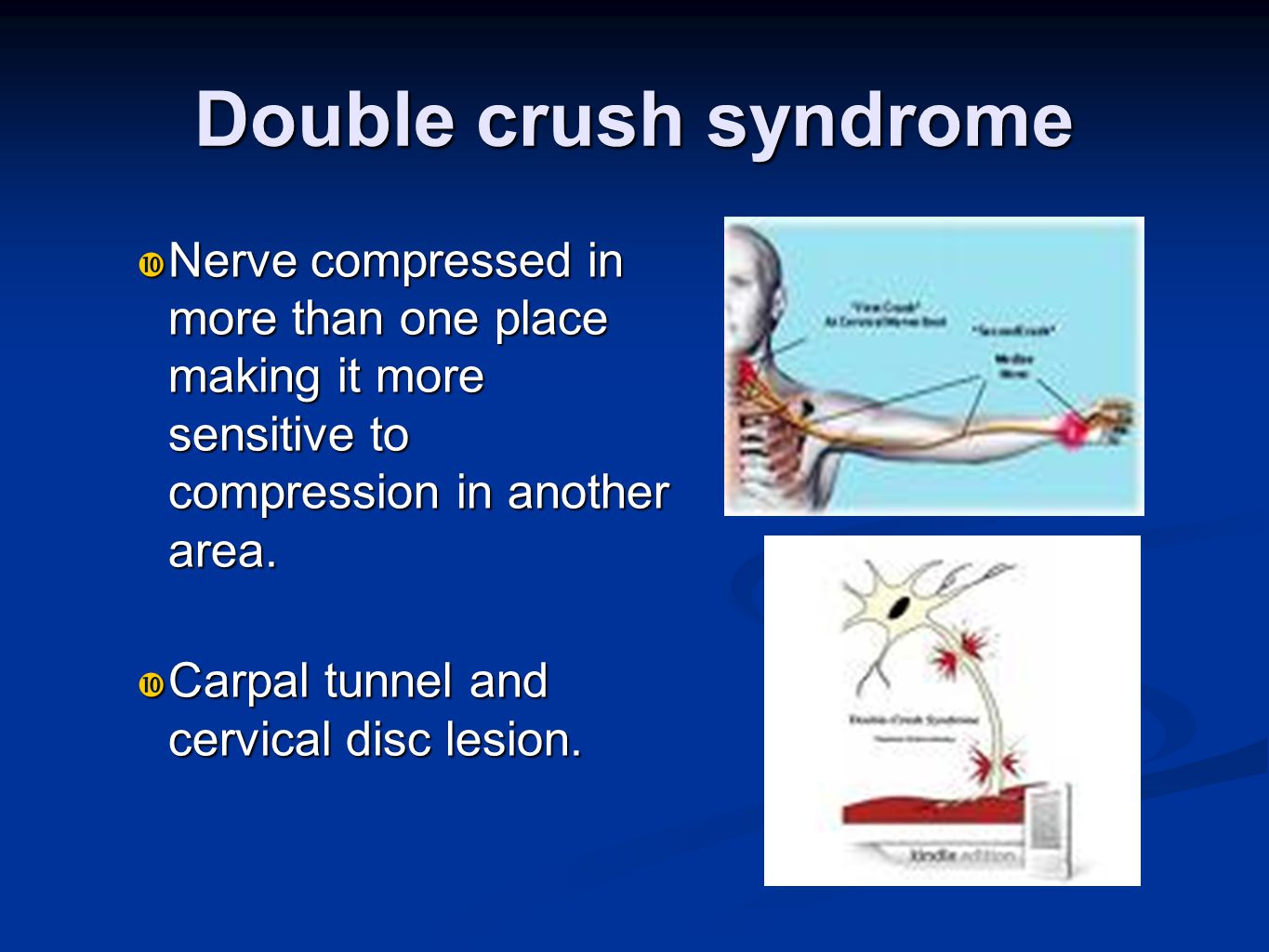
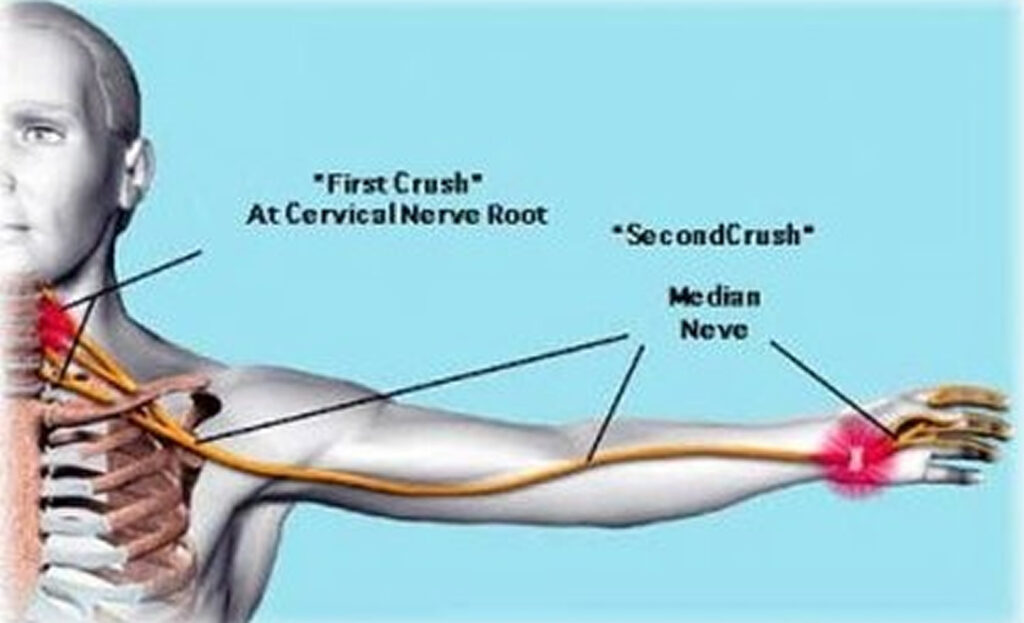
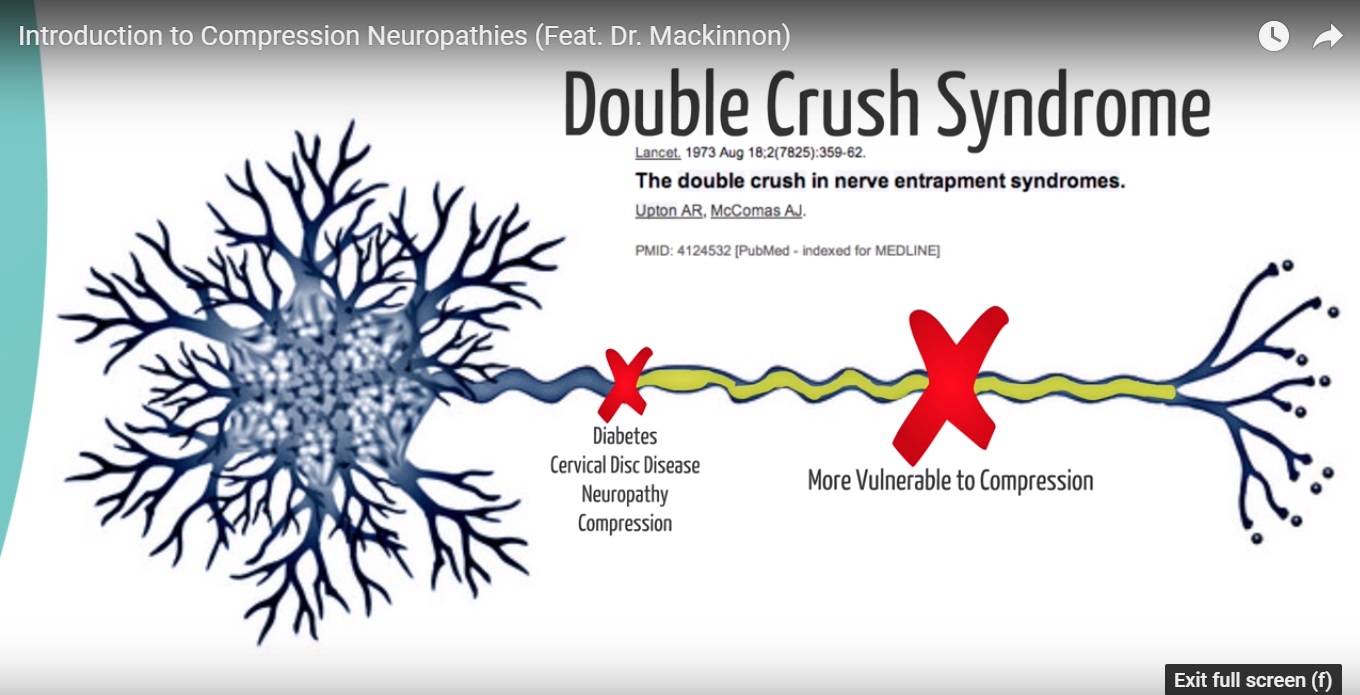
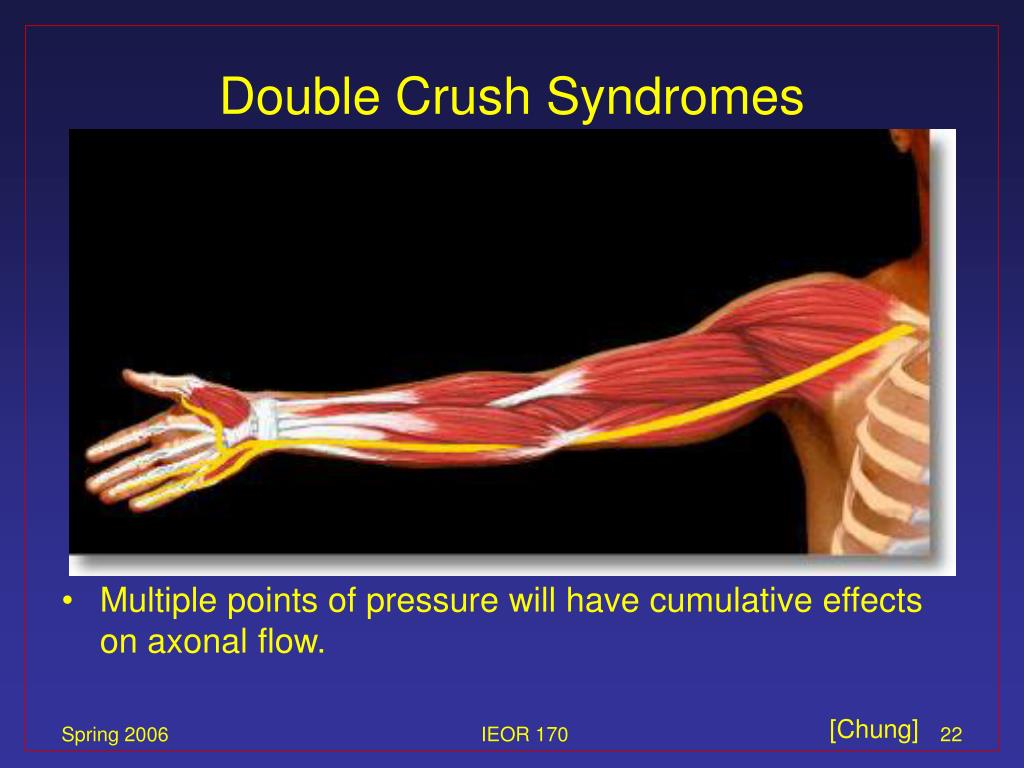
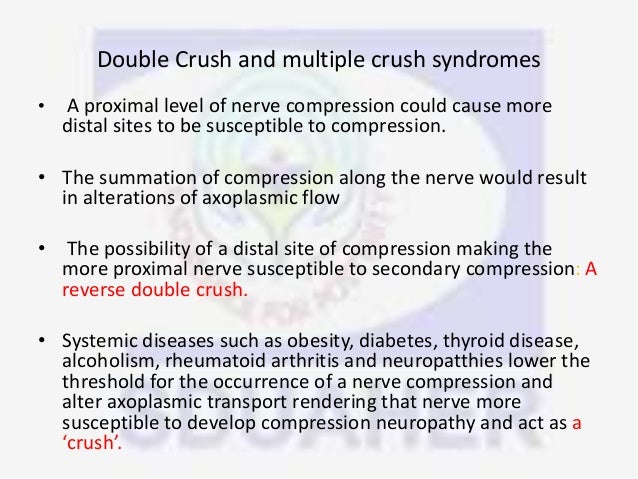
Double Crush Syndrome (DCS) represents a complex clinical entity wherein compression or irritation occurs at two or more sites along a single nerve pathway. First described by Upton and McComas in 1973, the theory posits that a proximal nerve compression renders the nerve more susceptible to damage from a more distal compression. While initially controversial, subsequent research has lent credence to the concept, highlighting its significance in understanding and managing peripheral nerve disorders.
Causes of Double Crush Syndrome
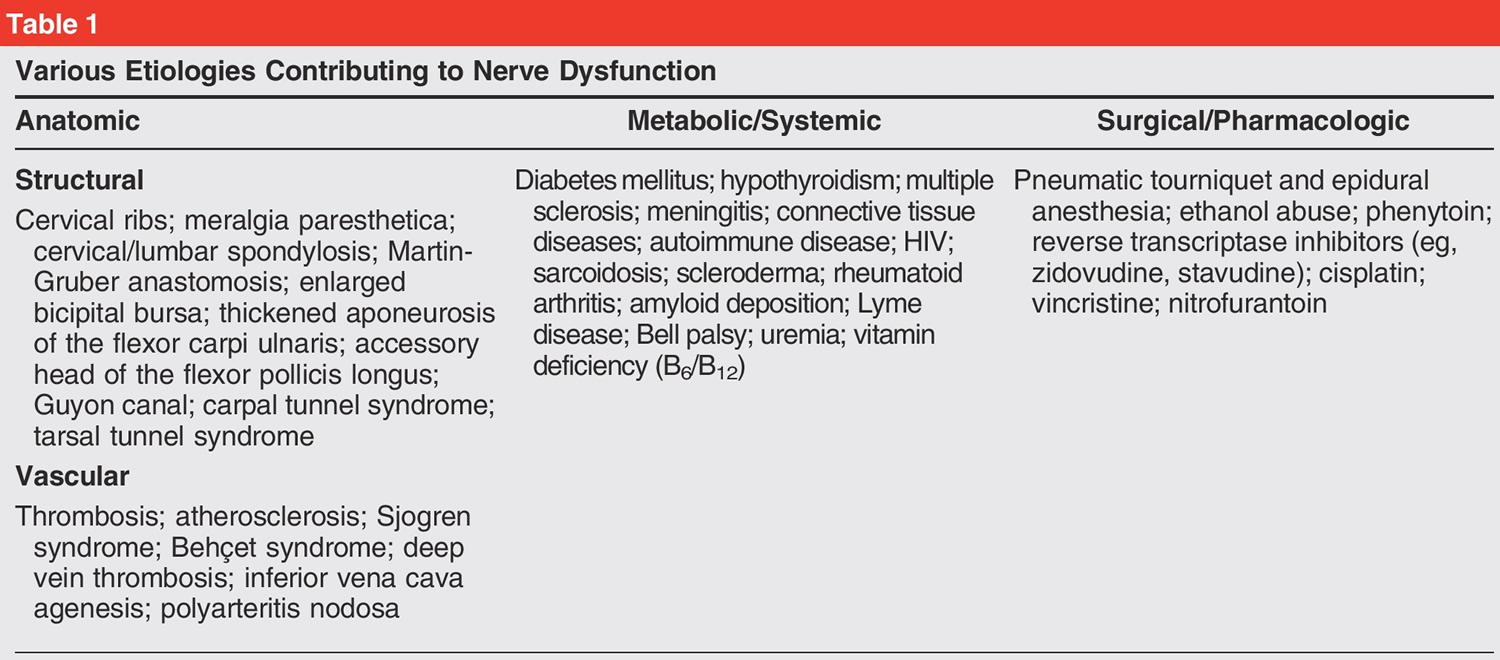
The etiology of DCS is multifactorial, encompassing a range of conditions that can compromise nerve function. The 'double crush' doesn't necessarily imply simultaneous injury. One site of compression might exist chronically, predisposing the nerve to injury at a second site. Some key contributing factors include:
Proximal Compression Sites:
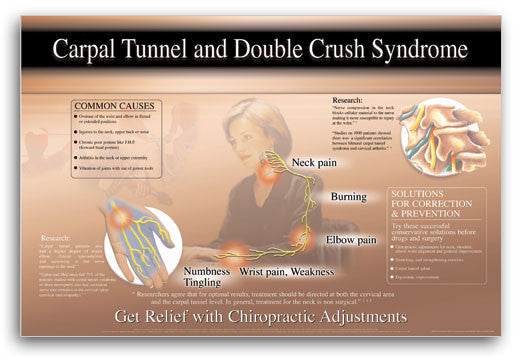
Frequently, the proximal compression occurs in the cervical spine or thoracic outlet. Cervical radiculopathy, stemming from disc herniation or spinal stenosis, can impinge on nerve roots exiting the spinal cord. Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS), affecting the brachial plexus as it passes through the space between the clavicle and first rib, is another common proximal cause. TOS can be neurogenic (affecting nerves), vascular (affecting blood vessels), or a combination of both.
"In a study published in the *Journal of Hand Surgery*, researchers found a statistically significant association between cervical spondylosis and carpal tunnel syndrome, suggesting a possible link consistent with the double crush phenomenon."
Distal Compression Sites:
Distal compression sites are varied, but carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), affecting the median nerve at the wrist, is the most prevalent. Cubital tunnel syndrome, involving the ulnar nerve at the elbow, and pronator syndrome, impacting the median nerve in the forearm, are other examples. These distal compressions often arise from repetitive motions, prolonged awkward postures, or direct trauma. For example, individuals performing repetitive keyboarding are at increased risk of developing both carpal tunnel syndrome and potentially a proximal compression such as cervical radiculopathy, creating the conditions for a double crush.
Underlying Systemic Factors:
Certain systemic conditions can predispose individuals to DCS. Diabetes mellitus, for instance, can impair nerve function and increase vulnerability to compression injuries. Other contributing factors include hypothyroidism, inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, and nutritional deficiencies. Smoking is also implicated, as it can impair microcirculation and nerve regeneration.
Signs and Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of DCS are complex and often overlap with those of individual nerve compression syndromes, making diagnosis challenging. Patients typically present with a combination of symptoms related to both proximal and distal nerve involvement. A thorough neurological examination and a detailed patient history are crucial for accurate diagnosis.
Pain and Sensory Disturbances:
Pain is a cardinal symptom, often described as burning, aching, or shooting in nature. It may radiate along the affected nerve pathway. Sensory disturbances, such as numbness, tingling (paresthesia), and a pins-and-needles sensation, are also common. These sensations may be exacerbated by specific movements or postures.
Motor Weakness:
Motor weakness can occur in the muscles innervated by the affected nerve. This may manifest as difficulty with grip strength, fine motor coordination, or lifting objects. In severe cases, muscle atrophy may develop over time.
Specific Symptom Patterns:
The specific symptoms will vary depending on the nerves involved. For example, a patient with cervical radiculopathy and carpal tunnel syndrome may experience neck pain radiating into the arm, accompanied by numbness and tingling in the thumb, index, and middle fingers. They may also have weakness in grip strength and difficulty with tasks requiring fine motor skills.
Provocative Maneuvers:
Physical examination often involves provocative maneuvers designed to elicit or worsen symptoms. These may include Spurling's test for cervical radiculopathy, Phalen's test and Tinel's sign for carpal tunnel syndrome, and Adson's test for thoracic outlet syndrome. Positive findings on these tests, in conjunction with the patient's history and other examination findings, can help support the diagnosis of DCS.
Effects and Implications
The presence of DCS can significantly impact a patient's quality of life and functional abilities. The combined effect of multiple nerve compressions can lead to more severe and persistent symptoms compared to single nerve compression syndromes. Failure to recognize and address both sites of compression can result in treatment failure and chronic pain.
Diagnostic Challenges:
Diagnosing DCS can be challenging due to the overlapping symptoms and the need to identify multiple compression sites. Electrodiagnostic studies, such as nerve conduction studies (NCS) and electromyography (EMG), are often used to assess nerve function and localize the sites of compression. However, these studies may not always be conclusive, and clinical correlation is essential.
Treatment Strategies:
Treatment of DCS typically involves addressing both proximal and distal compression sites. This may include a combination of conservative and surgical interventions. Conservative measures may include physical therapy, ergonomic modifications, activity modification, and pain management strategies. Surgical interventions may be considered if conservative measures fail to provide adequate relief. For example, a patient with both cervical radiculopathy and carpal tunnel syndrome might require cervical decompression surgery and carpal tunnel release.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes:
The prognosis for DCS depends on several factors, including the severity and duration of the compressions, the patient's overall health, and the effectiveness of treatment. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for optimizing outcomes. However, even with appropriate treatment, some patients may experience persistent symptoms or functional limitations. A multidisciplinary approach involving physicians, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and other healthcare professionals is often necessary to provide comprehensive care.
Implications for Research and Clinical Practice:
Further research is needed to better understand the pathophysiology of DCS and to develop more effective diagnostic and treatment strategies. Studies investigating the biomechanical and neurophysiological interactions between different nerve compression sites are warranted. In clinical practice, it is important to consider the possibility of DCS in patients presenting with symptoms of peripheral nerve compression. A thorough evaluation, including a detailed history, physical examination, and electrodiagnostic studies, is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
Broader Significance
The concept of Double Crush Syndrome highlights the interconnectedness of the nervous system and the importance of considering the entire nerve pathway when evaluating and treating patients with peripheral nerve disorders. It serves as a reminder that seemingly isolated symptoms may be related to underlying biomechanical or systemic factors affecting the nerve at multiple levels. By recognizing and addressing these factors, clinicians can provide more comprehensive and effective care, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life. The understanding of DCS encourages a holistic approach to musculoskeletal health, prompting practitioners to look beyond the immediate site of pain or dysfunction to identify potential contributing factors elsewhere in the body. This broader perspective is crucial for effective diagnosis and management of a wide range of conditions, not just peripheral nerve disorders. The recognition of DCS underscores the need for collaborative care among different healthcare specialties, fostering a more integrated and patient-centered approach to medicine. Furthermore, the ongoing research into DCS can potentially reveal valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms of nerve injury and repair, paving the way for the development of novel therapeutic interventions. Ultimately, the study of DCS provides a valuable lens through which to view the complex interplay of biomechanics, physiology, and neurological function in the human body.