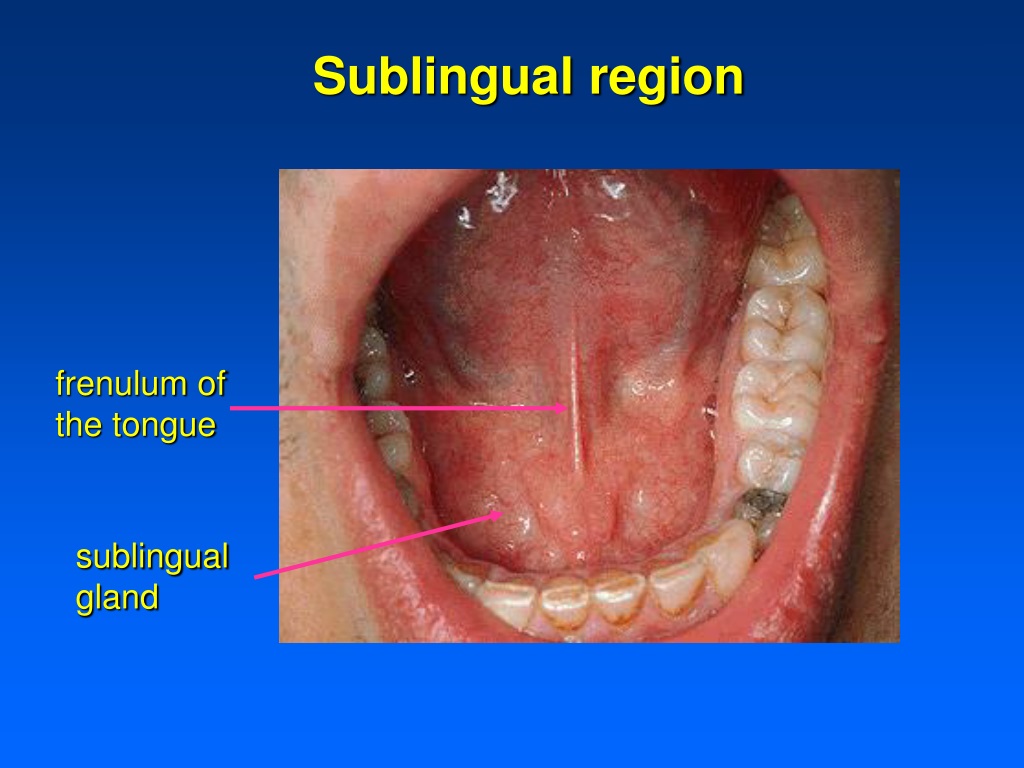
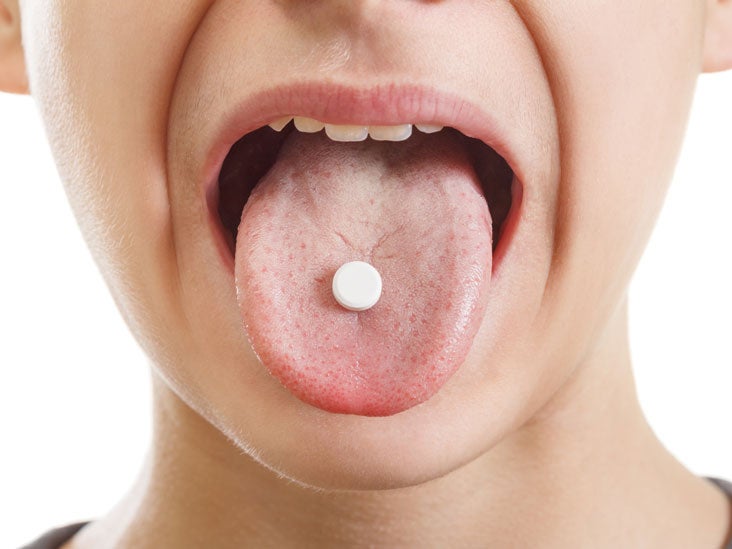
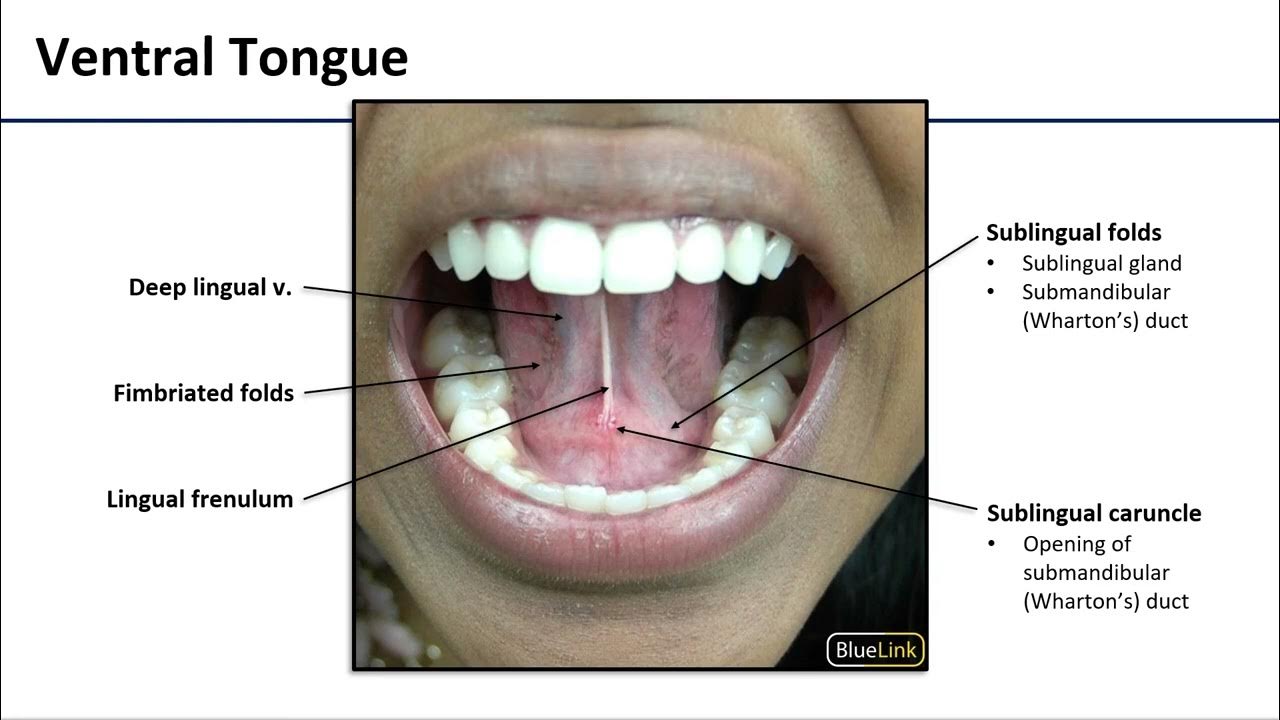
Sublingual Administration: Optimizing Absorption
Sublingual administration, involving placement of a substance under the tongue, offers a direct route to the bloodstream. This method bypasses the first-pass metabolism in the liver, potentially leading to faster onset and higher bioavailability compared to oral ingestion. The duration for which a substance is held under the tongue is a critical factor in determining its efficacy.
Factors Influencing Absorption Time
Several variables affect the optimal hold time for sublingual medications and supplements:
- Molecular Properties: The size and lipophilicity (fat solubility) of the molecule dictate how readily it can permeate the sublingual mucosa. Smaller, more lipophilic molecules tend to absorb more rapidly.
- Formulation: The formulation of the sublingual product, including the presence of excipients and the method of delivery (e.g., tablet, spray, lozenge), plays a crucial role. Certain formulations are designed for faster disintegration and dissolution.
- Individual Physiology: Factors such as salivary flow rate, mucosal thickness, and individual metabolic variations can influence absorption rates.
- Dosage: While hold time is primary, higher doses may exhibit a slightly longer absorption window.
General Guidelines for Hold Time
While specific instructions should always be followed based on the product label or a healthcare professional's advice, some general guidelines apply to sublingual administration:
Standard Recommendations
The generally recommended hold time for most sublingual products ranges from 30 seconds to 2 minutes. This period allows sufficient time for the substance to dissolve and be absorbed through the sublingual mucosa. Extended hold times beyond this range may not necessarily increase absorption and could lead to increased swallowing of the substance, thereby reducing its bioavailability by subjecting it to gastrointestinal metabolism.
Specific Product Instructions
It is crucial to adhere to the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer or a healthcare provider. These instructions are based on the formulation and properties of the particular product and are designed to optimize its absorption and efficacy. Deviating from these instructions can result in reduced effectiveness or potential side effects.
Always consult the product label or a healthcare professional for specific instructions regarding the appropriate hold time for a sublingual medication or supplement.
The Science Behind Sublingual Absorption
The sublingual area, located beneath the tongue, is rich in blood vessels. This vascularity allows for direct absorption of substances into the bloodstream, bypassing the digestive system and liver. The mucosa in this region is also relatively thin, facilitating rapid diffusion.
The Role of Saliva
Saliva plays a vital role in the sublingual absorption process. It helps to dissolve the substance, allowing it to come into contact with the mucosal membrane. However, excessive swallowing of saliva during the hold time can reduce the amount of the substance absorbed sublingually, leading to decreased efficacy. It is generally advisable to minimize swallowing during the recommended hold time.
Minimizing Swallowing
To maximize sublingual absorption, avoid excessive swallowing during the recommended hold time. This can be achieved by tilting the head slightly forward or gently pressing the tongue against the roof of the mouth. After the recommended hold time, any remaining substance can be swallowed.
Potential Consequences of Incorrect Hold Time
Using an inappropriate hold time can lead to several undesirable outcomes:
Reduced Efficacy
Insufficient hold time may not allow for adequate absorption, resulting in a reduced therapeutic effect. This can be particularly problematic for medications requiring precise dosing.
Increased Side Effects
Prolonged hold times, while not necessarily harmful, could lead to increased swallowing of the substance. This can increase the risk of gastrointestinal side effects or alter the bioavailability of the product in an unpredictable manner.
Variability in Response
Inconsistent hold times can introduce variability in the response to a sublingual product. This can make it difficult to assess the true efficacy of the treatment and may necessitate adjustments to the dosage or frequency of administration.
Examples of Sublingual Products and Recommended Hold Times
The following examples illustrate the variability in recommended hold times for different sublingual products:
- Nitroglycerin (for angina): Typically requires a very short hold time, often only until dissolved (usually 1-2 minutes, or as directed by a physician). Its rapid absorption is critical for immediate relief.
- Buprenorphine/Naloxone (for opioid use disorder): Often requires a longer hold time (5-10 minutes) to ensure adequate absorption of both medications.
- Vitamin B12 (methylcobalamin): May have variable recommendations (30 seconds - 5 minutes), depending on the specific formulation.
These examples highlight the importance of adhering to the specific instructions for each product.
Considerations for Specific Populations
Certain populations may require special considerations when using sublingual administration:
- Children: May have difficulty holding a substance under their tongue for the required time. Supervision and encouragement are often necessary.
- Elderly: May have reduced salivary flow, which can affect absorption. They may require additional time for the substance to dissolve.
- Individuals with Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): May also experience reduced absorption due to insufficient saliva. Strategies to stimulate saliva production may be helpful.
Best Practices for Sublingual Administration
To optimize the effectiveness of sublingual administration, consider the following best practices:
- Follow Instructions Carefully: Always adhere to the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer or a healthcare professional.
- Minimize Swallowing: Avoid excessive swallowing during the recommended hold time.
- Avoid Eating or Drinking: Refrain from eating or drinking for at least 10-15 minutes before and after sublingual administration to avoid interfering with absorption.
- Maintain Oral Hygiene: Good oral hygiene can promote optimal absorption.
- Store Products Properly: Store sublingual products according to the manufacturer's instructions to maintain their stability and efficacy.
- Report Any Issues: If you experience any unexpected side effects or notice a lack of efficacy, consult with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
The duration for which a substance is held under the tongue during sublingual administration is a critical determinant of its effectiveness. Adhering to the recommended hold time, minimizing swallowing, and considering individual physiological factors are essential for maximizing absorption and achieving the desired therapeutic outcome. Always prioritize the specific instructions provided by the manufacturer or a healthcare professional. While general recommendations exist, the specific formulation and individual characteristics dictate the optimal approach.
Key Takeaways
- Sublingual absorption bypasses first-pass metabolism, offering faster onset and higher bioavailability.
- Optimal hold time typically ranges from 30 seconds to 2 minutes, but varies depending on the product.
- Always follow specific instructions provided by the manufacturer or a healthcare professional.
- Minimize swallowing during the recommended hold time to maximize absorption.
- Consider individual factors such as salivary flow and age when using sublingual administration.




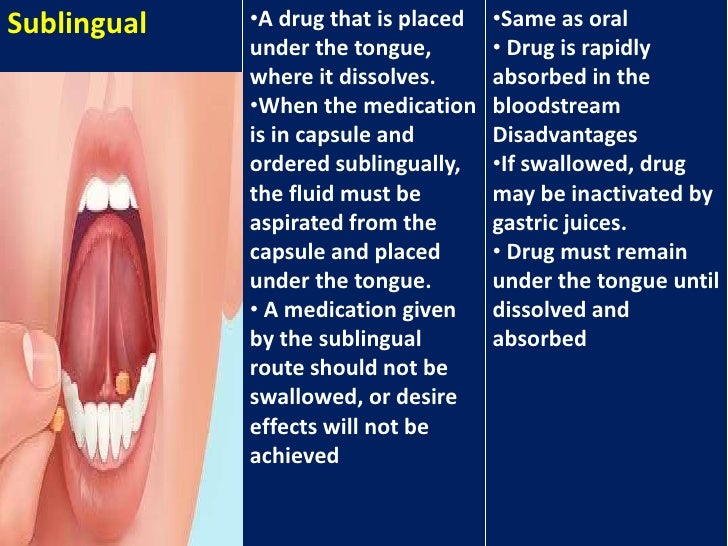

.jpg)