Okay, so picture this: I'm sweating. Seriously, like Niagara Falls in my living room. My old window AC unit had officially given up the ghost (RIP, trusty old friend). It was a sad day, marked mostly by me fanning myself with a magazine and Googling "fastest way to build a cryogenic chamber at home." Dramatic, I know. But then reality hit: I needed a new AC, and fast. But this time, I was determined to be smart about it. No more energy-hogging behemoths! Which led me down the rabbit hole of... wattage.
And that, my friends, is how we arrive at the burning question of the hour: How many watts does a small AC unit actually use? Because let's face it, nobody wants to spend a fortune cooling down their humble abode. (Especially not after spending all that money on avocado toast, am I right? 😉)
Deciphering the Wattage Puzzle
First things first: what *exactly* is a watt? Well, in the simplest terms, it's a unit of power. Think of it like this: your AC unit *needs* power to do its job of chilling your space. Watts are how we measure that power. The higher the wattage, the more power the AC unit consumes. More power consumption typically translates to a higher electricity bill. And nobody wants that.
So, how do we figure out the wattage of a small AC unit? There are a few ways to crack this code. Let's break it down:
1. The Obvious: Check the Label!
This might sound ridiculously simple, but trust me, it's often overlooked. Most AC units have a sticker or label somewhere on them (usually on the back or side) that clearly states the wattage. Look for a number followed by the letter "W". It could be hiding in plain sight!
Pro tip: Sometimes the label might list the amperage (amps) and voltage. Don't panic! You can easily calculate the wattage using this formula: Watts = Amps x Volts. In the US, standard voltage is usually 120V. So, if your AC unit says it draws 5 amps, the wattage would be 5 x 120 = 600 watts.
2. BTU to Watts: The Conversion Game
Okay, this is where things get a little bit more... "technical." You've probably seen AC units advertised based on their BTU (British Thermal Units). BTU is a measure of how much heat the AC unit can remove from a room per hour. A higher BTU rating generally means the unit can cool a larger space.
Now, there isn't a *perfect* direct conversion between BTU and watts, but there's a handy rule of thumb:
Generally, you can estimate the wattage by dividing the BTU rating by a number called the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER). The EER is basically a measure of how efficiently the AC unit converts electricity into cooling power. A higher EER means the unit is more efficient.
So, the formula looks like this: Watts = BTU / EER
Most window AC units have an EER between 8 and 12. Let's say you have a 5,000 BTU AC unit with an EER of 10. The estimated wattage would be 5000 / 10 = 500 watts.
Important caveat: This is just an estimate. The actual wattage can vary depending on the specific model and its operating conditions.
3. Online Resources and Product Specs
If you can't find the label or the EER number, don't give up! The internet is your friend! Find the model number of your AC unit (it's usually on that same label we talked about earlier) and search for it online. Most manufacturers will have detailed product specifications available on their websites or on retailer websites like Amazon or Home Depot. Look for the "power consumption" or "wattage" information.
So, How Many Watts *Typically* Do Small AC Units Use?
Alright, let's get down to the nitty-gritty. What can you expect in terms of wattage for different sizes of small AC units?
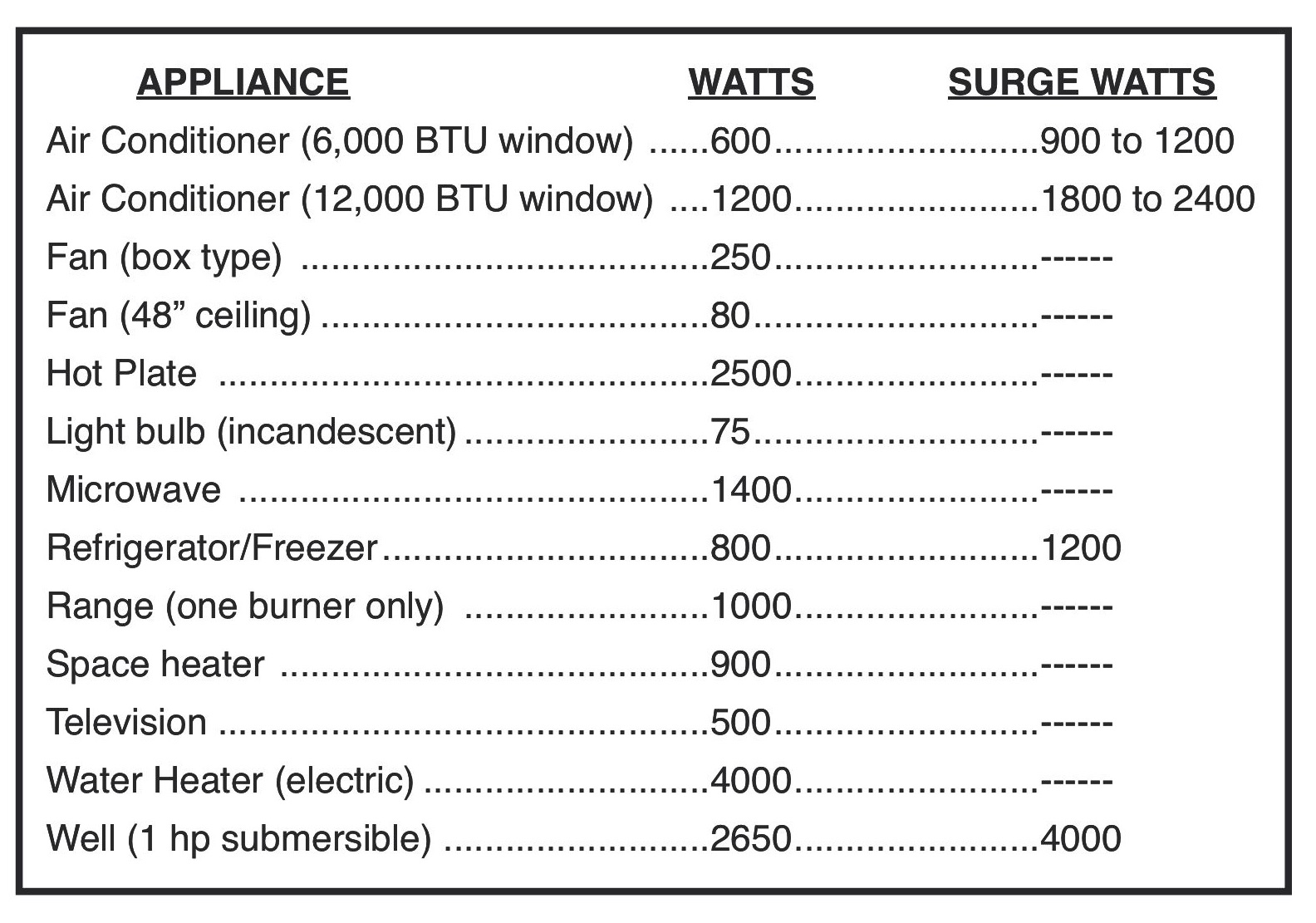
- 5,000 BTU: These are your super-portable, "dorm room" size AC units. They're great for cooling small spaces (think bedrooms or small offices). Expect them to use somewhere in the range of 450-600 watts.
- 6,000-8,000 BTU: A step up in cooling power, these units are good for slightly larger rooms. The wattage typically falls between 550-850 watts.
- 10,000 BTU: These are at the upper end of the "small" AC unit category. They can handle larger bedrooms or living rooms. Look for wattage in the 900-1200 watt range.
Remember, these are just typical ranges. The actual wattage can vary depending on the brand, model, and features of the AC unit. Always check the specific product information for the most accurate number.
Wattage Isn't Everything: The Importance of Efficiency
Okay, so you've figured out the wattage. Great! But hold on a second. There's more to the story than just raw power consumption. You also need to consider energy efficiency.
An AC unit with a *lower* wattage might seem like the obvious choice for saving money. But if it's not very efficient, it might take longer to cool the room, or it might not cool it as effectively. This means it'll run for longer periods, potentially negating any wattage savings.
That's where the EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) comes in. As we discussed earlier, a higher EER means the AC unit is more efficient. It can remove more heat from the room using less electricity. When you're shopping for an AC unit, pay attention to the EER rating. Look for models with an EER of 10 or higher.
Another important factor is the SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio). SEER is a measure of energy efficiency over an entire cooling season. It's a more comprehensive measure than EER, which is typically measured under specific conditions. Look for AC units with a high SEER rating to maximize your energy savings.
Beyond the Numbers: Practical Tips for Saving Energy
Okay, you've got the wattage and efficiency stuff down. Now, let's talk about some practical tips for saving energy with your small AC unit. Because let's be honest, we all want to keep those electricity bills as low as possible.
- Size Matters: Make sure you choose the right size AC unit for your room. An oversized unit will cycle on and off too frequently, wasting energy. An undersized unit will run constantly, also wasting energy. Use a BTU calculator to determine the appropriate size for your space. (Psst... You can easily find them online. Just Google "AC BTU calculator.")
- Seal the Deal: Prevent cool air from escaping by sealing any gaps around windows and doors. Use weather stripping or caulk to fill in any cracks. This simple step can make a big difference in energy efficiency.
- Close the Curtains: During the hottest part of the day, close your curtains or blinds to block out sunlight. This will help keep the room cooler, reducing the workload on your AC unit. Think of it as giving your AC a little vacation!
- Use a Fan: Fans don't actually cool the air, but they can make you *feel* cooler by circulating air and helping sweat evaporate. Use a fan in conjunction with your AC unit to improve comfort and potentially reduce the amount of time you need to run the AC.
- Regular Maintenance: Clean or replace your AC unit's filter regularly. A dirty filter restricts airflow, forcing the unit to work harder and use more energy. This is like giving your AC a much-needed spa day. (And it'll thank you with lower energy bills!)
- Smart Thermostats: Consider using a smart thermostat that allows you to schedule when your AC unit turns on and off. You can set it to automatically turn off when you're not home or when you're sleeping. This can save you a significant amount of energy over time.
Final Thoughts: Be Informed, Be Efficient, Be Cool (Literally!)
So, there you have it! Everything you need to know about the wattage of small AC units. By understanding how wattage and efficiency work, you can make an informed decision when choosing an AC unit for your home. And by implementing some simple energy-saving tips, you can keep your electricity bills under control while staying cool and comfortable.
Now, if you'll excuse me, I'm going to go crank up my *efficient* new AC unit and enjoy the blissful coolness. Stay cool, my friends!