Ion semiconductor DNA sequencing represents a significant advancement in genomic analysis, offering a rapid and cost-effective alternative to traditional sequencing methods. Understanding the patent landscape surrounding this technology is crucial for businesses involved in research, development, and commercialization within the life sciences sector. This article provides an overview of the patent application activity related to ion semiconductor DNA sequencing in the United States, focusing on key players, technological innovations, and notable legal considerations.
Fundamentals of Ion Semiconductor Sequencing
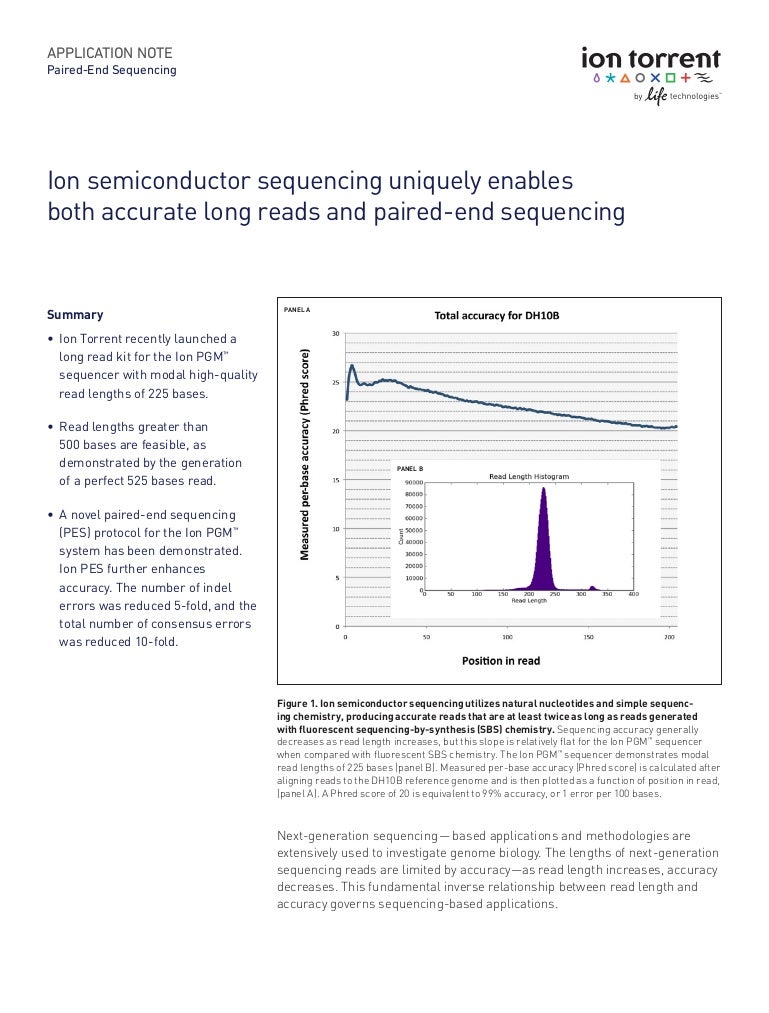
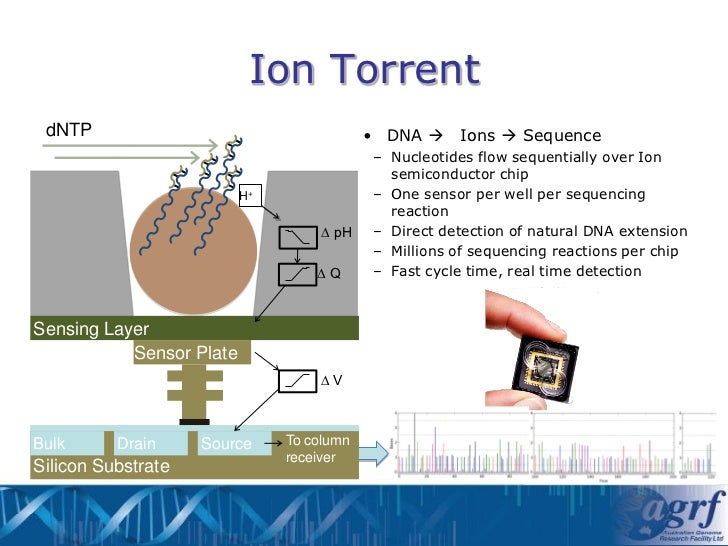
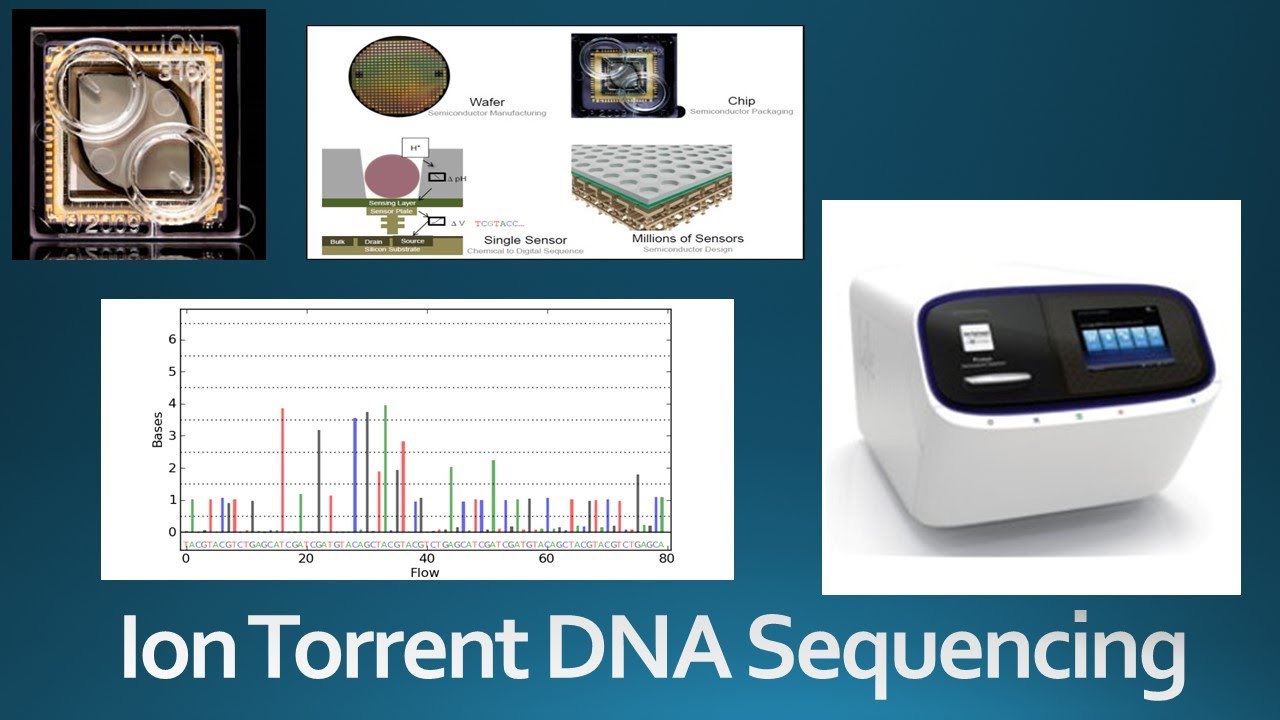
Ion semiconductor sequencing, often associated with Ion Torrent (now part of Thermo Fisher Scientific), employs a fundamentally different approach compared to chain-termination sequencing (Sanger sequencing) or sequencing by synthesis using fluorescent labels. It leverages the direct detection of hydrogen ions (H+) released during DNA polymerization. When a nucleotide is incorporated into a strand of DNA by DNA polymerase, an H+ ion is released, altering the pH of the solution. An array of ion sensors detects these changes in pH, allowing the identification of the nucleotide added at each step.
This method eliminates the need for expensive optical systems and labeled nucleotides, contributing to reduced sequencing costs and faster turnaround times. The technology's reliance on semiconductor manufacturing processes also allows for high-density arrays of sensors to be fabricated, enabling massively parallel sequencing.
Key Patent Holders and Applications
The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) records reveal a diverse range of patent applications related to ion semiconductor DNA sequencing. Thermo Fisher Scientific, by virtue of its acquisition of Ion Torrent, holds a significant portfolio of patents covering various aspects of the technology. However, other entities, including academic institutions and smaller biotechnology companies, also contribute to the patent landscape.
Thermo Fisher Scientific's Dominance
Thermo Fisher Scientific's patents often cover fundamental aspects of the ion sensing technology, including the design and fabrication of the sensor arrays, methods for nucleotide incorporation, and signal processing techniques. Their patent applications frequently describe improvements in accuracy, throughput, and scalability of the sequencing process. Examples include patents relating to:
- Sensor array architectures with improved sensitivity.
- Methods for reducing noise and improving signal-to-noise ratios.
- Fluidics systems for efficient delivery of reagents to the sensor array.
- Algorithms for base calling and error correction.
Analyzing Thermo Fisher Scientific's patent applications provides insights into the ongoing development of ion semiconductor sequencing and their strategies for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Academic and Other Contributions
Universities and research institutions play a vital role in developing novel approaches and improvements within the field. Their patent applications often focus on:
- New sensor materials and designs.
- Methods for enhancing the accuracy of homopolymer sequencing (sequences with multiple consecutive identical bases).
- Integration of ion semiconductor sequencing with microfluidic devices.
- Applications of the technology in specific areas, such as disease diagnostics or environmental monitoring.
These contributions can be crucial for driving innovation and expanding the applicability of ion semiconductor sequencing to new fields.
Technological Innovations and Patent Focus Areas
Several key areas of technological innovation are reflected in recent patent applications related to ion semiconductor DNA sequencing:
Sensor Technology Advancements
A primary focus is on improving the sensitivity and reliability of the ion sensors. This includes exploring new materials, such as graphene or other nanomaterials, to enhance the detection of pH changes. Patent applications in this area often describe novel sensor designs and fabrication techniques aimed at reducing noise and increasing signal strength.
Fluidics and Reagent Delivery
Efficient and precise delivery of reagents to the sensor array is critical for achieving high throughput and accuracy. Patent applications related to fluidics systems describe microfluidic designs that minimize reagent consumption, reduce dead volume, and enable rapid cycling of reagents.
Data Analysis and Error Correction
Accurate base calling from the raw signal data is a significant challenge, particularly in homopolymer regions. Patent applications in this area focus on developing sophisticated algorithms for signal processing, error correction, and base calling. These algorithms often incorporate machine learning techniques to improve accuracy and reduce false positives.
Sample Preparation and Library Construction
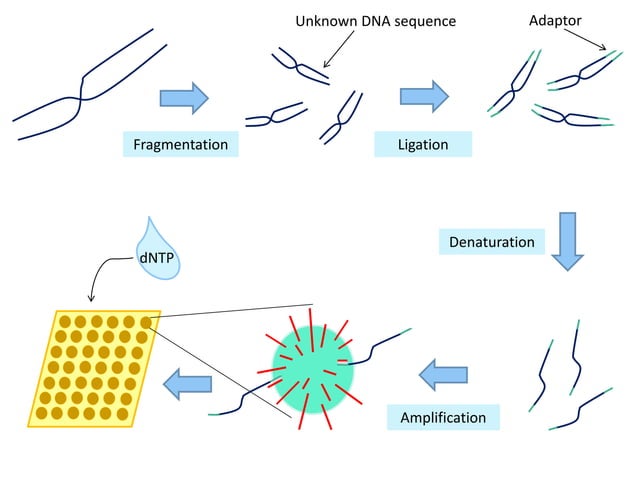
The quality of the DNA library used for sequencing significantly impacts the accuracy and reliability of the results. Patent applications related to sample preparation and library construction describe methods for improving DNA fragmentation, adapter ligation, and amplification, resulting in higher-quality libraries and improved sequencing performance.
Legal and Business Considerations
The patent landscape surrounding ion semiconductor DNA sequencing presents several legal and business considerations for companies operating in this field:
Freedom to Operate
Before commercializing any product or service based on ion semiconductor sequencing, it is crucial to conduct a thorough freedom-to-operate analysis. This involves identifying existing patents that may cover the technology and assessing the risk of infringement. A comprehensive search of the USPTO database and consultation with patent attorneys are essential steps in this process.
Patent Licensing and Cross-Licensing
Given the complex patent landscape, companies may need to negotiate licenses with patent holders to gain access to necessary technologies. Cross-licensing agreements, where companies exchange rights to their respective patents, can be a valuable strategy for avoiding infringement disputes and fostering collaboration.
Patent Strategy and Portfolio Development
Developing a robust patent strategy is crucial for protecting a company's innovations and securing a competitive advantage. This involves identifying patentable aspects of the technology, filing patent applications in relevant jurisdictions, and actively monitoring the patent landscape to identify potential infringement or licensing opportunities.
Patent Litigation
Patent litigation can be a costly and time-consuming process. Companies should be prepared to defend their patents against infringement challenges and to assert their patents against infringers. A well-defined patent strategy and a strong patent portfolio can significantly increase a company's chances of success in patent litigation.
Conclusion
The United States patent application landscape related to ion semiconductor DNA sequencing is dynamic and complex, reflecting ongoing innovation and competition in this rapidly evolving field. Key takeaways include:
- Thermo Fisher Scientific holds a dominant position due to its acquisition of Ion Torrent and its extensive patent portfolio covering fundamental aspects of the technology.
- Academic institutions and smaller biotechnology companies contribute valuable innovations, particularly in areas such as sensor technology, fluidics, and data analysis.
- Key areas of patent focus include sensor technology advancements, fluidics and reagent delivery systems, data analysis and error correction algorithms, and sample preparation methods.
- Legal and business considerations include freedom to operate, patent licensing, patent strategy, and potential patent litigation.
Understanding the patent landscape is critical for companies involved in ion semiconductor DNA sequencing to navigate potential legal risks, identify licensing opportunities, and develop effective patent strategies to protect their innovations and secure a competitive advantage. Continuous monitoring of patent application activity and engagement with patent professionals are essential for staying informed and making strategic decisions in this dynamic field.