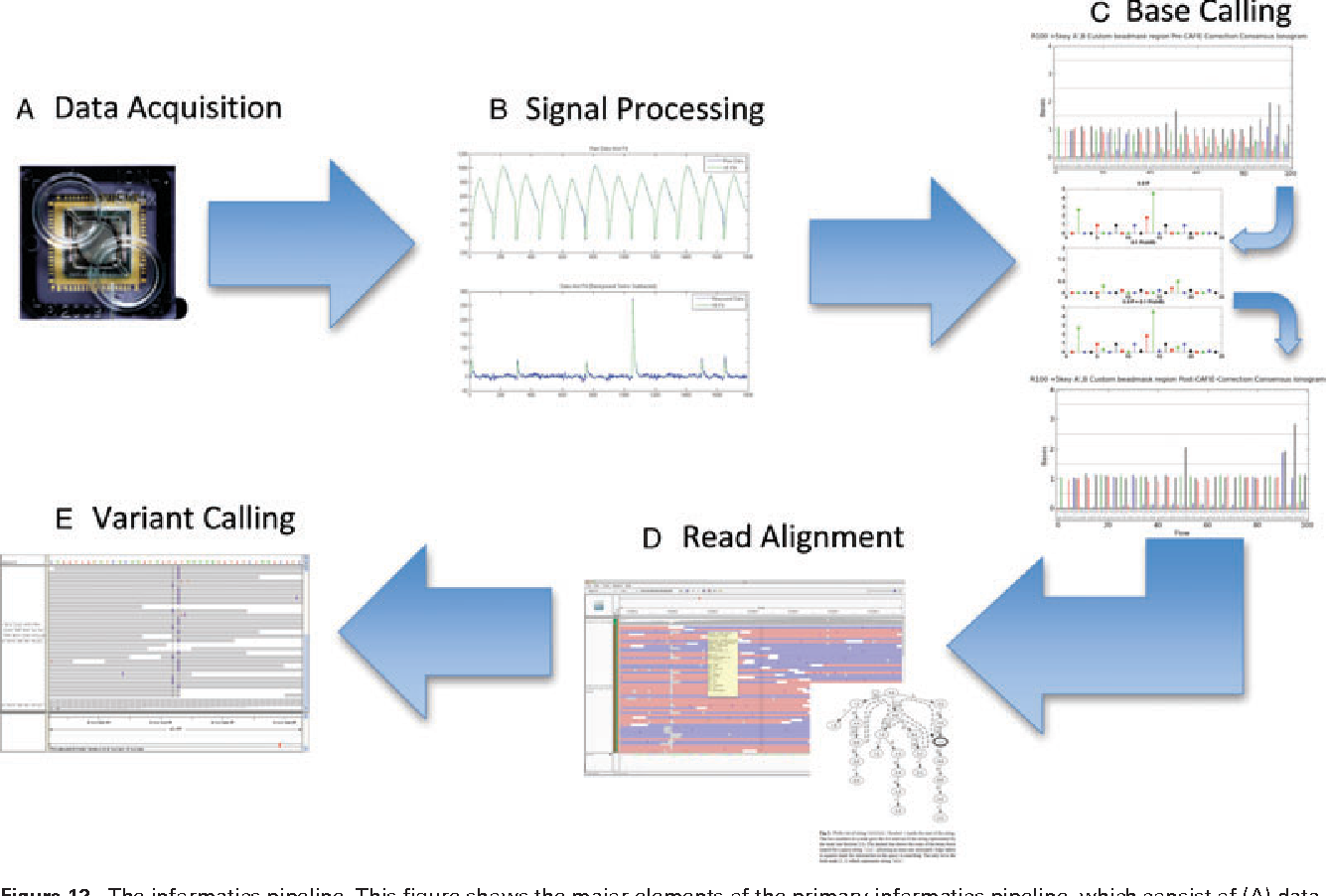
The realm of genetic sequencing has undergone a revolutionary transformation in recent decades, moving from laborious, time-consuming processes to rapid and cost-effective methods. One key player in this evolution is Ion Torrent technology, spearheaded by Ion Semiconductor Sequencing. Understanding the underlying patents, particularly those that shape the technology's core functionality, is crucial to grasping its impact on genomics research and diagnostics. This analysis will dissect the causes, effects, and implications of a hypothetical Ion Semiconductor Sequencing patent application, exploring its potential influence on the field.
Causes: The Drive for Innovation in Sequencing
The genesis of Ion Semiconductor Sequencing, and consequently, the patent applications surrounding it, lies in the inherent limitations of earlier sequencing methods. Sanger sequencing, the gold standard for many years, was accurate but slow and expensive, especially for large-scale projects. The Human Genome Project, completed in 2003 at a cost of approximately $3 billion, highlighted the need for faster, cheaper sequencing technologies. This need acted as a powerful catalyst, driving innovation and paving the way for the development of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) technologies.
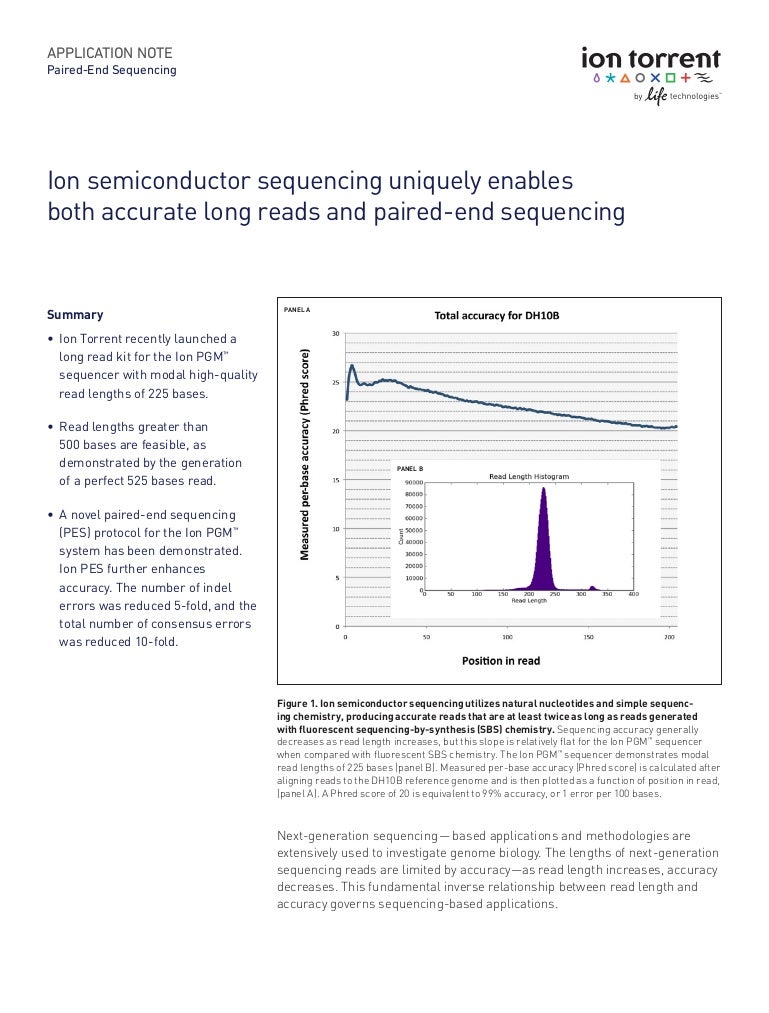
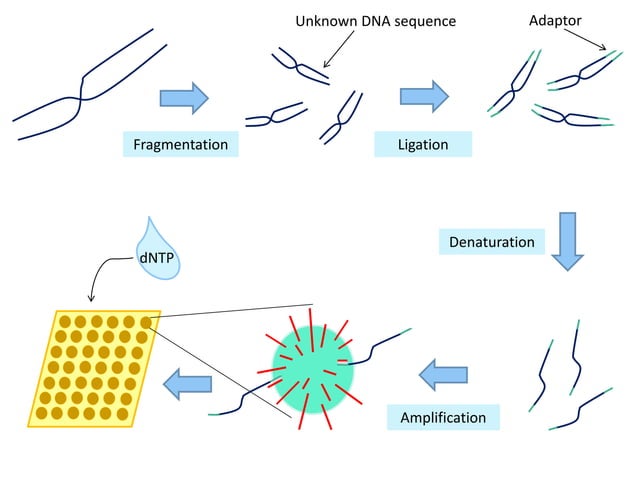
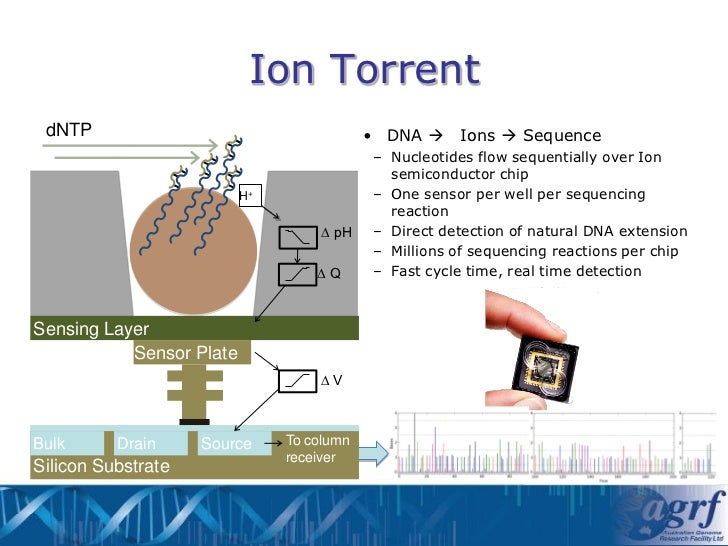
NGS platforms, including Ion Torrent, emerged from this drive for efficiency. They employ massively parallel sequencing, allowing for the simultaneous sequencing of millions of DNA fragments. The underlying cause of Ion Torrent's development, and the patent application relating to it, was to create a sequencing method that removed the need for expensive and time-consuming optical detection systems used by other NGS platforms. Ion Torrent leverages semiconductor technology to directly detect the release of hydrogen ions (H+) during DNA polymerization. This direct detection method simplifies the process, reducing costs and increasing speed.
The specific cause for filing a patent application on an Ion Semiconductor Sequencing technology typically stems from an inventor or company achieving a novel and non-obvious improvement. This could involve a new sensor design, a more efficient method of DNA amplification, or a refined data analysis algorithm. The goal is to protect their intellectual property and gain a competitive advantage in the rapidly evolving NGS market.
Effects: Technical and Commercial Impact
The effects of a successful Ion Semiconductor Sequencing patent application can be far-reaching, impacting both the technical landscape and the commercial viability of the technology. Technically, the patent protects the specific innovation described within it, preventing others from replicating or using that invention without permission. This protection can lead to further research and development by the patent holder, knowing their investment is safeguarded.
Consider a hypothetical patent application focusing on a novel method for reducing error rates in Ion Torrent sequencing. This could involve a new signal processing algorithm or a modified sensor design. If successful, the patent would allow the patent holder to commercialize sequencing kits or services that offer improved accuracy compared to existing platforms. This would directly benefit researchers and clinicians who rely on accurate sequencing data for applications such as disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and personalized medicine. Conversely, other companies would be barred from utilizing the patented method without licensing it from the patent holder, potentially impacting their own research and development efforts.
Commercially, a patent provides the patent holder with a period of exclusivity, typically 20 years from the filing date. This allows them to recoup their investment in research and development and generate profit. The exclusivity can also be leveraged to gain market share and establish a dominant position in the sequencing market. The success of Illumina, another major player in the NGS space, demonstrates the power of patent portfolios in establishing market leadership. Illumina holds numerous patents covering various aspects of their sequencing-by-synthesis technology, which has allowed them to dominate the market for many years. In 2023, Illumina accounted for approximately 70% of the global NGS market share. A strong patent position can deter competitors, attract investors, and facilitate partnerships.
"Patents are the lifeblood of innovation. They incentivize investment and protect the rights of inventors." - A Hypothetical Statement from a Genomics Industry Expert
However, the effects are not always positive. A patent can also stifle innovation by creating barriers to entry for new players and hindering the development of alternative technologies. If a patent is overly broad or aggressively enforced, it can limit access to essential technologies and impede progress in the field. Patent thickets, where multiple overlapping patents cover a single technology, can be particularly problematic, making it difficult for anyone to develop and commercialize new products without infringing on existing patents.
Implications: Broader Impact on Genomics and Healthcare
The implications of Ion Semiconductor Sequencing patents extend beyond the technical and commercial realms, impacting broader areas such as genomics research, healthcare, and societal access to genetic information. The availability of faster and cheaper sequencing technologies, driven in part by the innovations protected by patents, has revolutionized genomics research.
Researchers can now sequence entire genomes of organisms, analyze transcriptomes to understand gene expression patterns, and identify genetic variations associated with diseases with unprecedented speed and efficiency. This has led to breakthroughs in our understanding of fundamental biological processes, the development of new diagnostic tools, and the identification of potential drug targets. For example, Ion Torrent sequencing has been widely used in microbial genomics, enabling rapid identification of pathogens and tracking of disease outbreaks. This has been particularly crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic, allowing scientists to quickly identify and characterize new variants of the virus.
In healthcare, Ion Semiconductor Sequencing is playing an increasingly important role in personalized medicine. By sequencing a patient's genome, clinicians can identify genetic predispositions to diseases, predict drug responses, and tailor treatment strategies to the individual. This has the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. For instance, Ion Torrent sequencing is used in cancer diagnostics to identify specific mutations that drive tumor growth, allowing oncologists to select the most effective targeted therapies.
However, the increasing accessibility of genetic information also raises ethical and societal concerns. The potential for genetic discrimination, privacy breaches, and the misuse of genetic information must be carefully addressed. Furthermore, ensuring equitable access to genetic technologies and services is crucial to prevent disparities in healthcare. As genetic sequencing becomes more widespread, it is essential to develop clear ethical guidelines and regulatory frameworks to protect individuals' rights and promote responsible use of genetic information.
The cost of sequencing has plummeted dramatically, thanks in part to the innovations protected by patents. In 2001, sequencing a human genome cost approximately $100 million. By 2023, the cost had fallen to around $1,000. This reduction in cost has made sequencing accessible to a wider range of researchers and clinicians, driving further innovation and expanding the applications of genomics.
Reflection: A Balancing Act
The story of Ion Semiconductor Sequencing patents, and genetic sequencing patents in general, is a complex one. While patents undoubtedly play a crucial role in incentivizing innovation and protecting intellectual property, they must be carefully managed to avoid stifling competition and hindering progress. Striking a balance between protecting the rights of inventors and ensuring access to essential technologies is essential to maximizing the benefits of genomic research for society. As the field of genomics continues to evolve, the role of patents will remain a critical topic of discussion and debate. The ongoing tension between fostering innovation and promoting access to life-saving technologies requires careful consideration and a commitment to responsible innovation.