Lung cancer remains a significant global health challenge, and advancements in understanding its molecular underpinnings are crucial for improving patient outcomes. Among the various genetic mutations implicated in lung cancer development, mutations in the KRAS gene have emerged as particularly important. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of KRAS mutations in lung cancer, focusing on their impact on survival rates and recent therapeutic developments.
Understanding KRAS Mutations
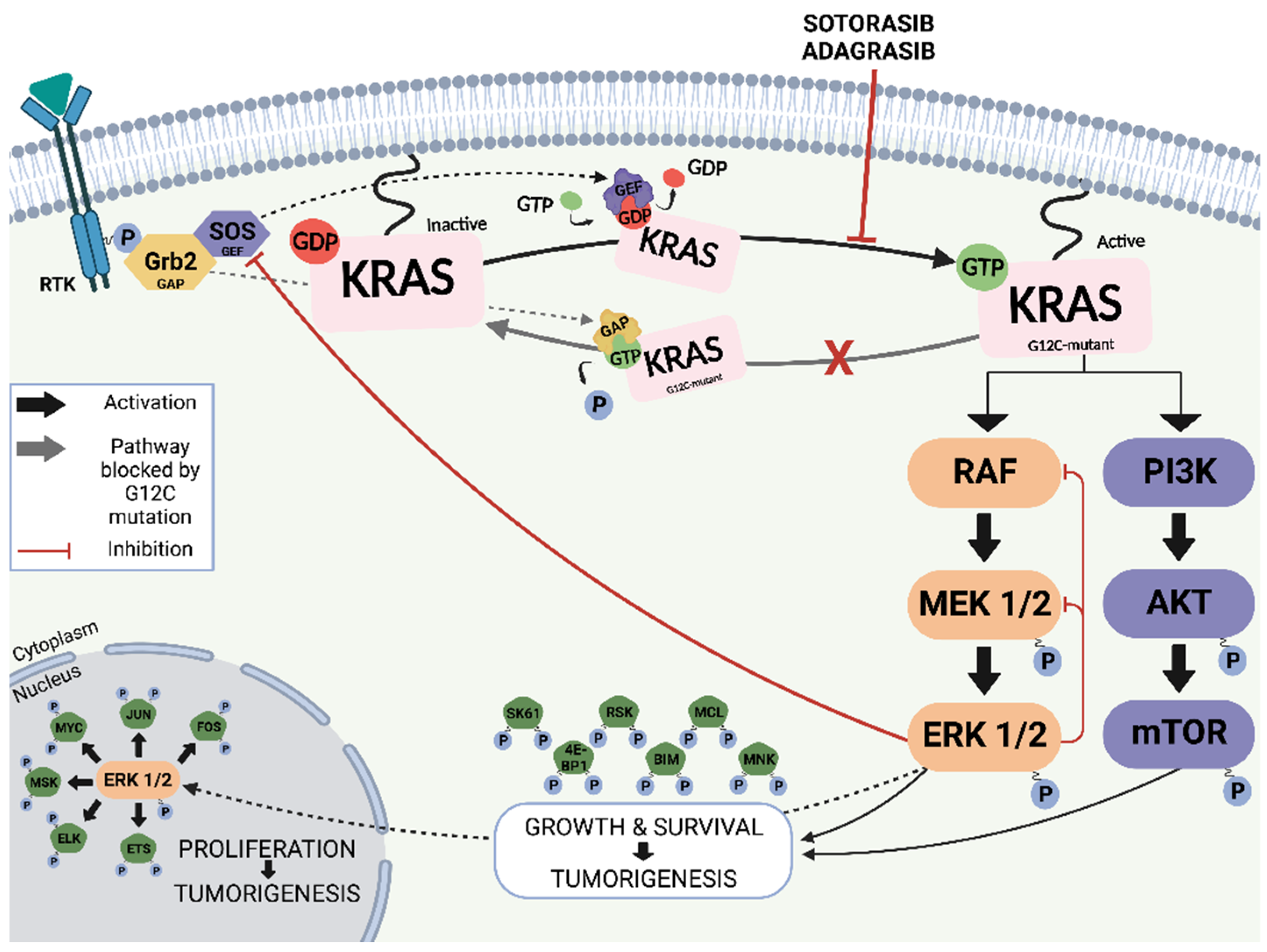
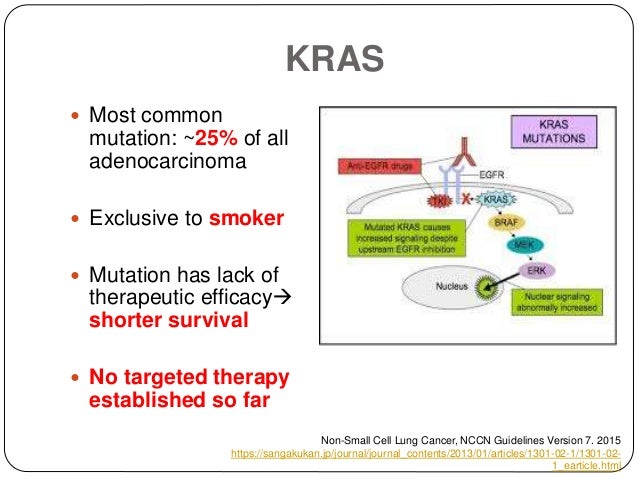
The KRAS gene encodes a protein that acts as a molecular switch, controlling cell growth, differentiation, and survival. It belongs to the RAS family of genes, which are involved in signaling pathways that regulate these essential cellular processes. In normal cells, the KRAS protein cycles between an "on" and "off" state, responding to external growth signals. However, when the KRAS gene is mutated, the resulting protein can become permanently "on," leading to uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation, a hallmark of cancer.
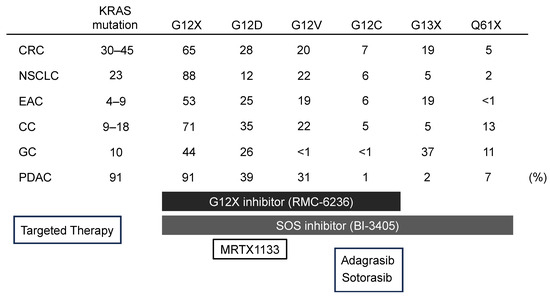
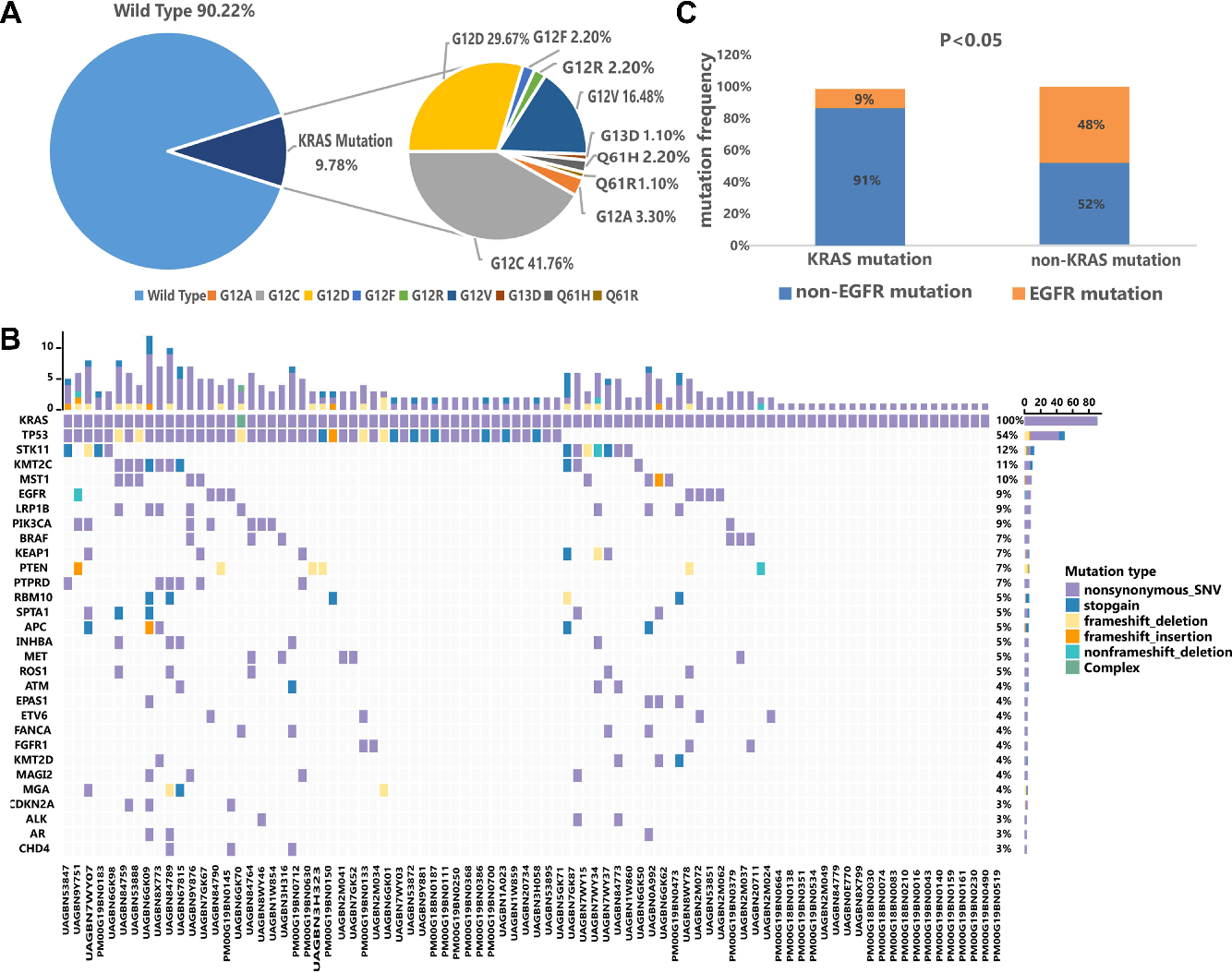
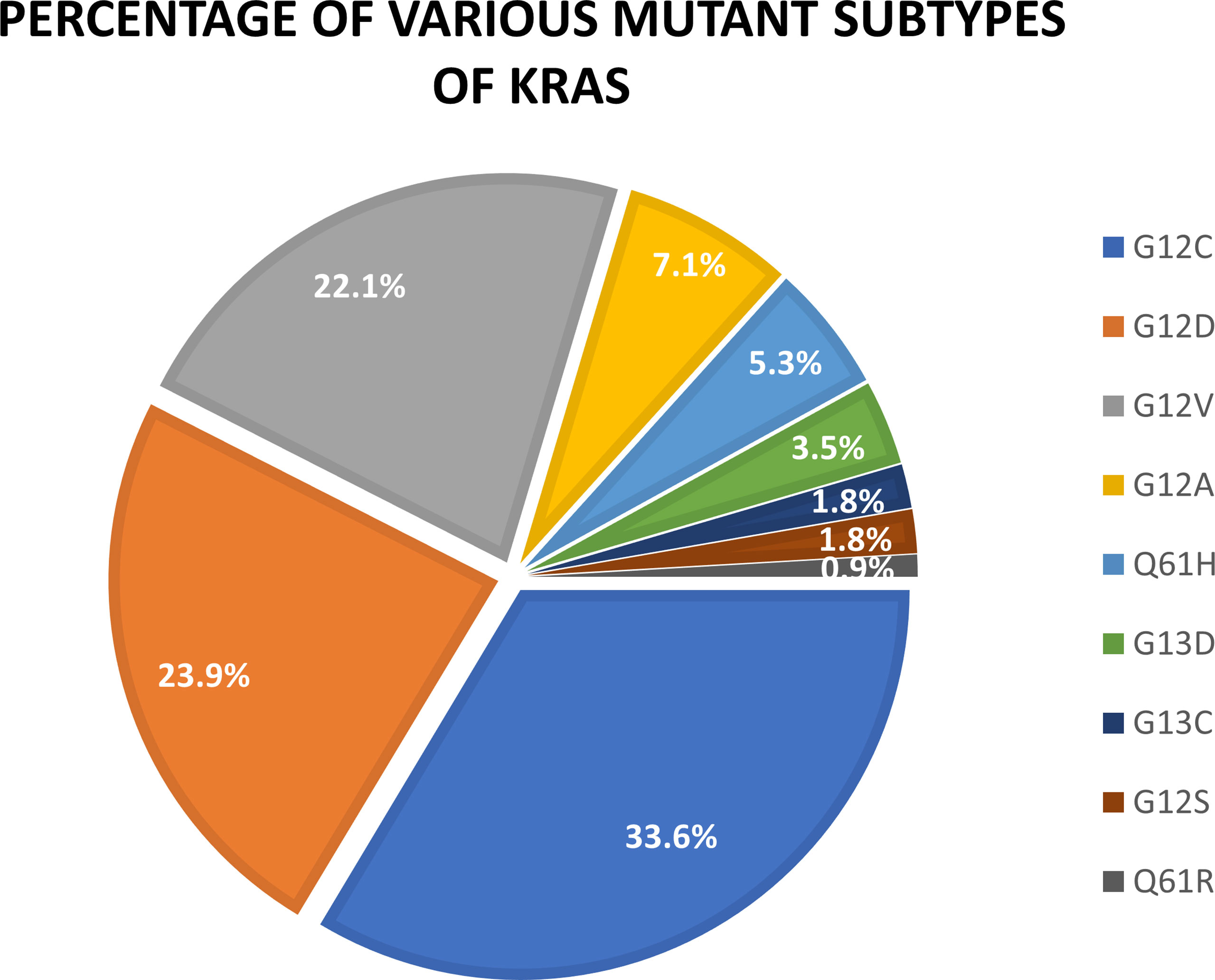
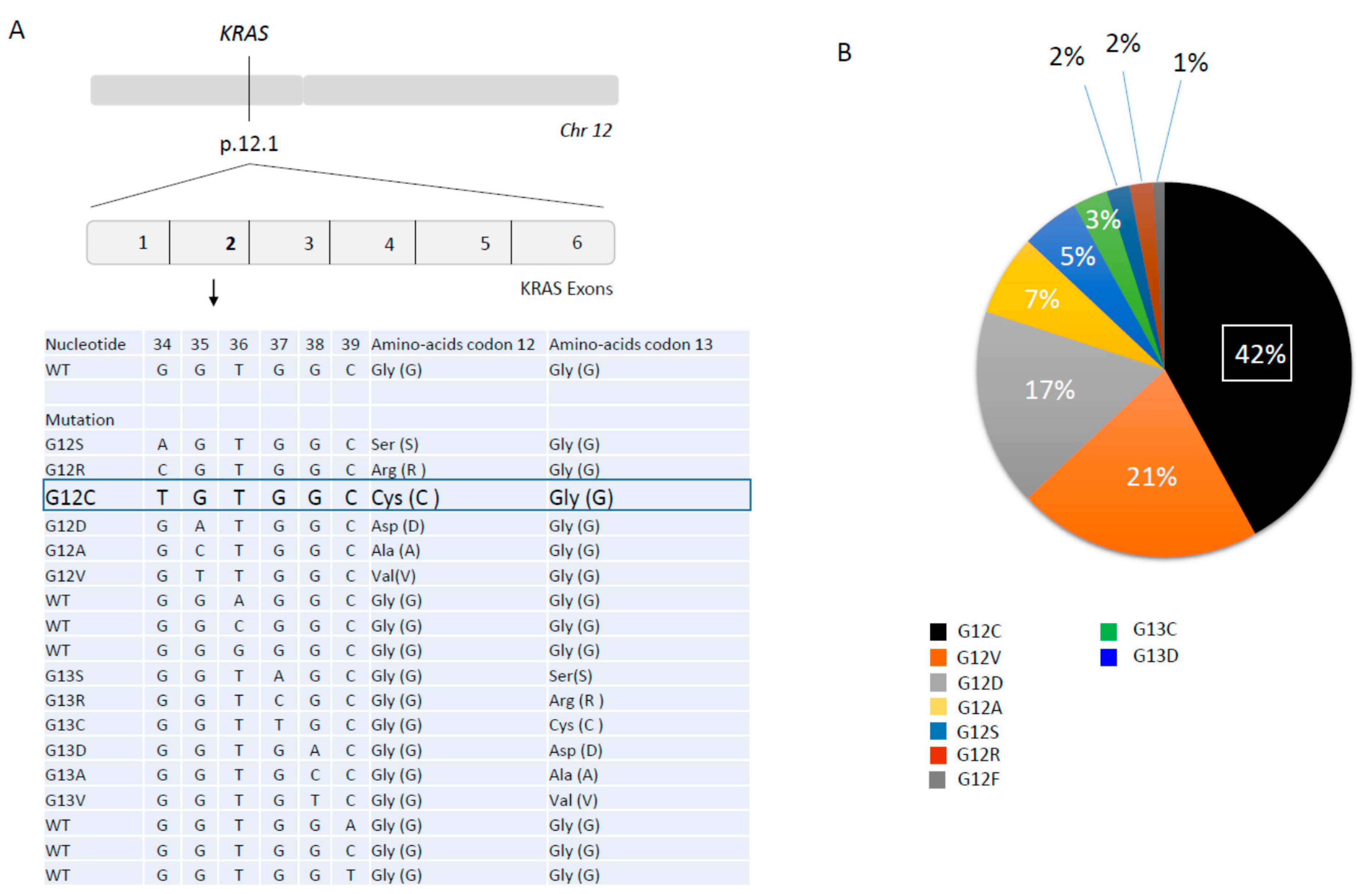
KRAS mutations are frequently found in various types of cancer, including lung cancer, colorectal cancer, and pancreatic cancer. In lung cancer, they are particularly prevalent in adenocarcinoma, a subtype of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). These mutations often occur at specific locations within the KRAS gene, such as codon 12, 13, or 61, with G12C being the most common KRAS mutation in NSCLC.
KRAS Mutation and Survival Rate in Lung Cancer
The presence of a KRAS mutation in lung cancer has historically been associated with a poorer prognosis compared to patients without the mutation. Several studies have indicated that patients with KRAS-mutated lung cancer tend to have shorter overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). This is partly attributed to the fact that KRAS-mutated tumors often exhibit resistance to conventional chemotherapy and other targeted therapies.
The exact impact of KRAS mutations on survival can vary depending on several factors, including:
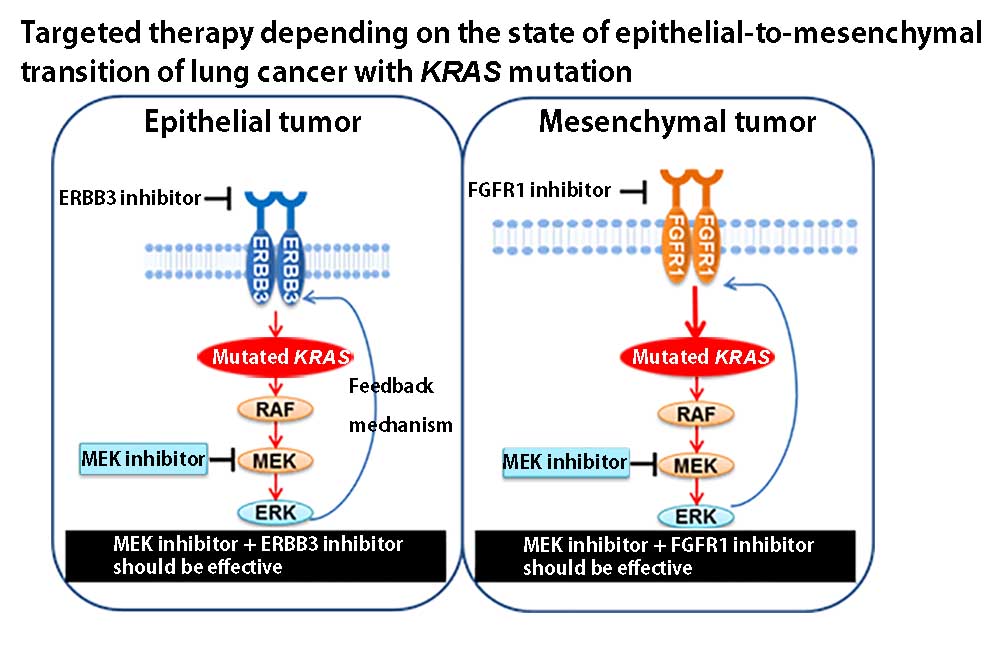
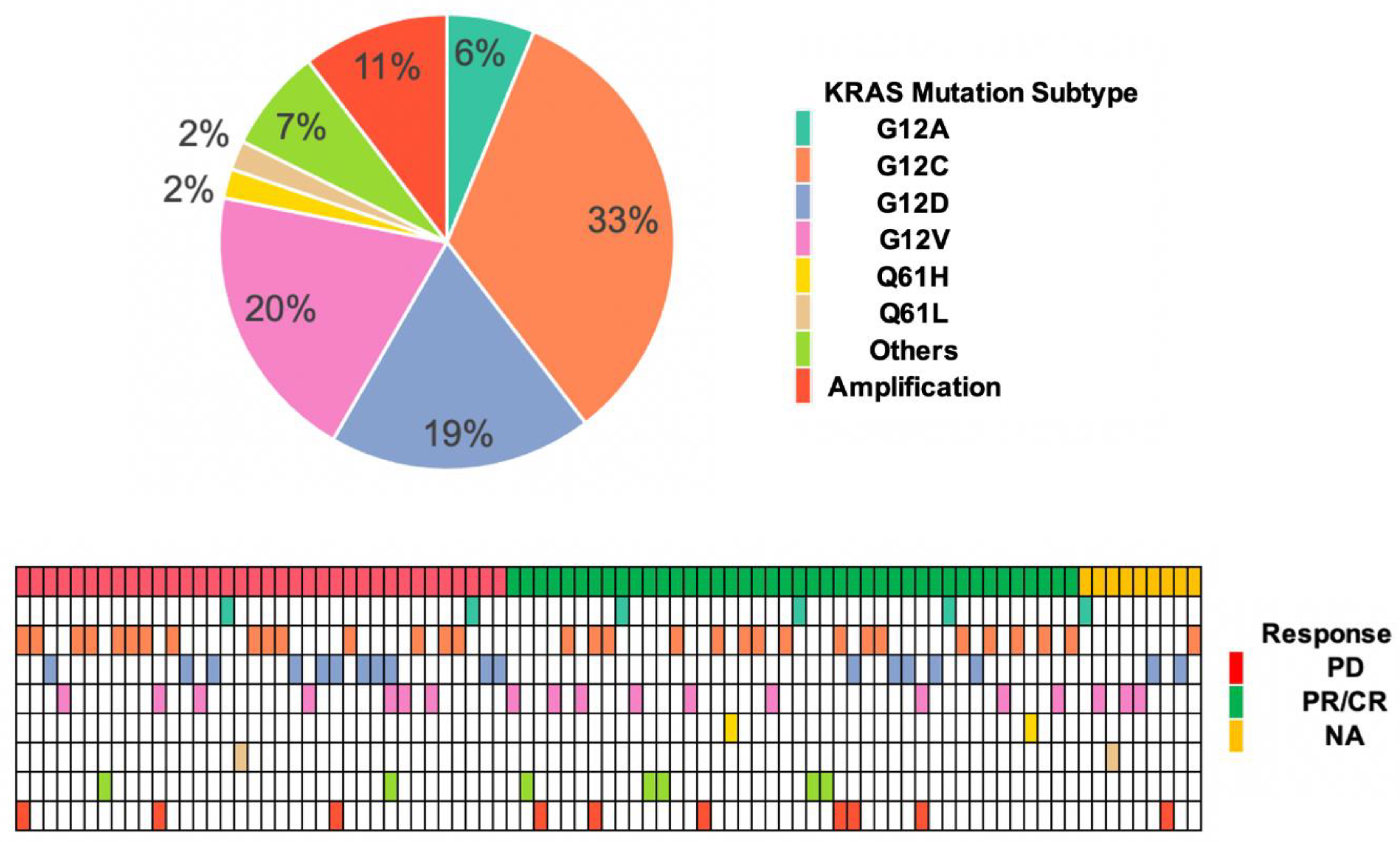
- Specific KRAS Mutation Subtype: Different KRAS mutations may have varying effects on tumor behavior and response to treatment. For example, the G12C mutation, now targetable with specific inhibitors, has a different survival landscape compared to other KRAS mutations.
- Stage of the Cancer: The stage at which the cancer is diagnosed plays a crucial role. Patients diagnosed with early-stage KRAS-mutated lung cancer who undergo surgical resection may have a better prognosis than those diagnosed with advanced-stage disease.
- Treatment Regimen: The type of treatment received can significantly influence survival outcomes. The advent of KRAS G12C inhibitors has dramatically changed the survival prospects for patients with this specific mutation.
- Overall Health and Performance Status: A patient's overall health and ability to tolerate treatment are also important factors that affect survival.
Historically, before the development of targeted therapies, the prognosis for patients with KRAS-mutated lung cancer was less favorable. However, recent advancements in treatment strategies, particularly the development of KRAS G12C inhibitors, have led to improved outcomes for patients with this specific mutation.
The Rise of KRAS G12C Inhibitors
For decades, the KRAS protein was considered "undruggable" due to its smooth surface and lack of obvious binding sites for small molecule inhibitors. However, innovative research efforts led to the development of selective inhibitors that specifically target the KRAS G12C mutant protein. These inhibitors work by binding to the mutant protein and locking it in an inactive state, thereby preventing it from driving uncontrolled cell growth.
Several KRAS G12C inhibitors have been developed and are currently approved for use in patients with KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC. These include:
- Sotorasib: The first KRAS G12C inhibitor to receive FDA approval. Clinical trials have demonstrated that sotorasib can lead to significant tumor shrinkage and improved PFS in patients with previously treated KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC.
- Adagrasib: Another KRAS G12C inhibitor that has shown promising results in clinical trials. Adagrasib has demonstrated similar efficacy to sotorasib in terms of tumor response and PFS, and it is also being investigated in combination with other therapies.
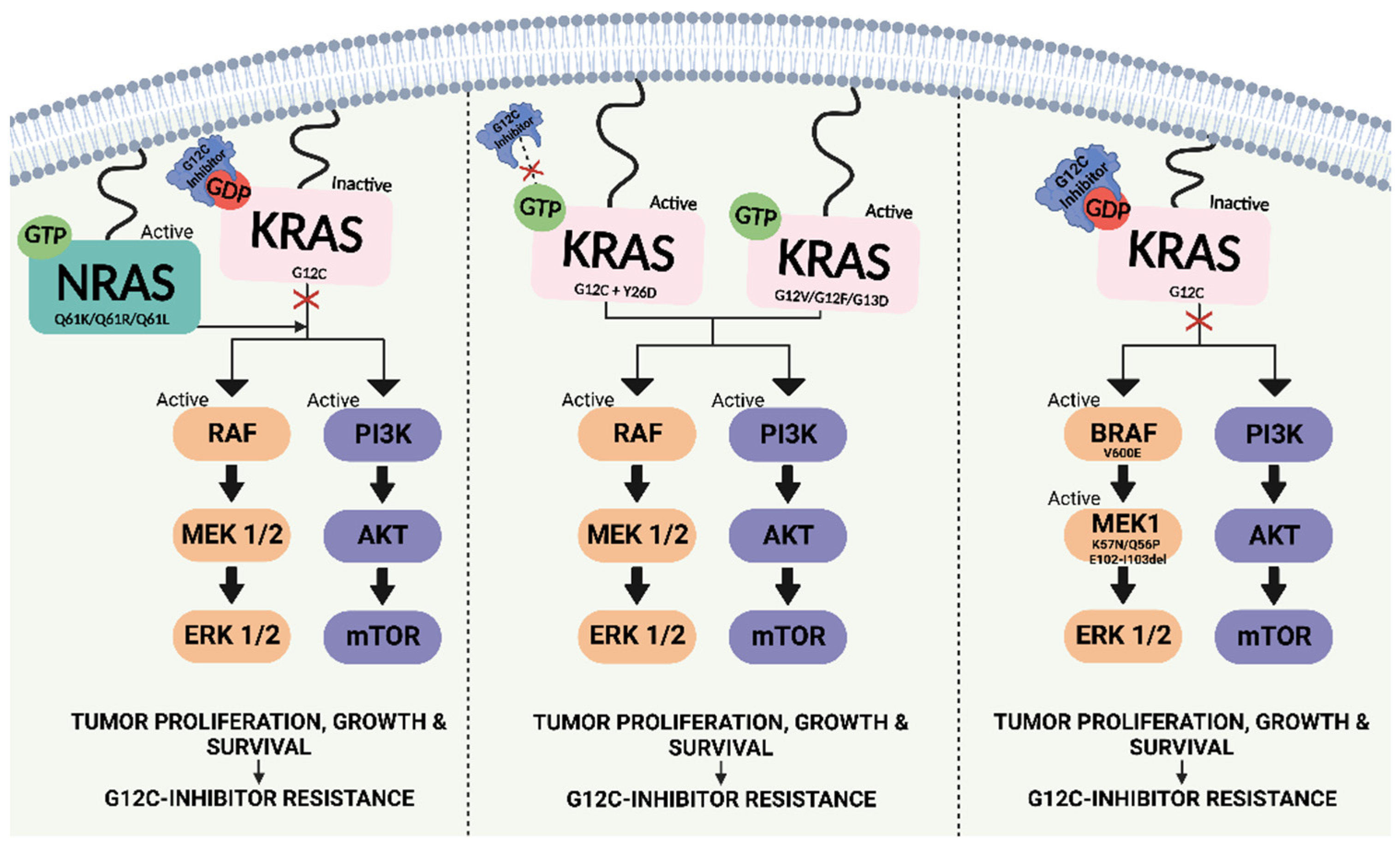
The introduction of KRAS G12C inhibitors represents a major breakthrough in the treatment of KRAS-mutated lung cancer. These agents have shown the ability to improve survival outcomes and quality of life for patients with this previously difficult-to-treat disease. However, it's important to note that resistance to these inhibitors can develop over time, highlighting the need for continued research into novel therapeutic strategies.
Future Directions and Ongoing Research
While KRAS G12C inhibitors have significantly improved the treatment landscape for patients with this specific mutation, there is still a need for better therapies for patients with other KRAS mutations. Ongoing research efforts are focused on:
- Developing inhibitors that target other KRAS mutations: Scientists are working to develop inhibitors that can selectively target other common KRAS mutations, such as G12D and G12V.
- Combining KRAS inhibitors with other therapies: Researchers are investigating the potential of combining KRAS inhibitors with other targeted therapies, immunotherapy, or chemotherapy to enhance their efficacy and overcome resistance.
- Identifying biomarkers for predicting response to KRAS inhibitors: Identifying biomarkers that can predict which patients are most likely to benefit from KRAS inhibitors is an important area of research. This could help to personalize treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes.
- Understanding mechanisms of resistance to KRAS inhibitors: Understanding how tumors develop resistance to KRAS inhibitors is crucial for developing strategies to overcome this resistance and improve the durability of treatment responses.
The development of KRAS G12C inhibitors has opened up new avenues for treating KRAS-mutated lung cancer, and ongoing research efforts are aimed at expanding these benefits to a wider range of patients with this challenging disease.
The Importance of KRAS Mutation Testing
Given the availability of targeted therapies for KRAS G12C-mutated lung cancer, it is crucial for all patients diagnosed with NSCLC to undergo comprehensive genomic testing to determine their KRAS mutation status. This testing can help identify patients who are eligible for treatment with KRAS G12C inhibitors and guide treatment decisions.
Genomic testing for KRAS mutations can be performed using various methods, including:
- Next-generation sequencing (NGS): A comprehensive sequencing approach that can detect a wide range of genetic mutations, including KRAS mutations.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based assays: These assays are designed to specifically detect common KRAS mutations.
The choice of testing method may depend on factors such as the availability of testing resources and the specific needs of the patient. It is important to discuss the benefits and limitations of different testing methods with your healthcare provider.
Conclusion
KRAS mutations are common in lung adenocarcinoma and historically portended a poorer prognosis. However, the development of KRAS G12C inhibitors has revolutionized the treatment landscape for patients with this specific mutation, offering improved survival outcomes and quality of life. Ongoing research is focused on developing inhibitors for other KRAS mutations and combining KRAS inhibitors with other therapies to further enhance their efficacy. Routine KRAS mutation testing is essential for identifying patients who may benefit from these targeted therapies. In summary, understanding KRAS mutations and their impact on lung cancer survival is crucial because it directly influences treatment decisions, offers hope through targeted therapies, and highlights the ongoing advancements in precision medicine aimed at improving patient outcomes in this challenging disease.











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/kras-g12c-mutation-in-nsclc-4843957-v3-456bf340786c481b857d044b6a8cb307-b4828f2507074811b94472745e488299.png)