Nitrogen generators are critical pieces of equipment on oil and gas ships, playing a vital role in maintaining safety and operational efficiency. Understanding their function and application can significantly benefit anyone working in the maritime sector, especially those involved in operations, maintenance, and safety management.
Understanding the Basics
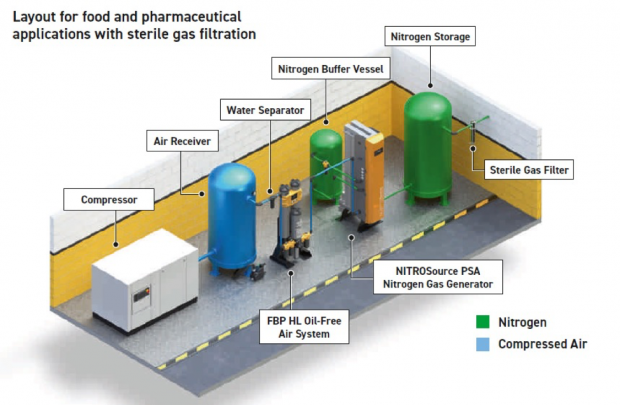
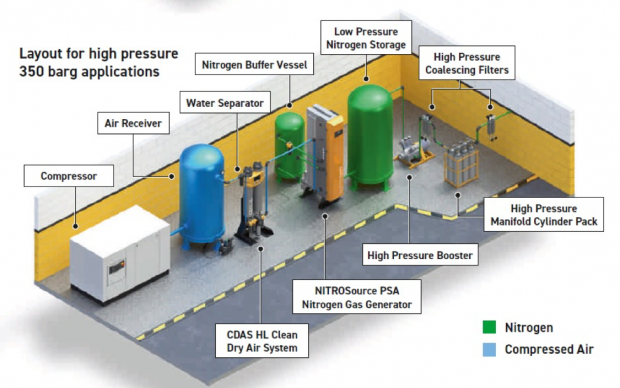
Nitrogen generators on ships primarily serve to produce nitrogen gas from compressed air. This on-demand generation eliminates the need for storing large quantities of nitrogen cylinders, which present logistical and safety challenges. The two main types of nitrogen generators are Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA) and membrane separation systems.
PSA generators use specialized adsorbent materials to selectively remove oxygen, water vapor, and other gases from compressed air, leaving behind high-purity nitrogen. The process involves cycles of adsorption and desorption, where the adsorbent material is regenerated for continuous nitrogen production.
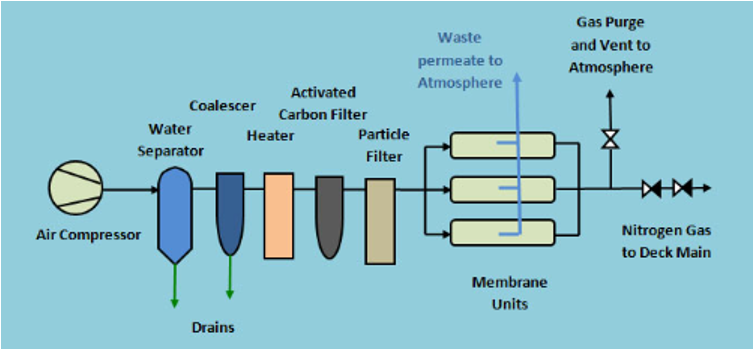
Membrane separation systems utilize semi-permeable membranes that allow nitrogen to pass through while blocking other gases. The driving force behind this separation is the difference in partial pressures of the gases across the membrane.
Daily Relevance and Practical Applications
The knowledge of nitrogen generators and their applications directly impacts various daily tasks on oil and gas ships. Here’s how:
- Inerting of Tanks and Pipelines: Nitrogen is used to displace flammable gases in tanks and pipelines, preventing explosions and fires. Knowing the nitrogen purity requirements for different applications is essential. For example, a higher purity might be needed for delicate chemical processes compared to simple tank inerting. Always refer to safety data sheets (SDS) and operational manuals for specific purity requirements.
- Purging Equipment: Before maintenance or repairs on equipment containing flammable or toxic substances, nitrogen is used to purge the system, ensuring a safe working environment. Understanding the purging procedure and the required nitrogen flow rate is critical. Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and follow lock-out/tag-out (LOTO) procedures meticulously.
- Blanketing: Nitrogen blanketing protects products from oxidation and contamination by creating an inert atmosphere above the liquid or solid material. This is especially important for sensitive chemicals and fuels. Regularly monitor the nitrogen pressure and flow rate in the blanketing system to ensure its effectiveness.
- Leak Testing: Nitrogen can be used for leak testing of pipelines and equipment. Pressurizing the system with nitrogen and then monitoring for pressure drops indicates leaks. Utilize appropriate leak detection methods, such as soap solution or electronic leak detectors, and ensure the system is properly isolated before pressurizing.
- Fire Suppression: In some fire suppression systems, nitrogen is used to displace oxygen, extinguishing the fire. Understanding the operation of these systems and the response procedures is crucial for emergency situations. Participate in regular fire drills and familiarize yourself with the location of fire suppression equipment.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Tips
Effective operation and maintenance of nitrogen generators are essential for reliable performance and longevity. Here are some practical tips:
- Regular Monitoring: Monitor the nitrogen purity, pressure, and flow rate regularly. Deviations from the normal operating parameters can indicate problems with the generator. Keep a log of these parameters for trend analysis and early detection of potential issues.
- Filter Maintenance: Compressed air filters are crucial for removing contaminants that can damage the nitrogen generator. Clean or replace filters according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Inspect filters regularly for signs of clogging or damage.
- Adsorbent Replacement (PSA): In PSA generators, the adsorbent material eventually degrades and needs to be replaced. Follow the manufacturer's instructions for replacement intervals and procedures. Use only approved replacement materials to ensure optimal performance.
- Membrane Inspection (Membrane Systems): Inspect the membrane modules for leaks or damage. Replace damaged modules promptly to maintain nitrogen purity. Regularly check the differential pressure across the membrane.
- Leak Detection: Regularly check for leaks in the nitrogen generator and distribution system. Use soap solution or electronic leak detectors to identify leaks. Repair leaks promptly to prevent nitrogen loss and maintain system efficiency.
- Preventive Maintenance: Follow the manufacturer's recommended preventive maintenance schedule. This includes lubricating moving parts, inspecting electrical connections, and calibrating instruments. Keep accurate records of all maintenance activities.
Safety Considerations
Working with nitrogen requires adherence to strict safety protocols. While nitrogen is non-toxic, it can displace oxygen, leading to asphyxiation in confined spaces.
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation when working with nitrogen in enclosed spaces. Use oxygen monitors to verify that the oxygen level remains within safe limits.
- Confined Space Entry: Follow proper confined space entry procedures when working in areas where nitrogen may be present. This includes testing the atmosphere, providing ventilation, and having a standby person.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear appropriate PPE, such as gloves and eye protection, when handling nitrogen.
- Training: Ensure that all personnel working with nitrogen generators are properly trained in their operation, maintenance, and safety procedures.
- Emergency Procedures: Familiarize yourself with the emergency procedures for nitrogen leaks and asphyxiation. Know the location of emergency equipment, such as oxygen resuscitators.
Utilizing Nitrogen in Daily Tasks
Applying this knowledge can improve efficiency and safety in numerous daily tasks. For example, if you're preparing to perform hot work on a pipeline, understanding the nitrogen purging procedure will ensure that all flammable gases are removed, minimizing the risk of fire or explosion. Knowing how to properly monitor nitrogen purity will help you ensure that the inerting process is effective. By understanding the troubleshooting steps for nitrogen generators, you can quickly identify and resolve issues, minimizing downtime and ensuring the continuous availability of nitrogen for critical applications.
Effective communication is also paramount. Report any abnormalities or concerns regarding the nitrogen generation system to the appropriate personnel. Accurate record-keeping of maintenance activities and operational parameters will contribute to the overall reliability and safety of the ship.
Remember, a well-maintained and properly operated nitrogen generator is a crucial asset for ensuring safety and operational efficiency on oil and gas ships. Your understanding and diligent application of these principles contribute directly to a safer working environment and the successful completion of your tasks.
Checklist for Effective Nitrogen Generator Management
Use this checklist as a guideline for daily and periodic activities:
- ✅ Verify nitrogen purity meets application requirements.
- ✅ Monitor nitrogen pressure and flow rates regularly.
- ✅ Inspect and maintain air filters as scheduled.
- ✅ Check for leaks in the nitrogen generator and distribution system.
- ✅ Follow the manufacturer's recommended maintenance schedule.
- ✅ Ensure adequate ventilation when working with nitrogen in enclosed spaces.
- ✅ Use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- ✅ Adhere to confined space entry procedures when necessary.
- ✅ Report any abnormalities or concerns to the appropriate personnel.
- ✅ Keep accurate records of maintenance activities and operational parameters.