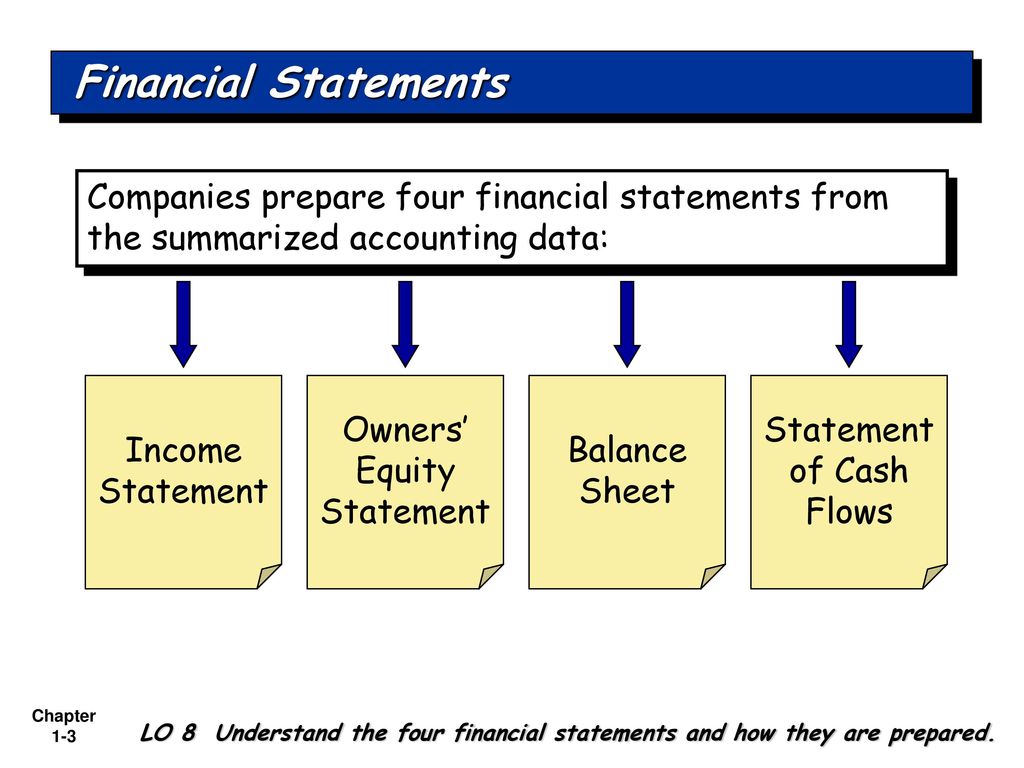
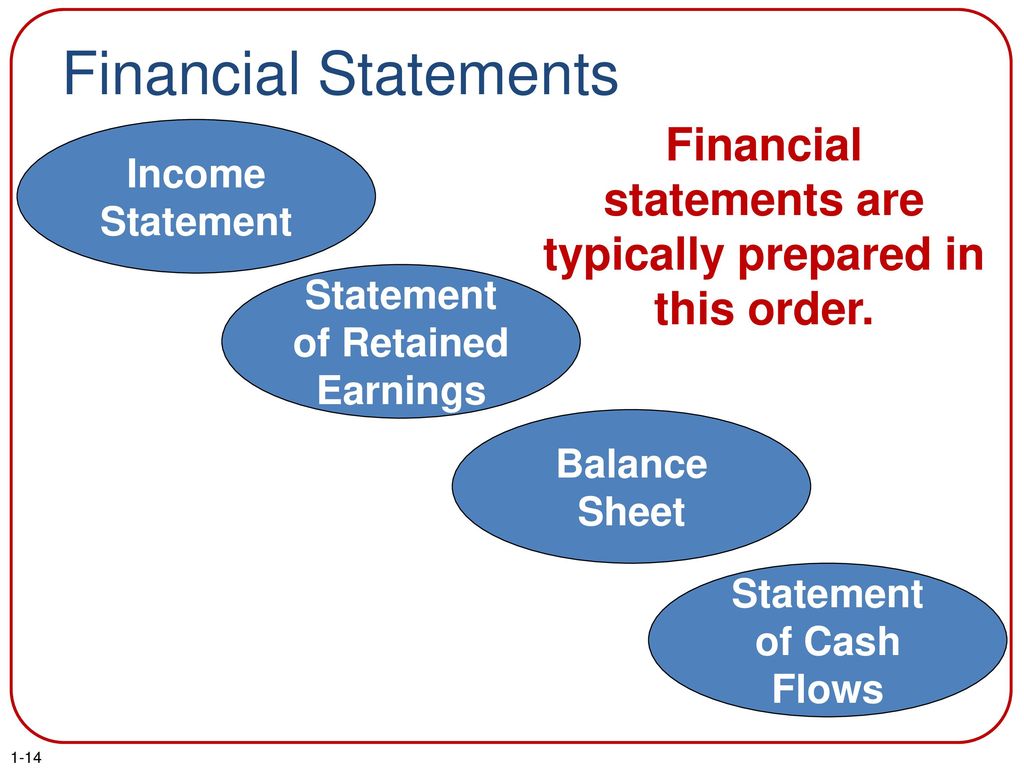
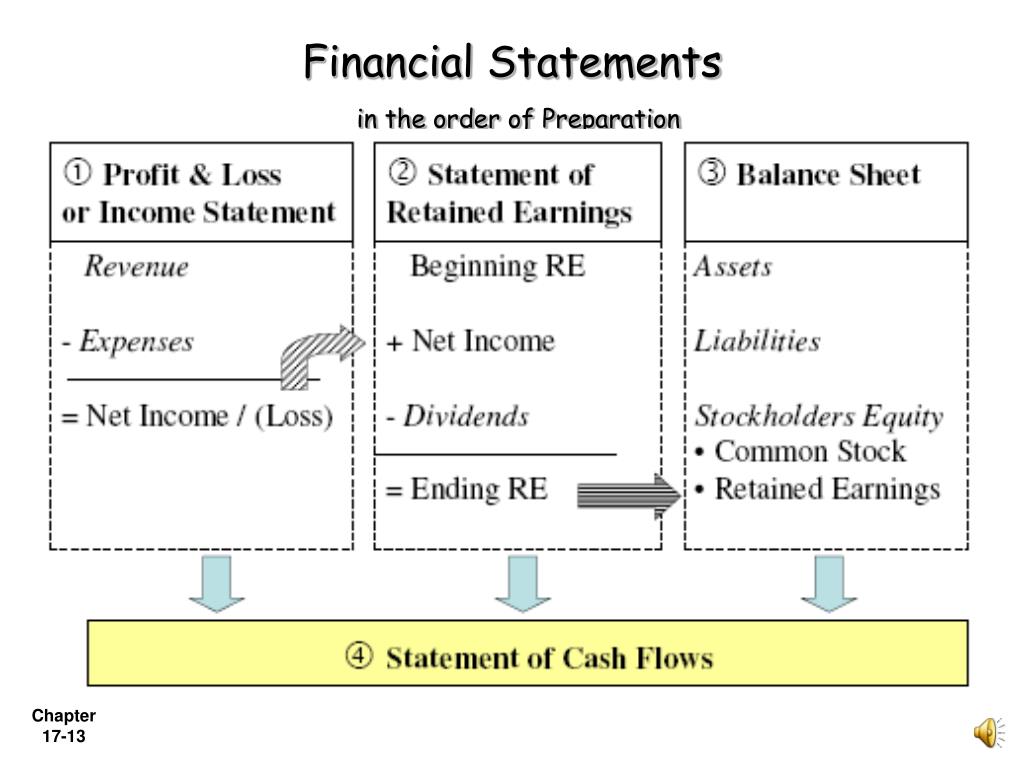
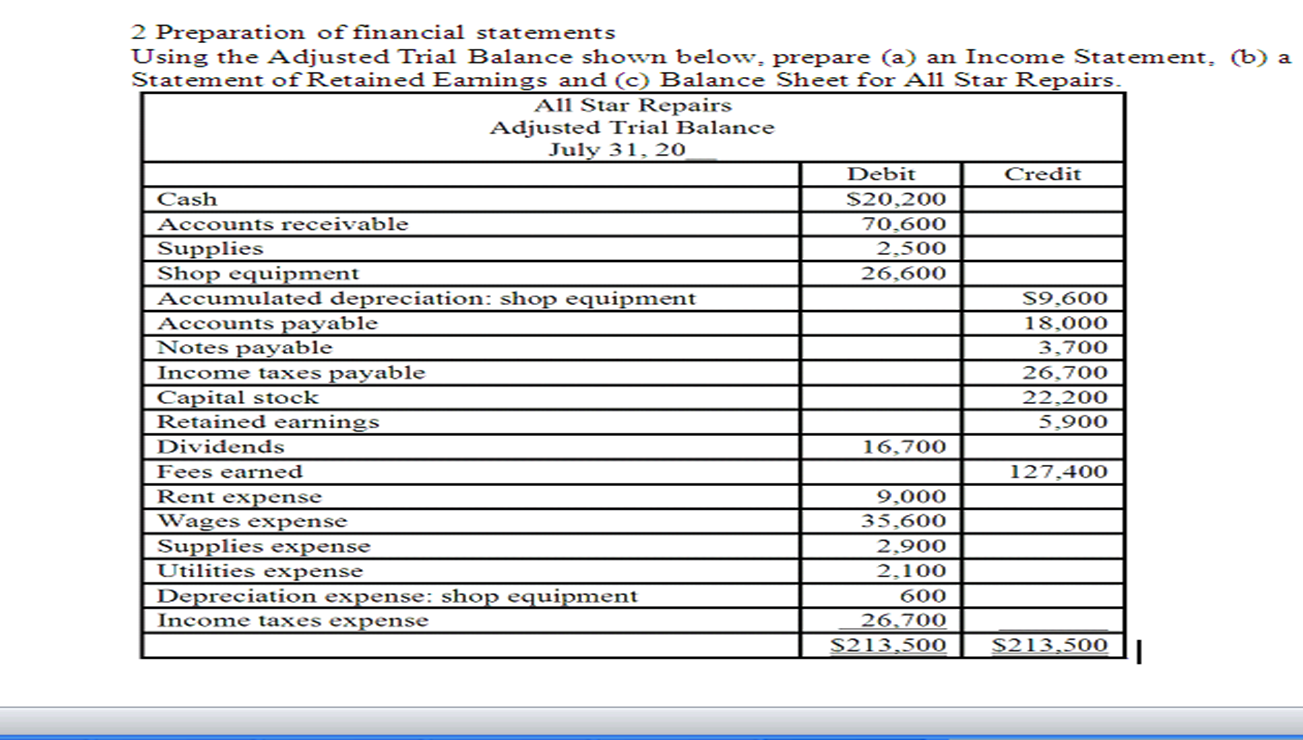
Understanding the order in which financial statements are prepared is crucial, not just for accountants, but for anyone managing a budget, running a small business, or even making personal financial decisions. Knowing this sequence provides a framework for interpreting financial data and making informed choices.
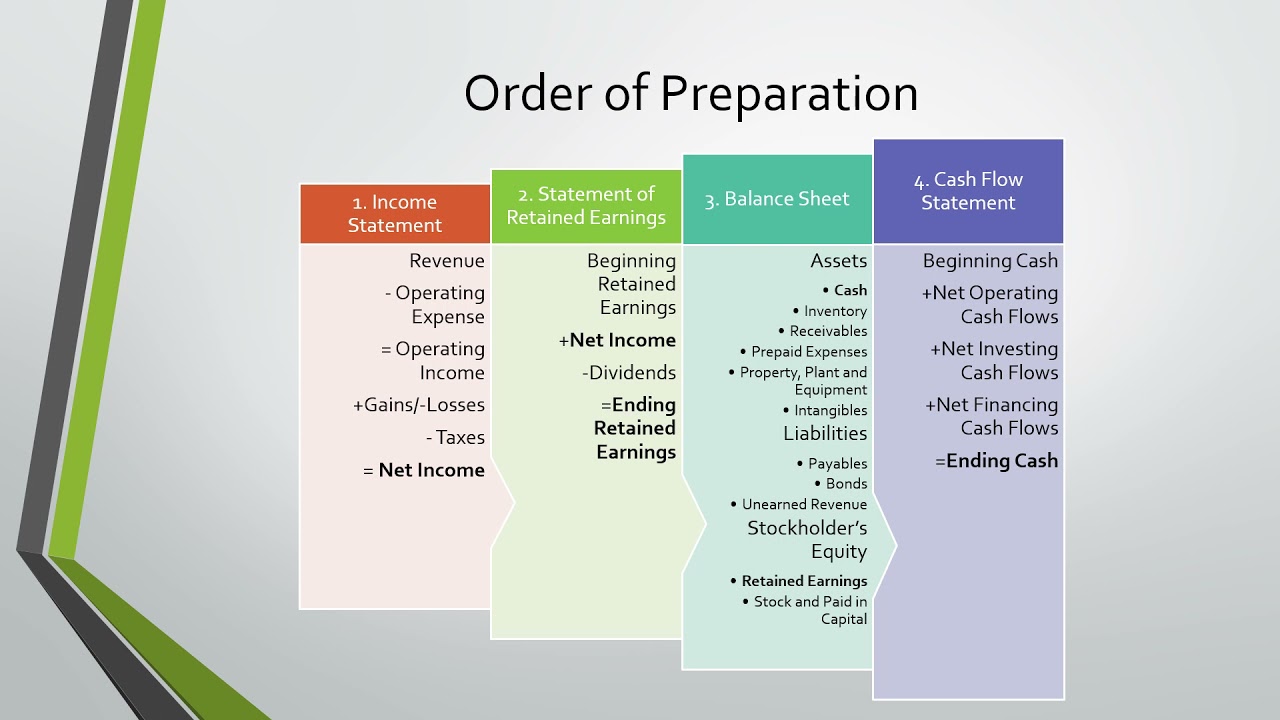
The Hierarchy: Income Statement First
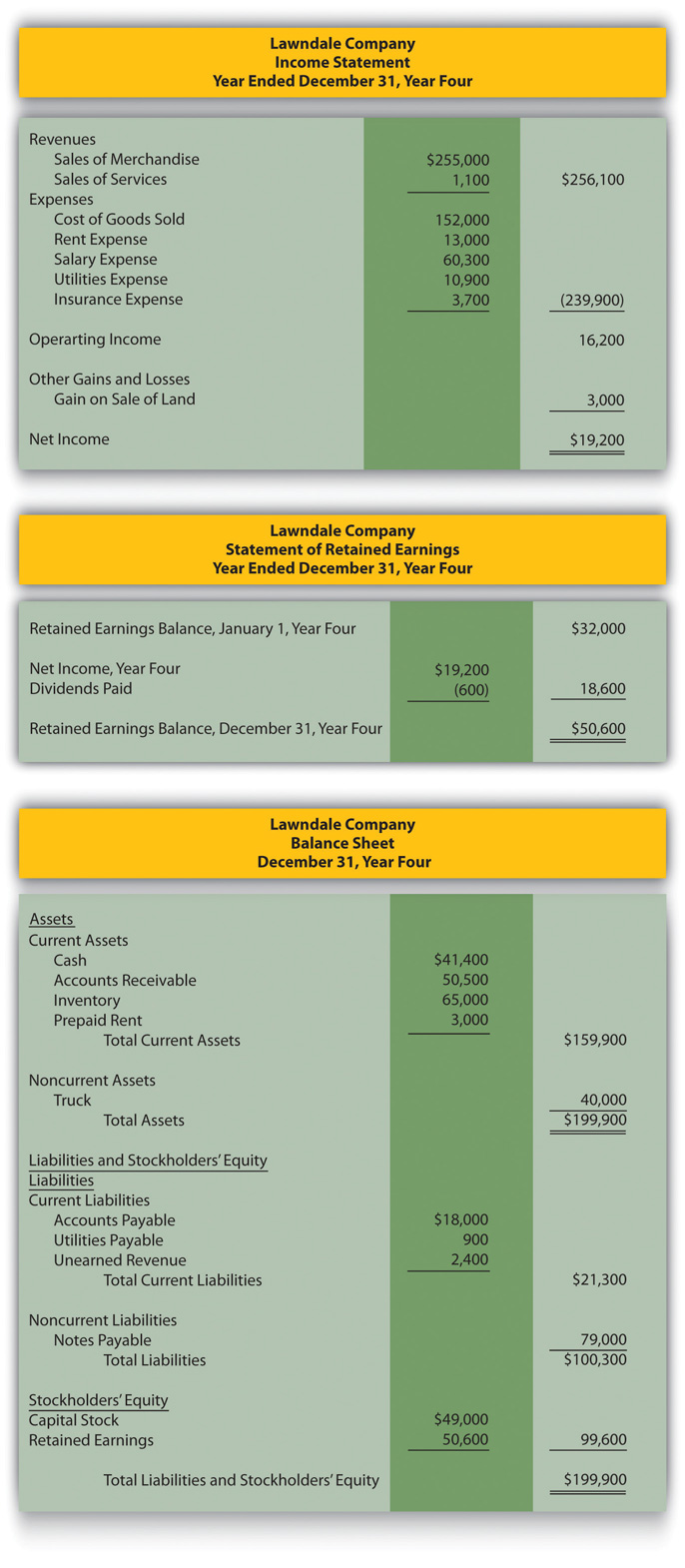
The process starts with the Income Statement, sometimes called the Profit and Loss (P&L) statement. This statement summarizes revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period, resulting in the net income or net loss for that period.
Practical Application: Business Performance Tracking
For a small business owner, the Income Statement is your report card. By comparing Income Statements from different periods (e.g., month-over-month, quarter-over-quarter, year-over-year), you can track your business's performance. Are sales increasing? Are expenses under control? Analyzing trends in your Income Statement helps you identify areas for improvement.
Example: Let’s say you run a bakery. Your Income Statement shows that your revenue increased by 15% compared to last year. However, your cost of goods sold (ingredients) increased by 20%. This signals that while your business is growing, your profitability is being squeezed. You might then investigate whether you can find cheaper suppliers or adjust your pricing.
Tip: Don't just look at the bottom line (net income). Analyze the individual components of the Income Statement to understand what's driving your profits or losses.
Practical Application: Personal Budgeting
Even if you're not a business owner, you create a personal "Income Statement" every month when you track your income and expenses. This simple exercise helps you understand your cash flow. Are you spending more than you earn? Where is your money going? Answering these questions is the first step towards financial stability.
Example: Use a spreadsheet or budgeting app to track your monthly income (salary, side hustle earnings) and expenses (rent, groceries, entertainment). Identify areas where you can cut back. Maybe you’re spending too much on dining out. By understanding your "personal Income Statement," you can make adjustments to achieve your savings goals.
The Next Step: Statement of Retained Earnings (or Equity)
The net income (or loss) calculated in the Income Statement is then used in the Statement of Retained Earnings (or Statement of Equity for other types of businesses like partnerships or LLCs). This statement shows how the company’s retained earnings have changed over a period. Retained earnings are the accumulated profits that a company has not distributed as dividends.
Practical Application: Understanding Profit Distribution (Business)
For business owners, the Statement of Retained Earnings provides insights into how profits are being used. Are you reinvesting profits back into the business for growth, or are you distributing them to owners? This decision has significant implications for the company's future.
Example: A small tech startup might choose to retain all of its earnings to fund research and development. A more mature company might distribute a portion of its earnings as dividends to shareholders. Understanding the Statement of Retained Earnings helps you assess the company's growth strategy and dividend policy.
Practical Application: Tracking Personal Investments
Think of your investment portfolio as a miniature company. The Statement of Retained Earnings is analogous to tracking the growth of your portfolio due to investment gains and the impact of withdrawals. Have your investments generated income (dividends, interest)? Have you withdrawn funds for personal use? Understanding these changes helps you assess the performance of your investment strategy.
Example: Track your investment gains (or losses) each year. Subtract any withdrawals you've made. The result is the change in your "retained earnings" (your portfolio value). This helps you understand whether your investments are growing at the rate you expect.
The Final Piece: Balance Sheet
Finally, the ending retained earnings balance from the Statement of Retained Earnings is used in the Balance Sheet. The Balance Sheet presents a company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. It follows the fundamental accounting equation: Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
Practical Application: Assessing Financial Health (Business)
The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot of your company's financial health. Are your assets sufficient to cover your liabilities? Do you have too much debt? Analyzing ratios derived from the Balance Sheet (e.g., debt-to-equity ratio, current ratio) helps you assess your company's liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability.
Example: If your company has a high debt-to-equity ratio, it means you're relying heavily on debt financing. This can be risky, especially if interest rates rise. The Balance Sheet alerts you to potential problems so you can take corrective action.
Practical Application: Personal Net Worth Calculation
You can create a personal Balance Sheet by listing your assets (cash, investments, property) and liabilities (loans, credit card debt). The difference between your assets and liabilities is your net worth. Tracking your net worth over time is a valuable way to monitor your financial progress.
Example: Make a list of everything you own (house, car, savings, investments) and everything you owe (mortgage, student loans, credit card balances). Subtract your liabilities from your assets to calculate your net worth. Aim to increase your net worth over time by paying down debt and increasing your savings and investments.
Understanding the order in which these statements are prepared and how they relate to each other unlocks a deeper understanding of financial health, whether in a business or personal context.
Statement of Cash Flows (Supplemental Information)
While not directly influencing the preparation order of the main three, the Statement of Cash Flows provides crucial insights. It analyzes the cash inflows and outflows during a period, categorized into operating, investing, and financing activities. This statement helps to bridge the gap between the Income Statement (which uses accrual accounting) and the actual cash position of the company.
Practical Application: Cash Management (Business)
The Statement of Cash Flows helps businesses understand how they are generating and using cash. Are you generating enough cash from your core operations to cover your expenses? Are you investing wisely? Monitoring cash flow is essential for survival, especially for small businesses.
Example: A company might show a profit on its Income Statement, but if it's struggling to collect payments from customers, it could face a cash flow crunch. The Statement of Cash Flows highlights these potential problems.
Practical Application: Tracking Personal Cash Flow
You can use the principles of the Statement of Cash Flows to track your personal cash flow. How much cash are you generating from your income? How much are you spending on essential expenses? Are you saving enough? Tracking your cash flow helps you identify areas where you can improve your financial habits.
Example: Categorize your income and expenses into operating (salary, groceries), investing (buying stocks), and financing (loan payments) activities. This will give you a clear picture of your personal cash flow.
Quick Checklist: Financial Statement Order and Application
- Income Statement: Track revenue, expenses, and net income/loss. Use to monitor performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Statement of Retained Earnings/Equity: Track changes in retained earnings due to profits, losses, and dividends/withdrawals. Understand how profits are being used.
- Balance Sheet: Assess assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time. Calculate net worth and assess financial health.
- Statement of Cash Flows: Analyze cash inflows and outflows to understand how cash is being generated and used. Monitor cash flow for survival and identify potential problems.