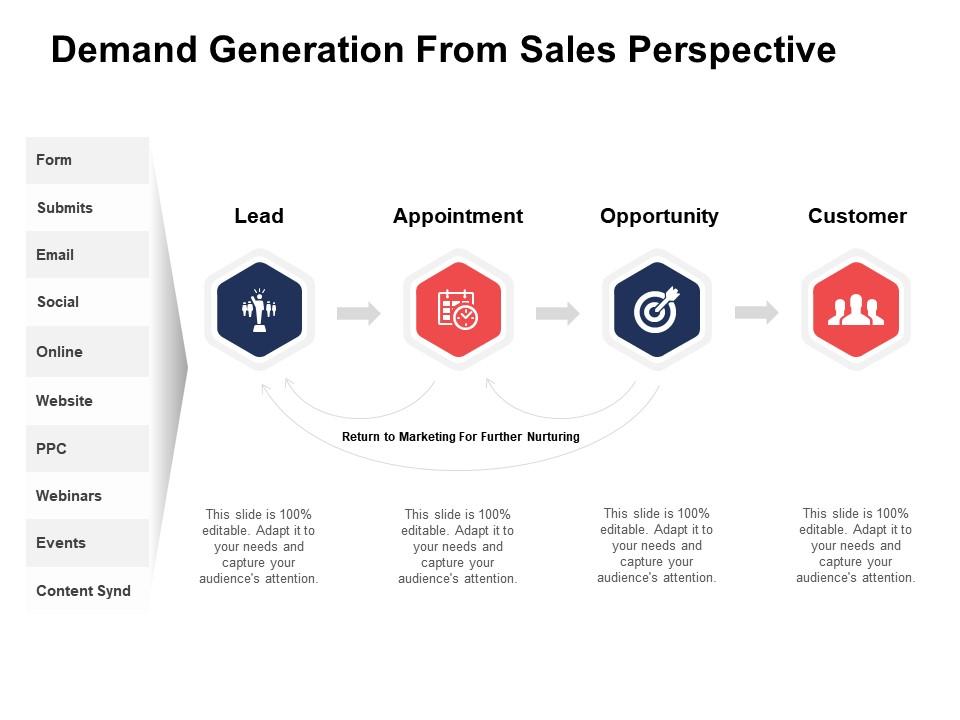
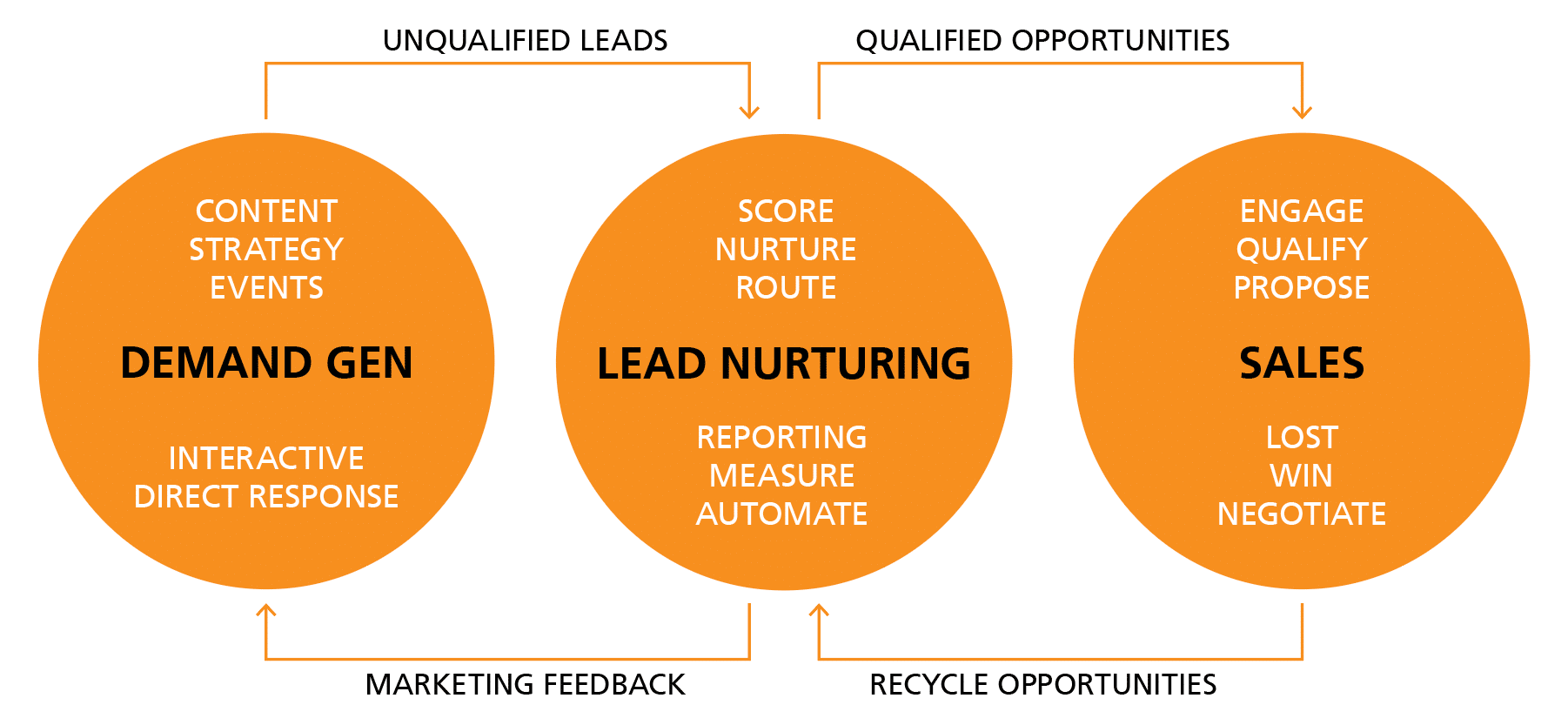
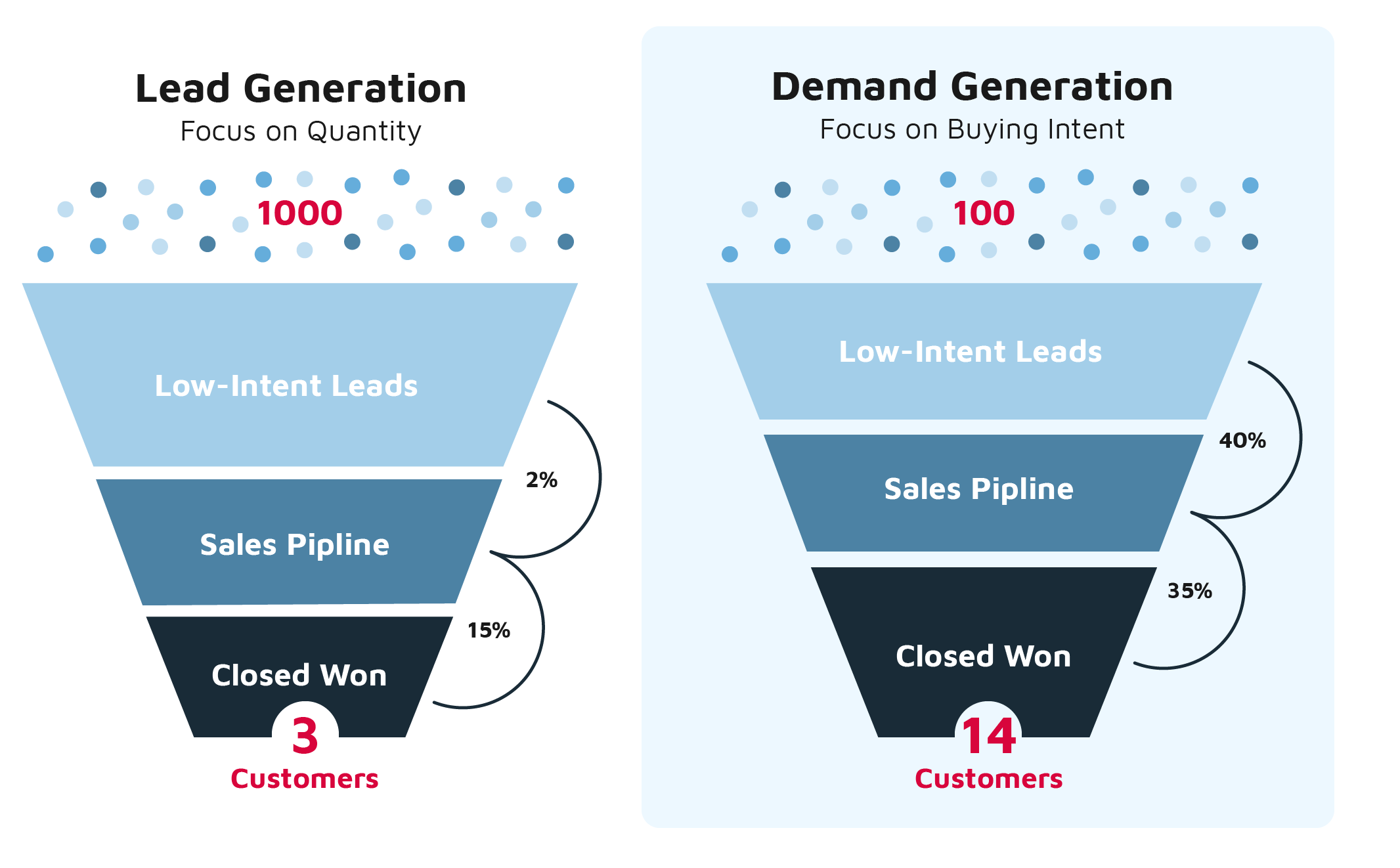
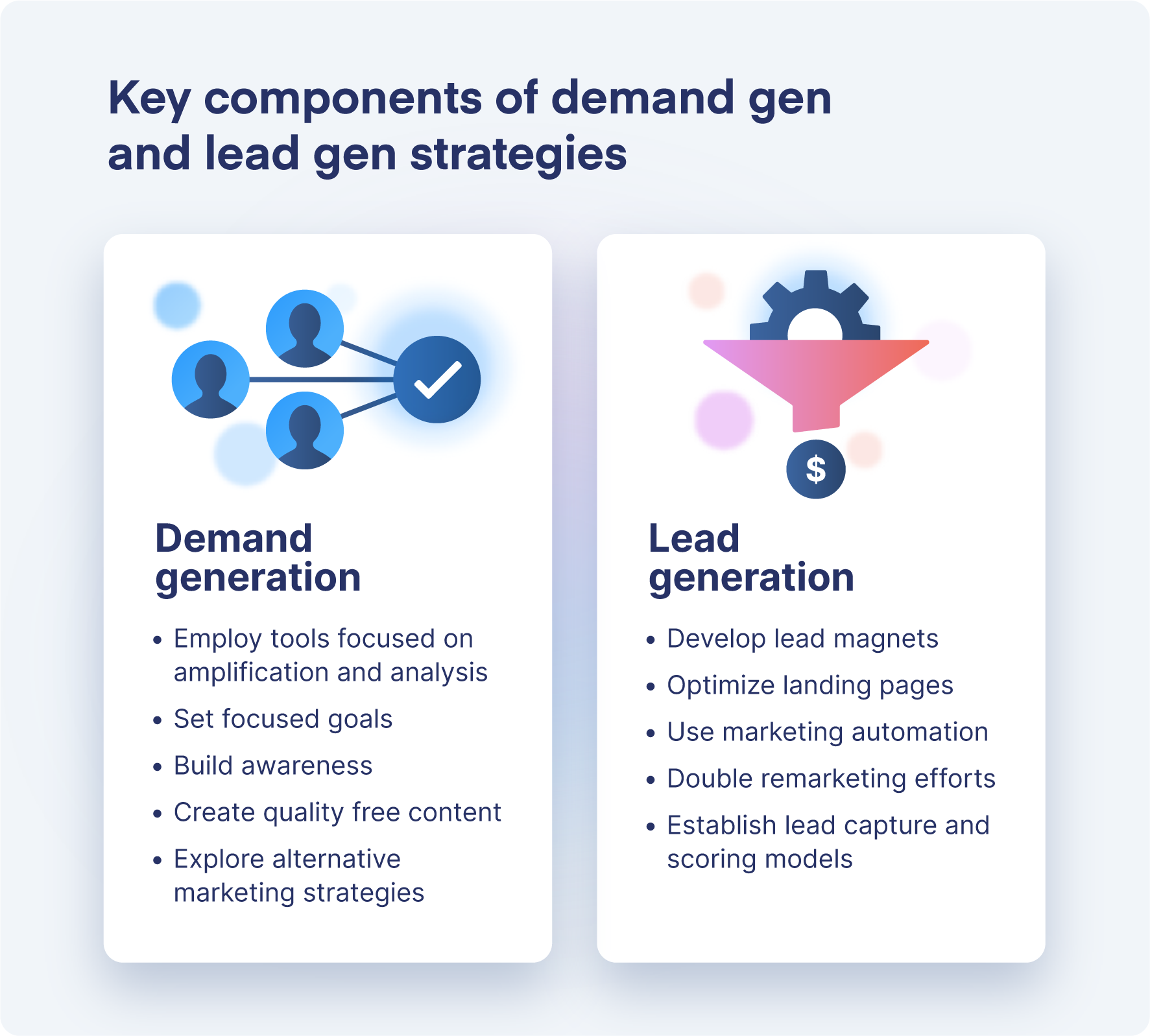
Product-centric demand generation represents a strategic shift in marketing and sales, placing the product itself at the forefront of attracting, engaging, and converting potential customers. This approach contrasts with more traditional methods that prioritize broad branding or general solution awareness before introducing specific product features and benefits.
Understanding the Core Principles
The central tenet of product-centric demand generation is that the product demonstrably solves a specific problem or fulfills a particular need for the target audience. Marketing efforts are therefore concentrated on showcasing the product's capabilities, highlighting its unique value proposition, and providing ample opportunities for potential customers to experience the product firsthand, often through free trials, demos, or freemium models.
Key Elements of a Product-Centric Approach
Several elements are crucial to successfully implementing a product-centric demand generation strategy:
- Deep Product Understanding: A thorough comprehension of the product's features, benefits, and ideal use cases is paramount. This includes knowing the target audience inside and out, understanding their pain points, and identifying how the product directly addresses those pain points.
- Compelling Product Demos and Trials: Providing prospective customers with tangible opportunities to interact with the product is essential. This could involve offering free trials with limited functionality, interactive product demos showcasing key features, or even freemium versions that allow users to experience the product indefinitely with some restrictions.
- Targeted Content Marketing: Content should focus on the product's specific features and how they solve real-world problems. This can include blog posts, case studies, webinars, and explainer videos demonstrating the product's capabilities and its benefits for specific user segments.
- Data-Driven Optimization: Tracking key metrics such as trial sign-ups, feature usage, conversion rates, and customer lifetime value is crucial for optimizing the demand generation process. This allows for continuous refinement of marketing messaging, targeting strategies, and product features.
- Seamless User Experience: From initial awareness to onboarding and ongoing usage, the entire user experience must be smooth and intuitive. This minimizes friction, maximizes user engagement, and ultimately drives product adoption.
Comparing Product-Centric to Traditional Demand Generation
Traditional demand generation often involves creating broad awareness of a company's brand and the general solutions it offers. While brand building is still important, product-centric demand generation takes a more direct and focused approach. Instead of starting with a general problem and then introducing the product as a solution, the product itself becomes the entry point for the conversation.
For example, a traditional approach might involve creating content about the challenges of project management and then briefly mentioning a project management software solution. A product-centric approach, on the other hand, would directly showcase the project management software's features, such as task assignment, progress tracking, and collaboration tools, and demonstrate how these features specifically address common project management challenges.
The table below highlights key differences:
| Feature | Traditional Demand Generation | Product-Centric Demand Generation |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Brand awareness and solution category | Specific product features and benefits |
| Content | General industry trends and problem statements | Product demos, case studies, and feature explanations |
| Metrics | Website traffic, lead generation, brand mentions | Trial sign-ups, product usage, conversion rates |
| Sales Cycle | Longer and more consultative | Shorter and more self-service oriented |
Benefits of a Product-Centric Approach
Adopting a product-centric approach to demand generation offers several potential benefits:
- Faster Time to Value: By showcasing the product's value upfront, businesses can accelerate the customer journey and drive quicker adoption.
- Higher Conversion Rates: When potential customers can directly experience the product's capabilities, they are more likely to convert into paying customers.
- Improved Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): By focusing marketing efforts on product-specific messaging, businesses can attract more qualified leads and reduce their CAC.
- Increased Customer Engagement: Providing opportunities for hands-on product interaction fosters engagement and builds stronger relationships with potential customers.
- Enhanced Product Feedback: By closely monitoring product usage and gathering user feedback, businesses can gain valuable insights for improving their product and tailoring it to customer needs.
Examples of Product-Centric Demand Generation in Action
Several companies have successfully implemented product-centric demand generation strategies. Consider the following examples:
Slack: From the very beginning, Slack focused on showcasing its collaboration features and integrations through free trials and compelling product demos. Their marketing highlighted how Slack could improve team communication and productivity, and users were encouraged to experience the product firsthand.
Zoom: Zoom's freemium model allows users to host meetings with limited features for free. This provides a tangible way for potential customers to experience the platform's ease of use and reliability, driving adoption among both individual users and businesses.
HubSpot: HubSpot offers a range of free tools and resources that allow users to experience the value of their platform before committing to a paid subscription. This approach helps attract qualified leads and demonstrate the power of HubSpot's marketing and sales solutions.
Implementing a Product-Centric Demand Generation Strategy
To effectively implement a product-centric demand generation strategy, consider the following steps:
- Define Your Target Audience: Clearly identify your ideal customer profile and understand their needs, pain points, and goals.
- Highlight Your Product's Value Proposition: Clearly articulate the unique benefits and value that your product offers to your target audience.
- Create Compelling Product Demos and Trials: Develop interactive demos, free trials, or freemium models that allow potential customers to experience the product firsthand.
- Develop Targeted Content: Create content that focuses on the product's specific features and how they solve real-world problems.
- Optimize Your Onboarding Process: Ensure that new users have a smooth and intuitive onboarding experience that guides them through the key features and benefits of your product.
- Track Key Metrics: Monitor trial sign-ups, product usage, conversion rates, and customer lifetime value to measure the effectiveness of your demand generation efforts.
- Continuously Iterate: Regularly analyze your data and gather user feedback to identify areas for improvement and optimize your product and marketing strategies.
Practical Advice and Insights
The principles of product-centric demand generation extend beyond the realm of marketing and sales. In everyday life, consider the following:
- Focus on Value: When presenting an idea or proposal, clearly articulate its benefits and demonstrate how it solves a specific problem or fulfills a particular need.
- Provide Tangible Examples: Instead of relying solely on abstract explanations, offer concrete examples and demonstrations to illustrate your point.
- Seek Feedback: Actively solicit feedback from others to identify areas for improvement and refine your approach.
- Emphasize User Experience: Consider the experience of the person on the receiving end of your message. Is it clear, concise, and easy to understand?
By focusing on value, providing tangible examples, seeking feedback, and emphasizing user experience, you can apply the principles of product-centric demand generation to improve your communication and persuasion skills in all aspects of your life.
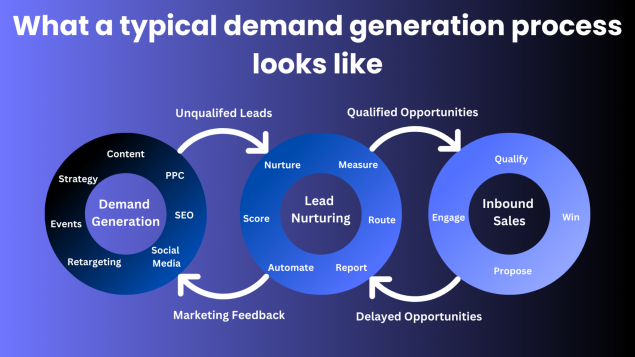
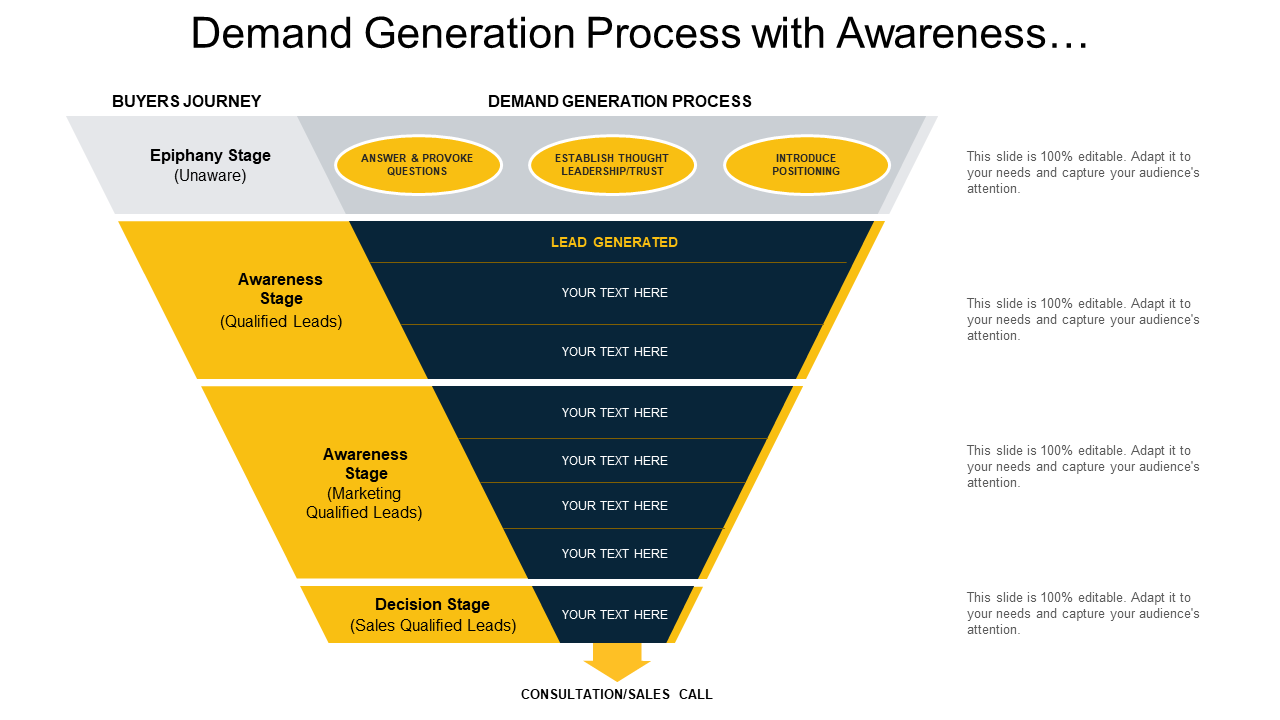
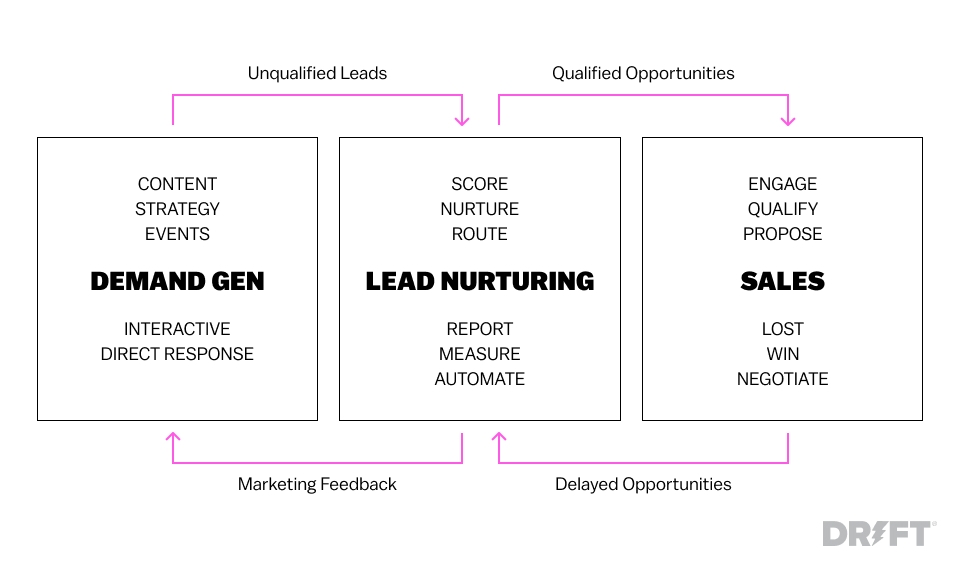


![B2B Demand Generation Explained [Definition & Strategies] - Product Centric Demand Generation Focuses On](https://www.blendb2b.com/hs-fs/hubfs/Demand Generation/Demand Gen Pillar Page/Demand Generation Funnel (2).jpg?width=2744&height=1292&name=Demand Generation Funnel (2).jpg)




.webp?width=635&name=Demand gen-01 (1).webp)