Alright, gather 'round, friends! Let's talk about pitch. Not baseball pitch, mind you, unless we're talking about the specific *frequency* of the umpire's enraged yell when a batter strikes out. No, we're diving headfirst into the wonderfully weird world of sound pitch. Prepare for a journey so informative, so hilarious, it'll make your ears ring… with knowledge!
So, What Exactly IS Pitch? (Besides Something You Throw)
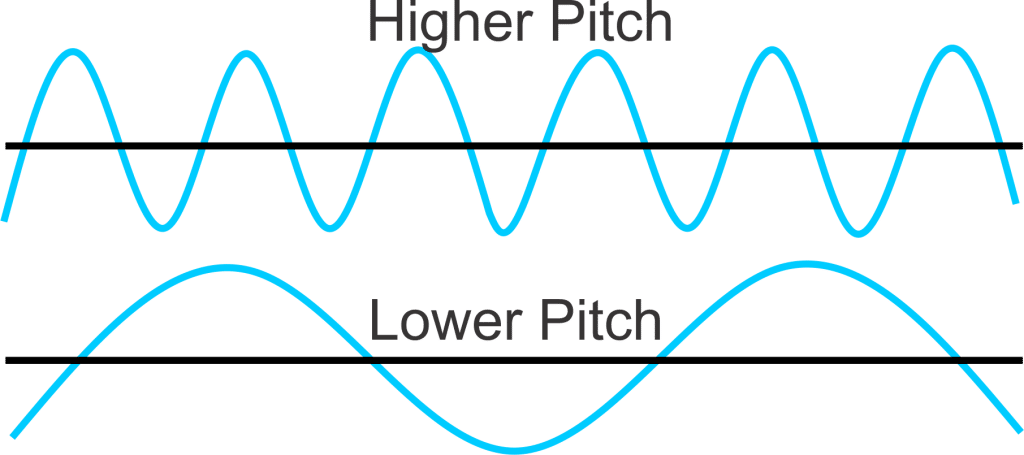
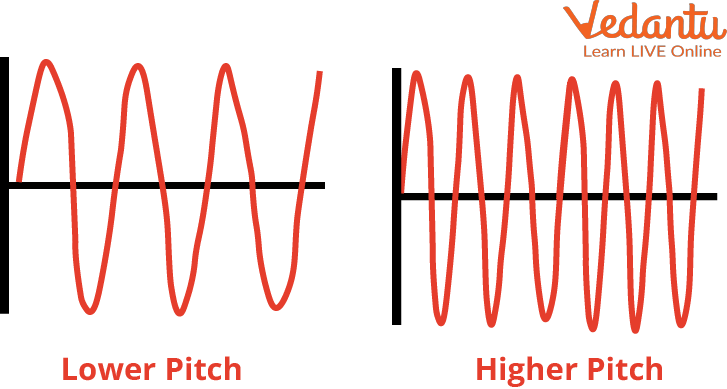
Imagine you're at a concert. The singer hits a really high note – glass-shattering high. Your dog starts howling. That, my friends, is a high pitch. Now, picture a tuba player rumbling out a note so low it makes your chest vibrate. That's a low pitch. In essence, pitch is how we perceive the highness or lowness of a sound. It's the subjective experience related to the *frequency* of a sound wave. Think of it like climbing stairs: each step up is a higher pitch, and each step down is a lower pitch.
But how do we *know* what's high and what's low? Is it some kind of mystical, auditory sixth sense? Nope! It’s all down to good ol’ science!
Frequency: The Secret Ingredient
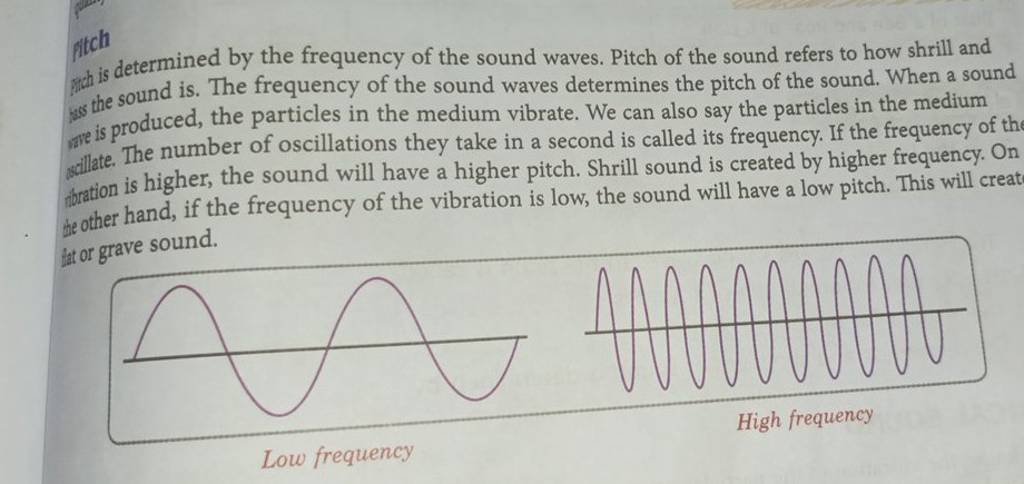
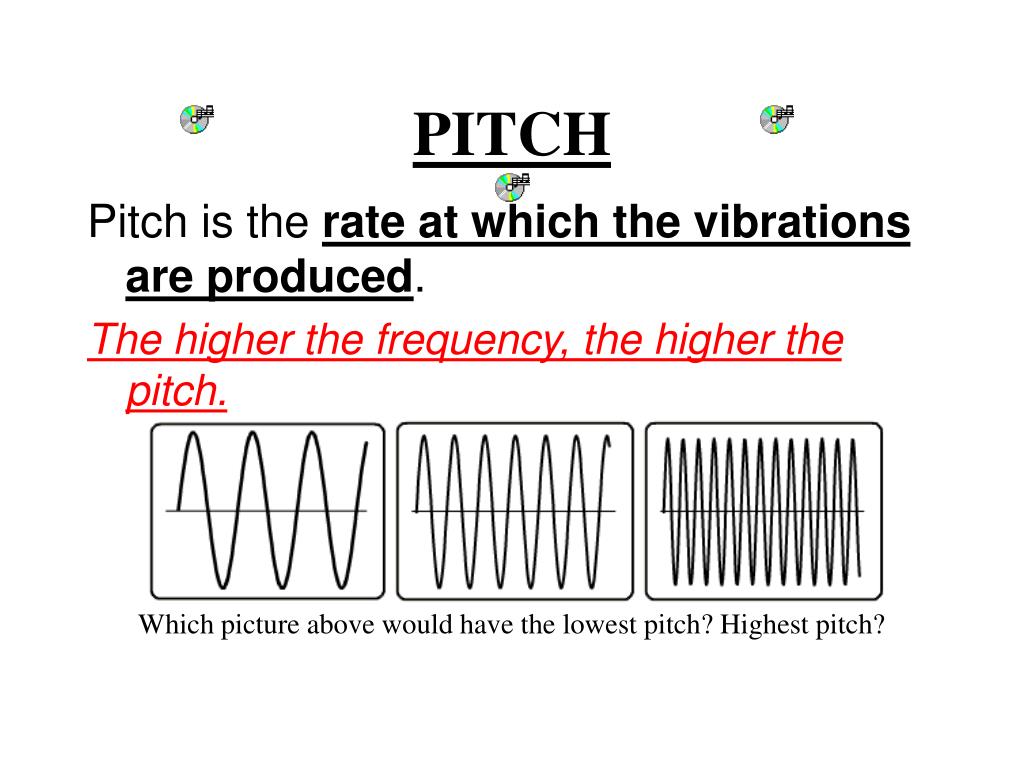
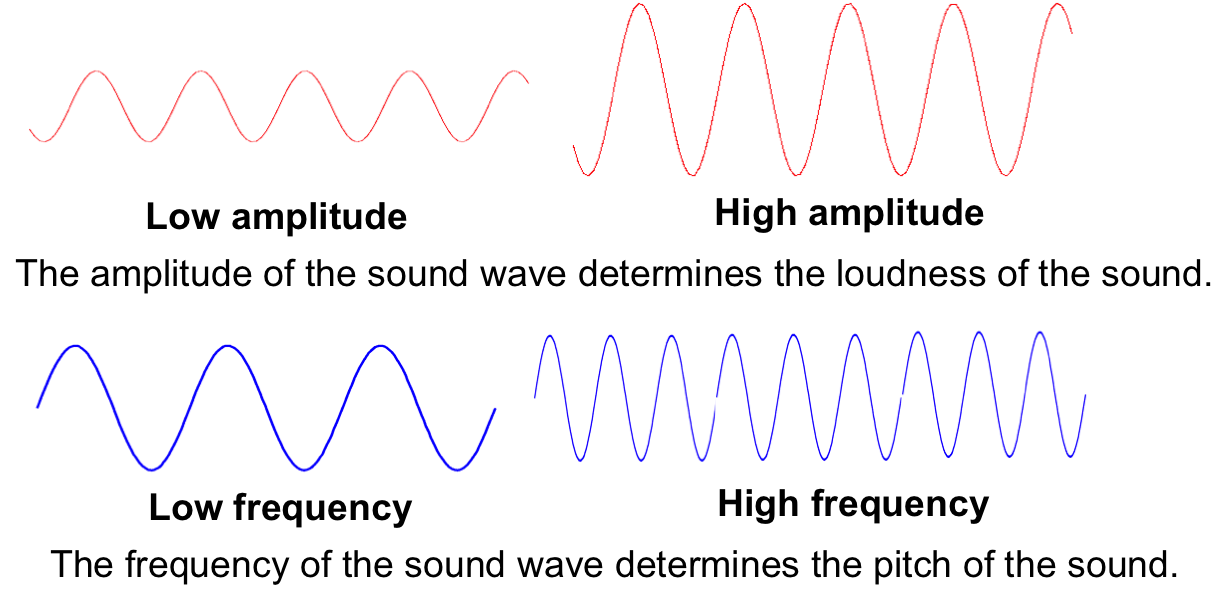
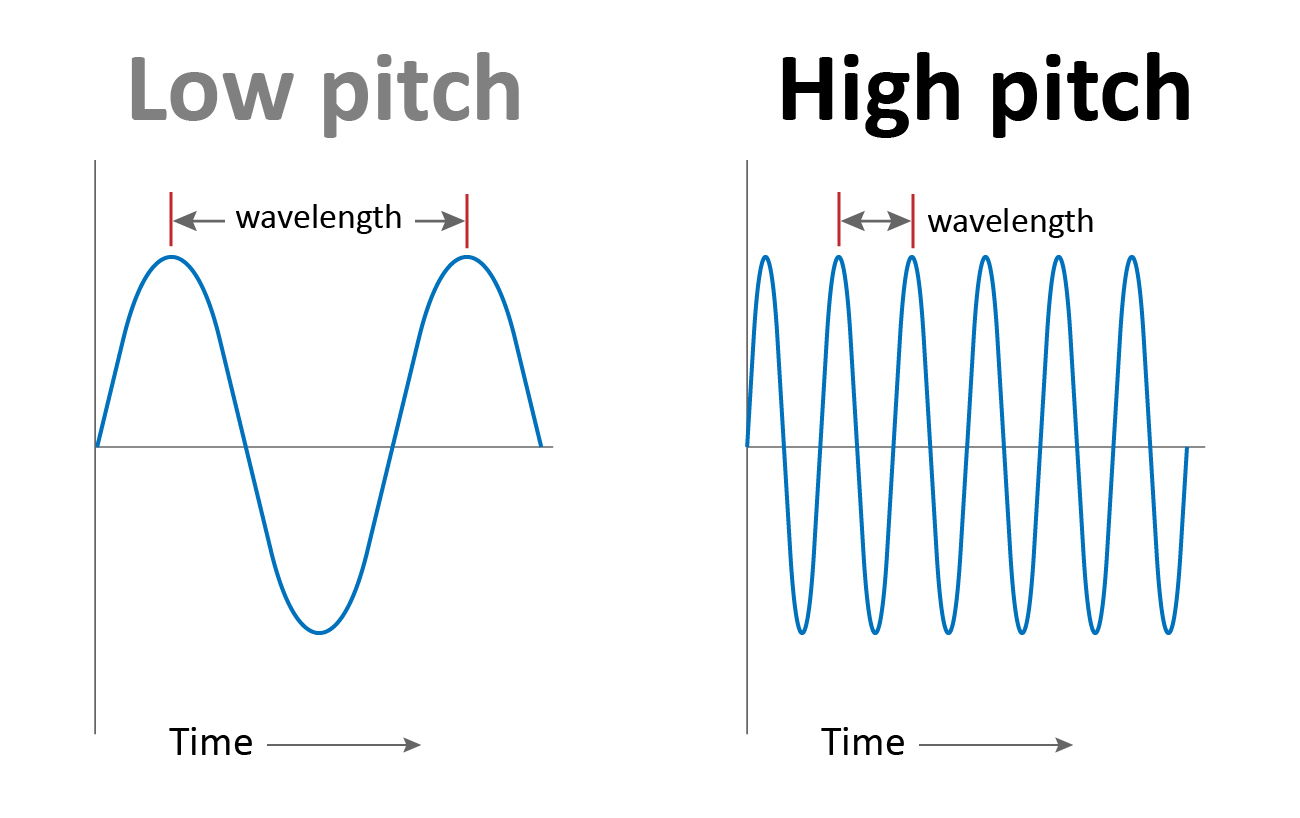
Okay, so remember that word "frequency" I casually tossed in there earlier? Yeah, that's the key player in our pitchy drama. Frequency, in the context of sound, refers to how many times a sound wave repeats itself in a given second. We measure this in Hertz (Hz). One Hertz means one cycle per second. Think of it like a tiny little drummer inside your speaker, banging away. The faster the drummer bangs, the higher the frequency, and the higher the pitch.
For example, the standard tuning note for an orchestra, A4 (the A above middle C), is usually tuned to 440 Hz. That means the sound wave is completing 440 cycles every second! That's a lot of drumming! If the orchestra suddenly decides to play A5 (an octave higher), the frequency doubles to 880 Hz. The poor drummer is now going twice as fast! Someone get them a Red Bull!
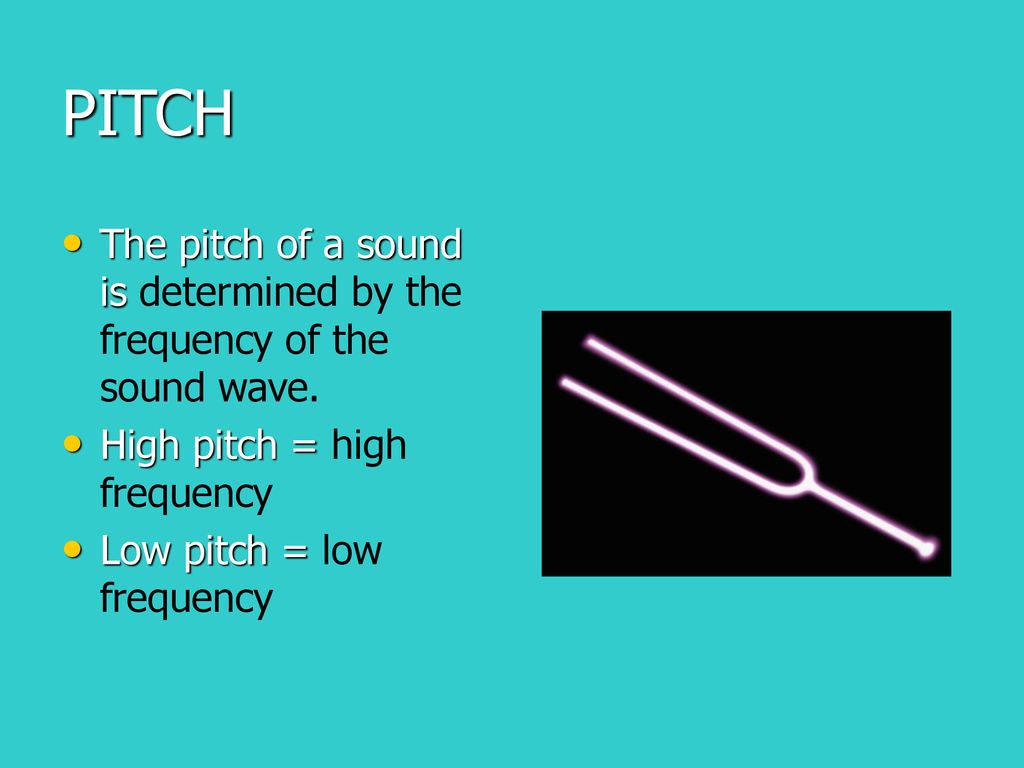
Here's the kicker: Higher frequency = Higher pitch. It's a direct relationship. No ifs, ands, or buts. It's as simple as that! Well, mostly...
The Science Behind the Sound Waves (Without Getting *Too* Science-y)
Sound, at its core, is a vibration. When you pluck a guitar string, it vibrates. This vibration creates tiny disturbances in the air around it. These disturbances travel outwards as sound waves, like ripples in a pond. Our ears, being the highly-sophisticated sound-detecting machines that they are, pick up these ripples.
These sound waves then tickle our eardrums (yes, tickle!), which sets off a chain reaction of tiny bones vibrating. These vibrations are then converted into electrical signals that are sent to our brains. And *voila*! Our brains interpret these signals as sound, complete with its own unique pitch. It's a wild ride, really, when you think about it.
Factors Affecting Frequency (and Therefore, Pitch!)
So, what affects how quickly something vibrates, and thus, the frequency of the sound it produces? Well, lots of things! Here are a few key players:
- Tension: Think about a guitar string. If you tighten it (increase the tension), it vibrates faster, and the pitch goes up. Loosen it, and the pitch goes down. That's why guitarists are always fiddling with those tuning pegs! They're tweaking the tension to get the exact frequency they need.
- Length: Shorter strings vibrate faster than longer strings, resulting in a higher pitch. This is why a violin is smaller than a cello – it needs to produce higher notes! Imagine trying to play a high note on a cello the size of a school bus! It just wouldn't work.
- Mass: Lighter objects vibrate faster than heavier objects. A thin cymbal will produce a higher-pitched sound than a thick, heavy one when struck. It's all about inertia, baby!
- Material: Different materials have different densities and stiffnesses, which affect how easily they vibrate. This is why a bell made of brass sounds different from a bell made of steel. It's not just about the shape or size; the material itself plays a crucial role.
These factors combine to determine the natural frequency of an object. This is the frequency at which the object will vibrate most readily when disturbed. It's like its favorite frequency, the one it's just *dying* to resonate at.
Pitch Perception: It's All in Your Head (Literally!)
Okay, we've talked about frequency, sound waves, and vibrating objects. But the actual perception of pitch happens entirely within our brains. Our ears are just the messengers, delivering the frequency information. The brain is the one that interprets it and tells us, "Yep, that's a high note," or "Whoa, that's a low rumble!"
And here's where things get really interesting: our perception of pitch is not always perfectly linear. The human ear is more sensitive to changes in frequency in the lower ranges than in the higher ranges. What does this mean? Well, a change of 10 Hz at 100 Hz will sound like a much bigger jump in pitch than a change of 10 Hz at 1000 Hz.
Also, our perception of pitch can be influenced by other factors, such as the loudness of the sound and the presence of other frequencies. This is why musicians often talk about "voicing" chords, which refers to the way the different notes are arranged in terms of pitch and loudness. A well-voiced chord sounds balanced and pleasing to the ear, while a poorly voiced chord can sound muddy and dissonant.
The Curious Case of Relative Pitch and Perfect Pitch
Have you ever heard of someone having "perfect pitch"? It's the ability to identify or produce a specific pitch without any external reference. It's like having a built-in tuning fork in your brain! It's relatively rare, and scientists believe it's a combination of genetic predisposition and early musical training.
Most musicians, however, have relative pitch, which is the ability to identify intervals (the distance between two notes) and chords. They can hear a note and then figure out what other notes are being played in relation to it. It's like having a musical GPS system in your head, guiding you through the landscape of sound.
So, Why Does Any of This Matter?
Well, for one thing, understanding how pitch works is crucial for musicians, sound engineers, and anyone who works with audio. It allows them to manipulate sound in precise and meaningful ways. But even if you're not a musician, understanding pitch can enhance your appreciation for music and sound in general.
Think about the last time you heard a really beautiful piece of music. The way the composer used pitch to create tension and release, to evoke emotions, to tell a story… it's all based on these fundamental principles of physics and perception. It's pretty amazing when you think about it.
And finally, knowing the science behind pitch gives you a great conversation starter at parties. Imagine casually dropping into a conversation, "Did you know that the frequency of a sound wave directly affects its perceived pitch?" Boom! Instant intellectual credibility! Just try not to be *that* guy.
So, there you have it! The wonderfully weird and slightly wacky world of pitch. Now go forth and listen… with a newfound appreciation for the science behind the sound!