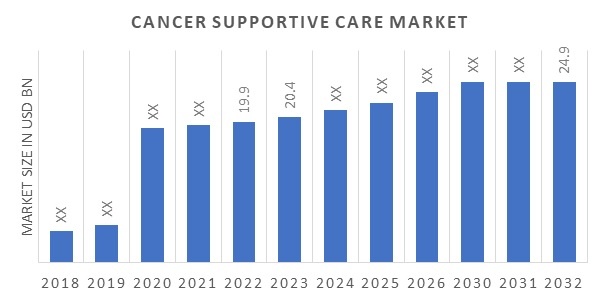
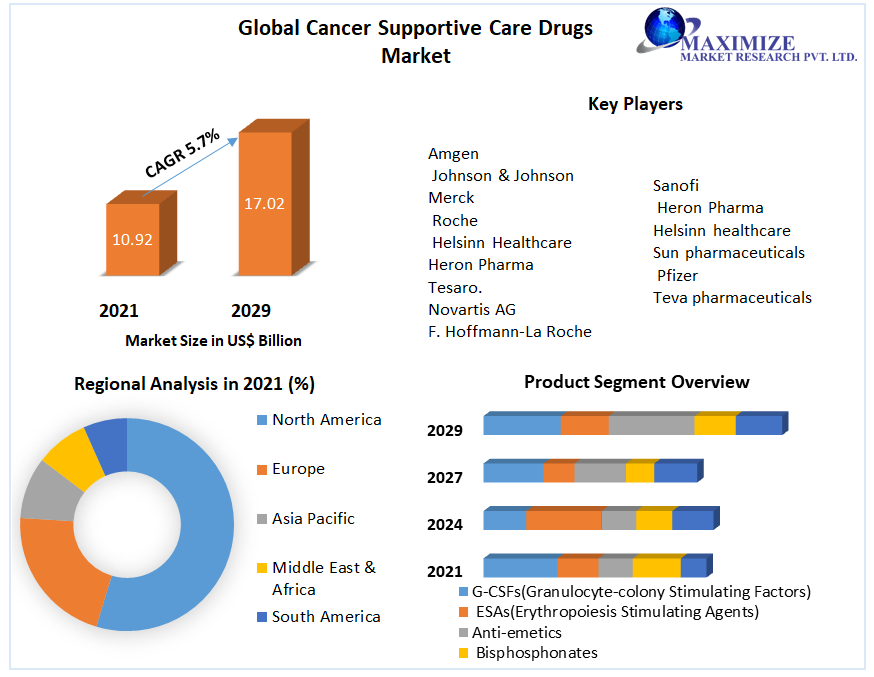
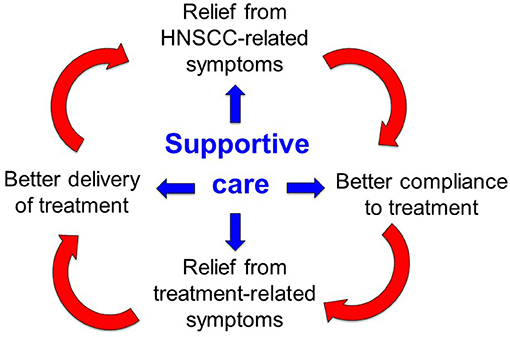
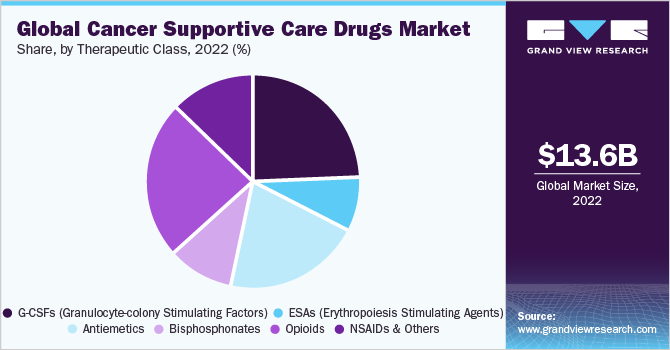
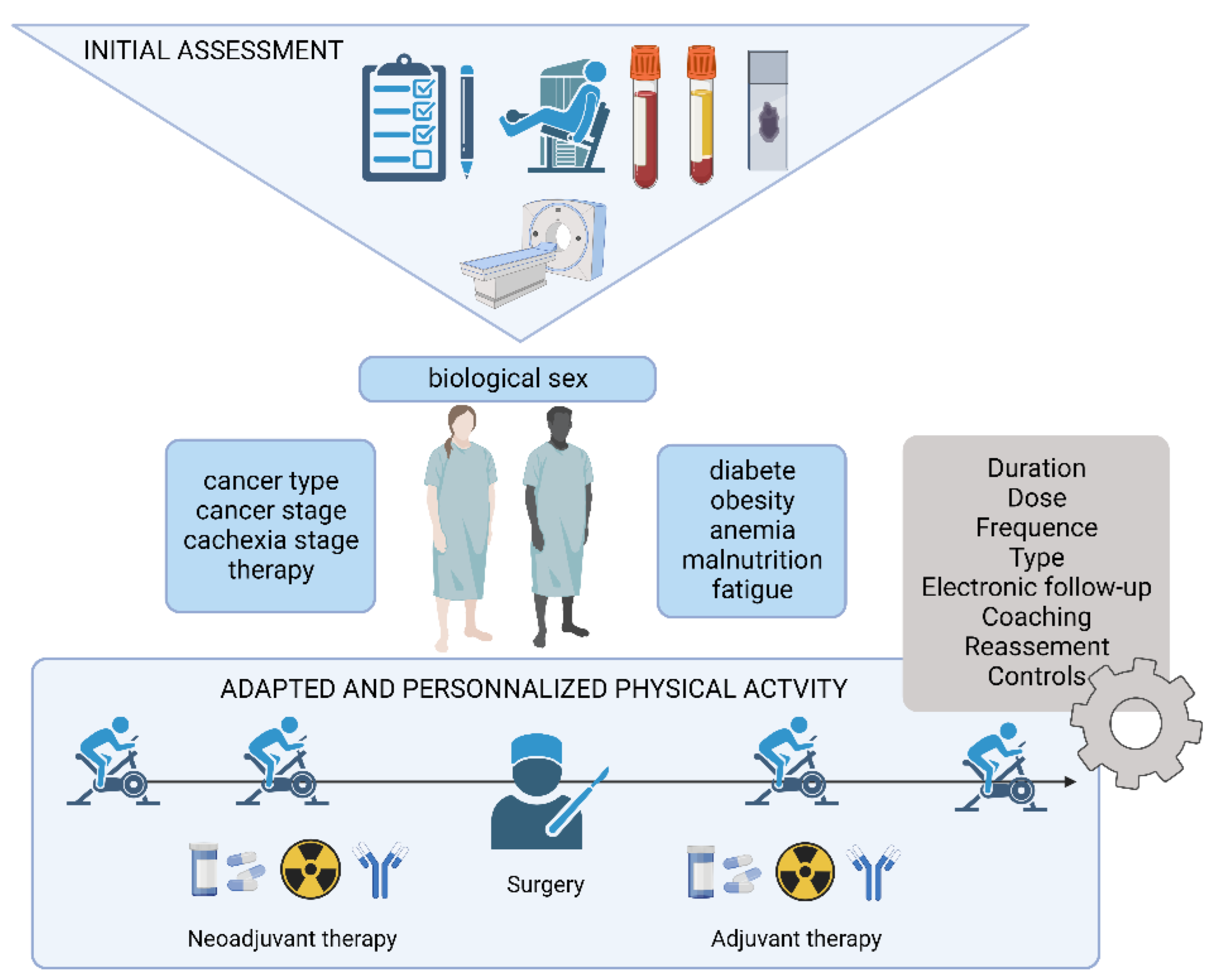
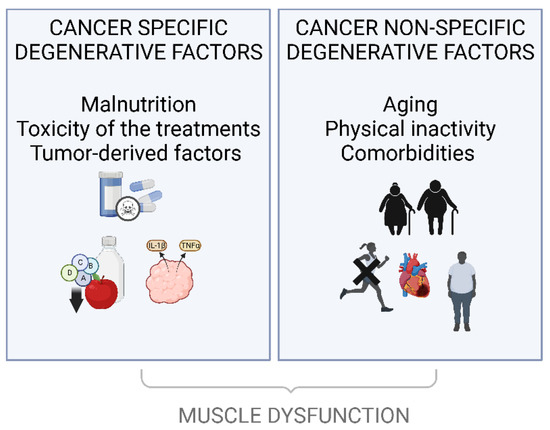
Supportive care in cancer is a multidisciplinary field focused on alleviating the adverse effects of cancer and its treatment. It encompasses a wide range of interventions aimed at improving the quality of life for patients and their families throughout the cancer trajectory, from diagnosis to survivorship or end-of-life care. This includes managing physical symptoms like pain, nausea, and fatigue, as well as addressing psychological, social, and spiritual needs.
Understanding the Impact Factor
The Impact Factor (IF) is a metric used to assess the relative importance or influence of a scholarly journal within its field. It is calculated annually by Clarivate Analytics (formerly part of Thomson Reuters) and published in the Journal Citation Reports (JCR). The IF is determined by dividing the number of current year citations to articles published in the journal during the previous two years by the total number of citable articles published in the journal during those same two years. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Impact Factor (Year X) = (Citations in Year X to articles published in Years X-1 and X-2) / (Number of citable articles published in Years X-1 and X-2)
For example, if a journal published 100 citable articles in 2021 and 2022 combined, and those articles received a total of 500 citations in 2023, then the journal's Impact Factor for 2023 would be 5.0.
Significance of the Impact Factor
The Impact Factor serves as a proxy indicator of a journal's quality and influence within its respective field. It is frequently used by researchers, academics, and institutions for various purposes:
- Journal Selection: Researchers often consider the IF when choosing where to submit their research articles. Higher IF journals are generally perceived as more prestigious and influential, increasing the visibility and impact of their published work.
- Research Evaluation: Universities and funding agencies sometimes use the IF as a criterion to evaluate the research output of their faculty or grant applicants. Publishing in high-IF journals can be seen as evidence of research excellence.
- Journal Ranking: The IF is used to rank journals within specific subject categories. Journals with higher IFs are generally considered to be leading publications in their field.
It is important to note that the Impact Factor is just one metric and should not be the sole determinant of a journal's quality or a researcher's merit. Other factors to consider include the journal's editorial board, peer-review process, scope, and readership, as well as the overall impact and significance of individual research articles, regardless of the journal in which they are published.
Impact Factor in Supportive Care
The Impact Factor is also relevant within the field of supportive care in cancer. Journals dedicated to publishing research on supportive care interventions, symptom management, palliative care, and related topics are often evaluated based on their IF. A higher IF for a supportive care journal indicates that the research published in that journal is being widely cited and is therefore considered to be influential within the field.
Researchers in supportive care often aim to publish their findings in journals with strong IFs to maximize the impact of their work and contribute to the advancement of the field. Clinicians and healthcare professionals may also use the IF to identify leading journals in supportive care and stay up-to-date on the latest evidence-based practices.
However, it is crucial to recognize the limitations of using the Impact Factor as the sole measure of a journal's or an article's value. The Impact Factor reflects the average citation rate of articles published in a journal, and individual articles within a journal can have varying levels of impact. Furthermore, the Impact Factor can be influenced by factors such as the journal's scope, the size of its readership, and the citation practices within the specific field.
Example: Interpreting the Impact Factor for a Supportive Care Journal
Let's say a hypothetical journal called "Supportive Care Oncology Journal" (SCOJ) has an Impact Factor of 4.5 for the year 2023. This means that, on average, articles published in SCOJ during 2021 and 2022 received 4.5 citations each in 2023. A higher IF, such as 4.5, suggests that SCOJ is a relatively influential journal within the field of supportive care oncology, compared to journals with lower IFs. Researchers might prioritize submitting their work to SCOJ to increase its visibility and impact. However, this does not guarantee that every article published in SCOJ will be highly cited, and important research might also appear in journals with lower IFs that are more specialized or newly established.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite its widespread use, the Impact Factor has several limitations that must be considered:
- Field-Specific Differences: Citation practices vary significantly across different academic fields. Journals in fields with large research communities and frequent publication rates tend to have higher IFs than journals in smaller or more specialized fields, even if the latter publish high-quality research. Therefore, comparing IFs across different fields is not meaningful.
- Citation Gaming: The IF can be manipulated through various strategies, such as self-citation (a journal citing its own articles) or citation cartels (groups of journals agreeing to cite each other). These practices can artificially inflate the IF and distort the true impact of a journal.
- Article Type: The IF does not differentiate between different types of articles, such as original research articles, review articles, editorials, or letters to the editor. Review articles, which typically synthesize existing research, tend to be cited more frequently than original research articles, which can skew the IF.
- Time Lag: The IF is calculated based on citations received during a specific two-year window. This time lag may not accurately reflect the long-term impact of research, particularly in fields where research findings take time to be adopted and implemented.
- Journal Scope: Journals with a broader scope may attract a wider readership and receive more citations than journals with a more narrow or specialized focus. This does not necessarily mean that the broader journal publishes higher-quality research.
Beyond the Impact Factor: A Holistic Approach
Given the limitations of the Impact Factor, it is essential to adopt a more holistic approach to evaluating journals and research. This includes considering a range of factors beyond the IF, such as:
- Journal Reputation: The reputation of a journal within its field is based on its history of publishing high-quality research, the expertise of its editorial board, and the rigor of its peer-review process.
- Article-Level Metrics: Metrics such as citation counts, Altmetric scores (which measure the online attention an article receives), and usage statistics (e.g., downloads and views) can provide a more nuanced assessment of an individual article's impact.
- Qualitative Assessment: Expert review and evaluation by peers remain crucial for assessing the quality, originality, and significance of research.
- Readership and Accessibility: The accessibility of a journal (e.g., whether it is open access) and the size and engagement of its readership can influence the dissemination and impact of its published research.
Practical Advice and Insights
For researchers in supportive care and related fields, here's some practical advice:
- Target High-Quality Journals: While aiming for journals with strong IFs is reasonable, prioritize journals that align with the scope and quality of your research and that are respected within your field.
- Focus on Impactful Research: Conduct research that addresses important clinical questions, contributes to the advancement of knowledge, and has the potential to improve the lives of cancer patients and their families.
- Promote Your Work: Actively disseminate your research findings through presentations at conferences, social media, and other channels to increase its visibility and impact.
- Engage with the Research Community: Participate in peer review, collaborate with other researchers, and contribute to the development of guidelines and best practices to shape the future of supportive care.
- Critically Evaluate Journals: When selecting journals for your research, consider the journal's reputation, editorial board, peer-review process, and scope, in addition to its Impact Factor.
Ultimately, the goal of research in supportive care is to improve the lives of cancer patients and their families. While the Impact Factor can provide some insights into the influence of a journal, it is essential to focus on conducting high-quality research and disseminating it effectively to make a meaningful difference.