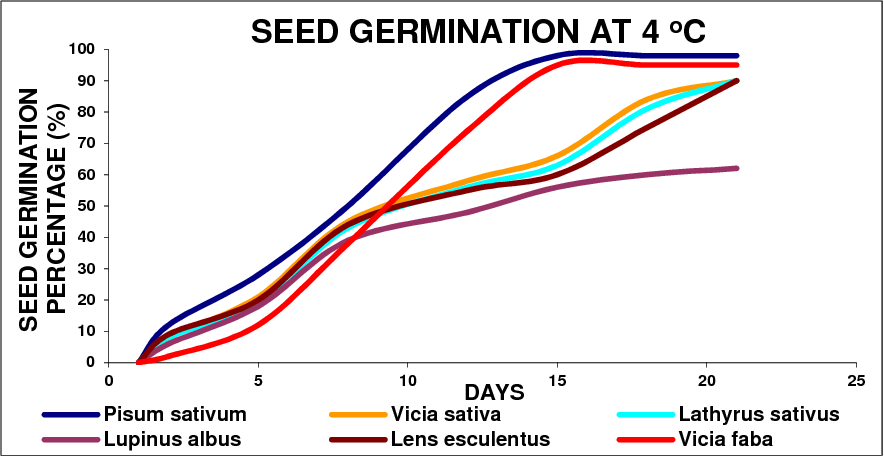
The germination rate is a crucial metric in agriculture, horticulture, and seed biology. It quantifies the percentage of seeds within a sample that successfully germinate and develop into seedlings within a specified timeframe and under controlled conditions. Understanding this rate is essential for efficient crop planning, resource allocation, and overall yield optimization.
Defining Germination Rate
Germination rate, often expressed as a percentage, reflects the viability and vigor of a seed lot. It's determined by conducting germination tests where seeds are placed in a suitable environment with adequate moisture, temperature, light (if required), and oxygen. The number of seeds that sprout, showing emergence of the radicle (root) and plumule (shoot), is then counted, and the percentage is calculated.
Factors Influencing Germination Rate
Several factors significantly impact the germination rate of seeds. These can be broadly categorized into internal and external factors.
Internal Factors: Seed Quality
The inherent quality of the seed plays a pivotal role. This includes:
- Seed Viability: The capacity of the seed embryo to germinate. Non-viable seeds are either dead or too damaged to germinate.
- Seed Dormancy: A state where seeds fail to germinate even under favorable conditions. This dormancy can be due to various factors, including hard seed coats, chemical inhibitors, or the need for a specific period of cold stratification (vernalization).
- Seed Maturity: Immature seeds often have low germination rates due to incomplete embryo development.
- Seed Genetics: Genetic makeup influences germination speed and overall viability. Some varieties are inherently more vigorous than others.
External Factors: Environmental Conditions
The external environment provides the necessary triggers and resources for germination. Critical environmental factors include:
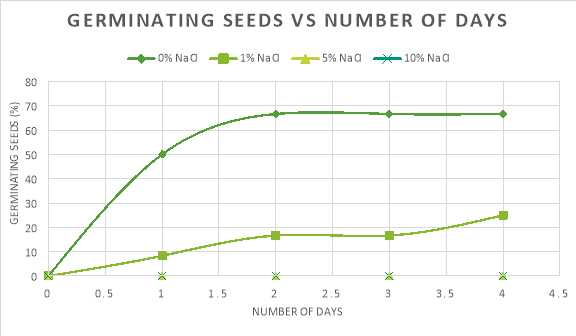
- Moisture: Water imbibition is crucial to activate enzymatic processes within the seed. Insufficient moisture inhibits germination, while excessive moisture can lead to seed rot.
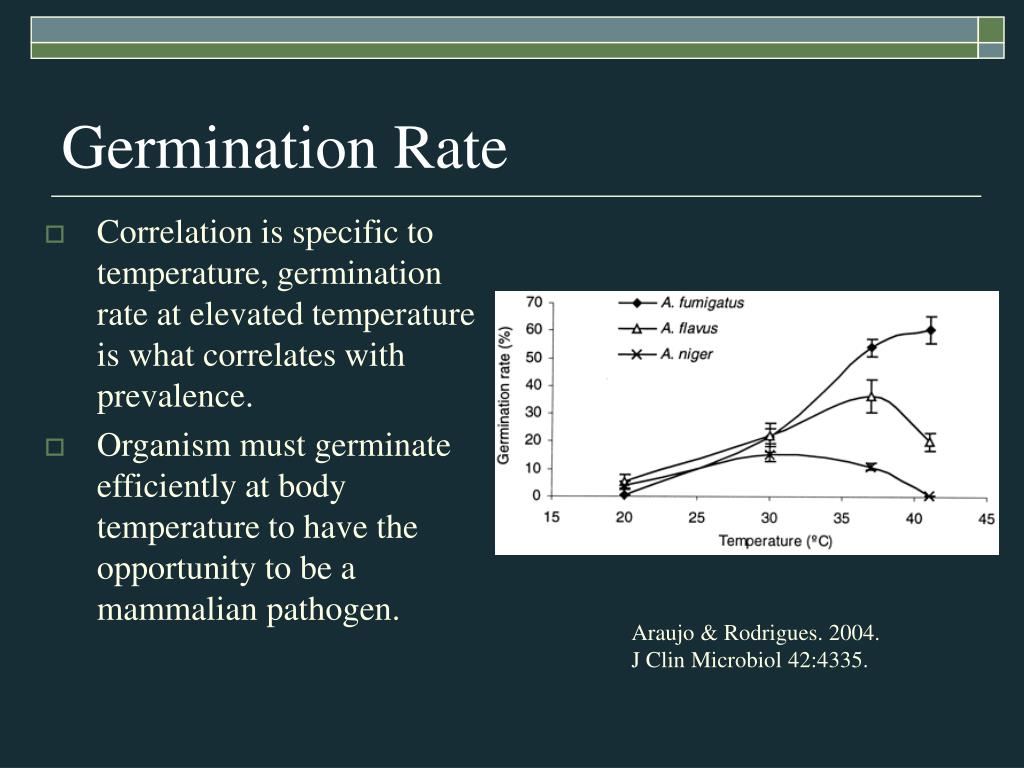
- Temperature: Each species has an optimal temperature range for germination. Temperatures outside this range can significantly reduce germination rate or prevent it altogether.
- Oxygen: Seeds require oxygen for respiration during germination. Waterlogged soils can deplete oxygen levels and hinder germination.
- Light: Some seeds are light-sensitive and require light exposure to germinate (photoblastic), while others are inhibited by light (dark-germinating).
- Substrate: The growing medium should provide adequate support, aeration, and drainage. It should also be free from pathogens and contaminants.
Calculating Germination Rate
The basic formula for calculating germination rate is:
Germination Rate (%) = (Number of Germinated Seeds / Total Number of Seeds Planted) x 100
However, it's crucial to standardize the conditions under which the germination test is conducted. This ensures reliable and comparable results.
Standardized Germination Testing
Organizations like the Association of Official Seed Analysts (AOSA) and the International Seed Testing Association (ISTA) have established standardized procedures for germination testing. These procedures specify:
- The type of substrate to use.
- The optimal temperature and humidity levels.
- The duration of the test.
- The criteria for determining germination.
Following these guidelines ensures that the results are accurate and reproducible.
Significance of Germination Rate
The germination rate is a critical indicator of seed lot quality and has significant implications for various sectors:
Agriculture and Horticulture
Farmers and horticulturists rely on germination rate data to:
- Determine Seeding Rates: A lower germination rate necessitates planting more seeds to achieve the desired plant density.
- Predict Crop Establishment: Accurate germination rate predictions allow for better planning and resource allocation.
- Evaluate Seed Quality: Germination tests help identify high-quality seed lots that will result in successful crop establishment.
Using seeds with a known and high germination rate minimizes the risk of crop failure and maximizes yield potential.
Seed Industry
Seed companies use germination tests for:
- Quality Control: To ensure that seed lots meet minimum quality standards.
- Labeling and Marketing: Germination rate is often displayed on seed packets to inform consumers about the expected performance.
- Research and Development: To evaluate the performance of new varieties and breeding lines.
Maintaining high germination rates is essential for maintaining the reputation and competitiveness of seed companies.
Ecological Restoration
In ecological restoration projects, germination rate is crucial for:
- Successful Reforestation: Ensuring that enough seeds germinate to establish a healthy forest stand.
- Habitat Restoration: Using native seeds with high germination rates to restore degraded ecosystems.
Selecting appropriate seeds with high germination rates is critical for the success of restoration efforts.
Improving Germination Rate
Several techniques can be employed to improve the germination rate of seeds:
Seed Priming
Seed priming involves pre-soaking seeds in water or specific solutions to initiate metabolic activity and prepare them for germination. This can shorten the germination time and improve overall germination rate, especially under suboptimal conditions.
Scarification
Scarification is a process that weakens the seed coat to allow water to penetrate and initiate germination. This is particularly important for seeds with hard or impermeable seed coats. Methods include mechanical scarification (e.g., rubbing seeds with sandpaper), acid scarification (using sulfuric acid), and hot water scarification.
Stratification
Stratification involves exposing seeds to cold, moist conditions for a specific period to break dormancy. This is often required for seeds of temperate-zone plants.
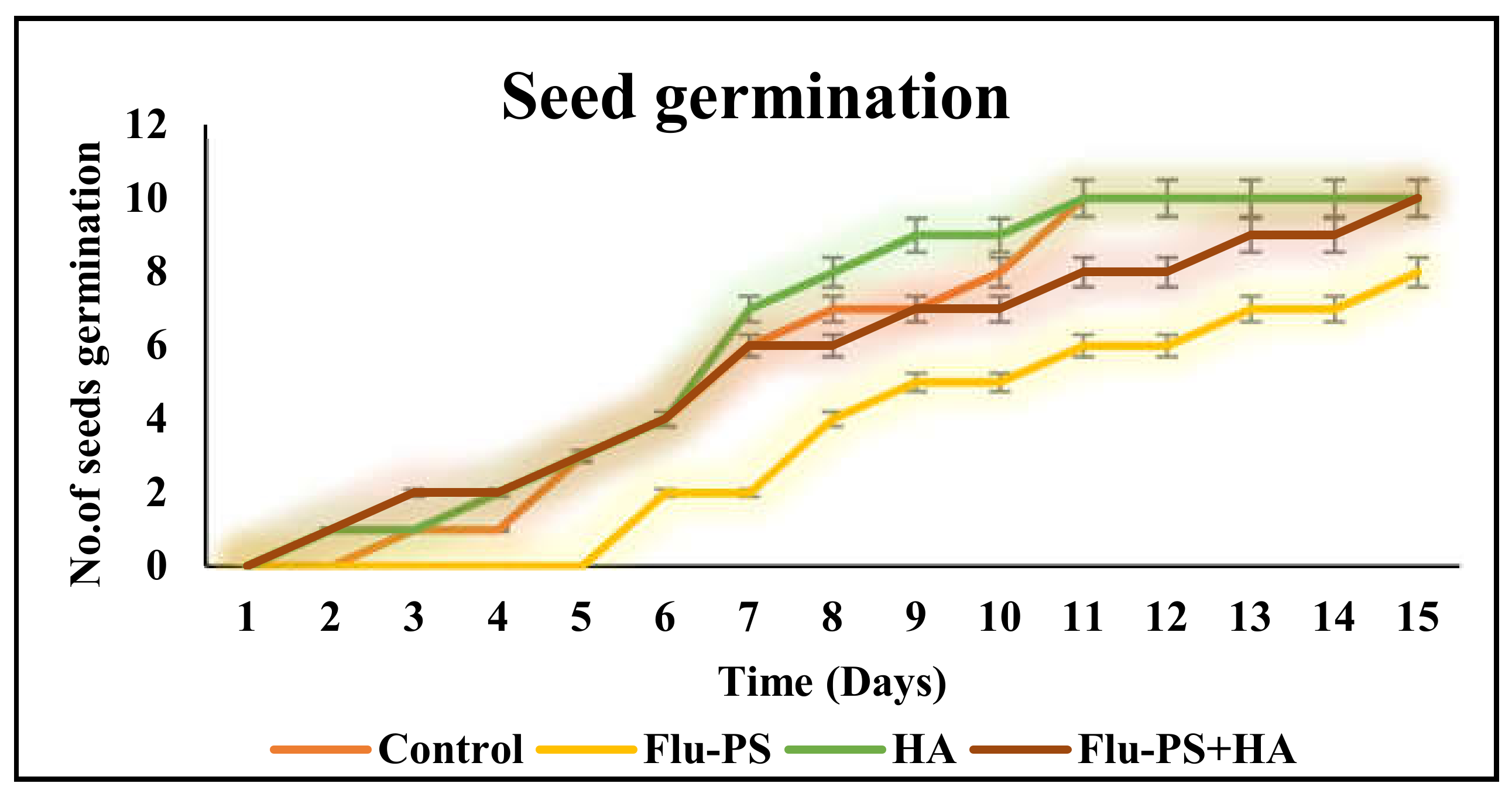
Fungicide Seed Treatment
Applying fungicides to seeds can protect them from soilborne pathogens that can cause seed rot and reduce germination rate.
Interpreting Germination Rate Results
While a high germination rate is generally desirable, it's important to interpret the results in context.
- Species-Specific Requirements: Different species have different germination requirements. What is considered a good germination rate for one species may be unacceptable for another.
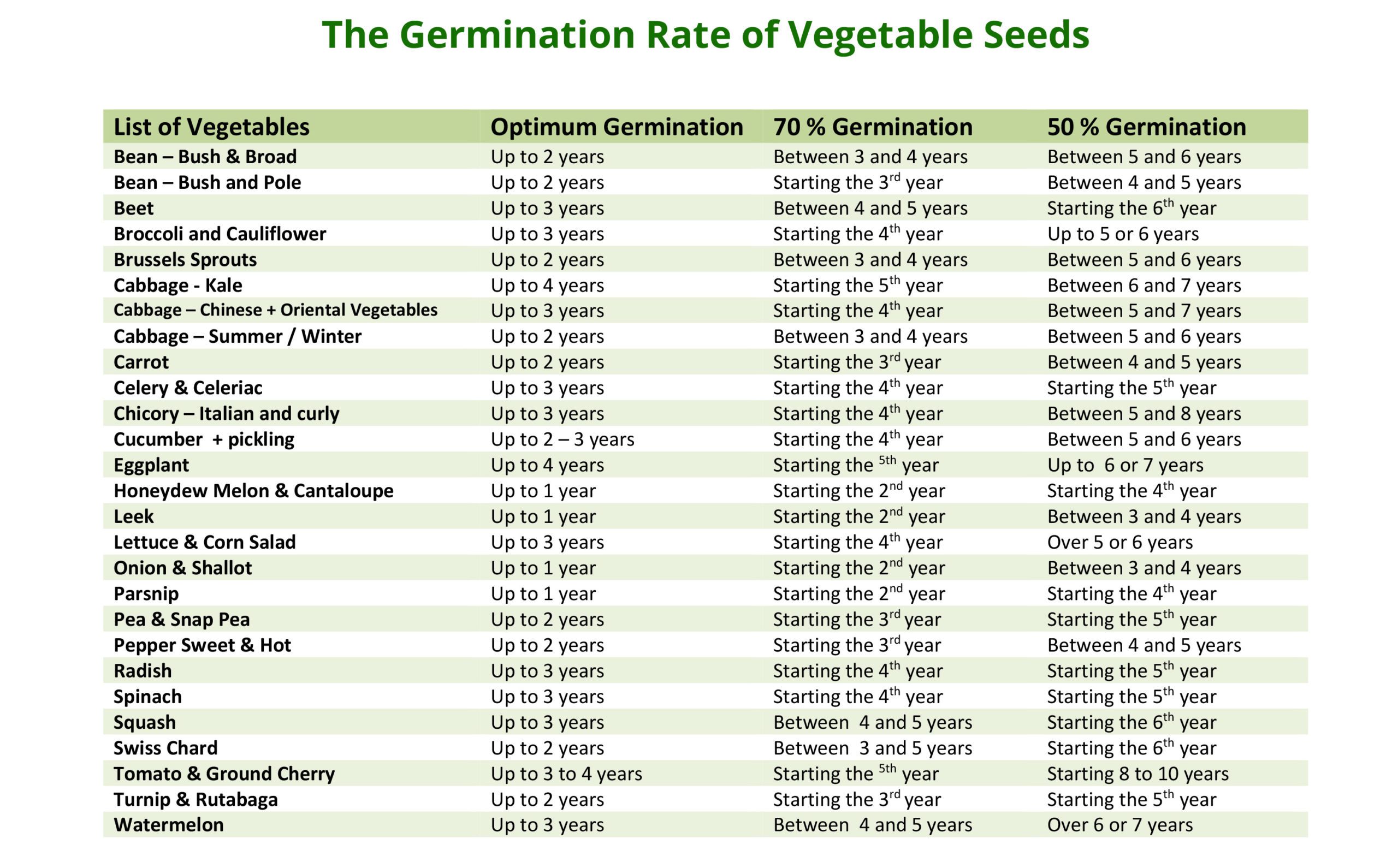
- Seed Age: Germination rate typically declines with seed age. Older seed lots may have lower germination rates than fresher seed lots.
- Storage Conditions: Improper storage conditions can significantly reduce seed viability and germination rate. Seeds should be stored in a cool, dry, and dark place.
It is important to consult with seed experts or refer to species-specific guidelines for interpreting germination rate results accurately.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways
The germination rate is a fundamental indicator of seed quality and a critical factor in various agricultural, horticultural, and ecological applications. Understanding the factors that influence germination rate, accurately calculating it, and implementing techniques to improve it are essential for maximizing crop yields, ensuring successful plant establishment, and restoring degraded ecosystems.
Key takeaways include:
- Germination rate is the percentage of seeds that successfully germinate under controlled conditions.
- Internal factors like seed viability and dormancy, and external factors like moisture, temperature, and oxygen, significantly influence germination rate.
- Standardized germination testing procedures ensure accurate and comparable results.
- Germination rate data is crucial for determining seeding rates, predicting crop establishment, and evaluating seed quality.
- Techniques like seed priming, scarification, and stratification can improve germination rate.
- Interpreting germination rate results requires considering species-specific requirements, seed age, and storage conditions.
By prioritizing seed quality and understanding the factors that affect germination rate, stakeholders can make informed decisions that lead to more sustainable and productive outcomes.