DNA sequencing is becoming increasingly important in various aspects of our lives, from personalized medicine to ancestry tracing. Ionic semiconductors are emerging as a promising technology to make DNA sequencing faster, cheaper, and more accessible. This article explores how you can apply knowledge about US patent applications related to DNA sequencing using ionic semiconductors in your daily life or work.
Understanding the Basics
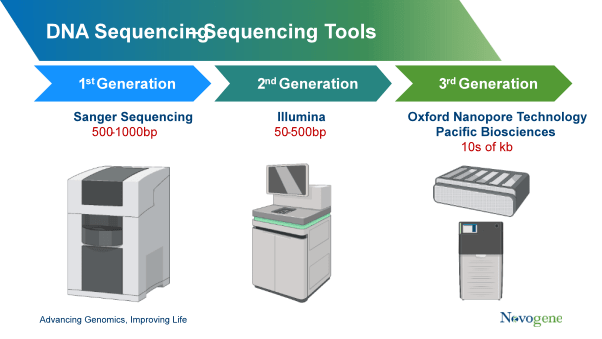
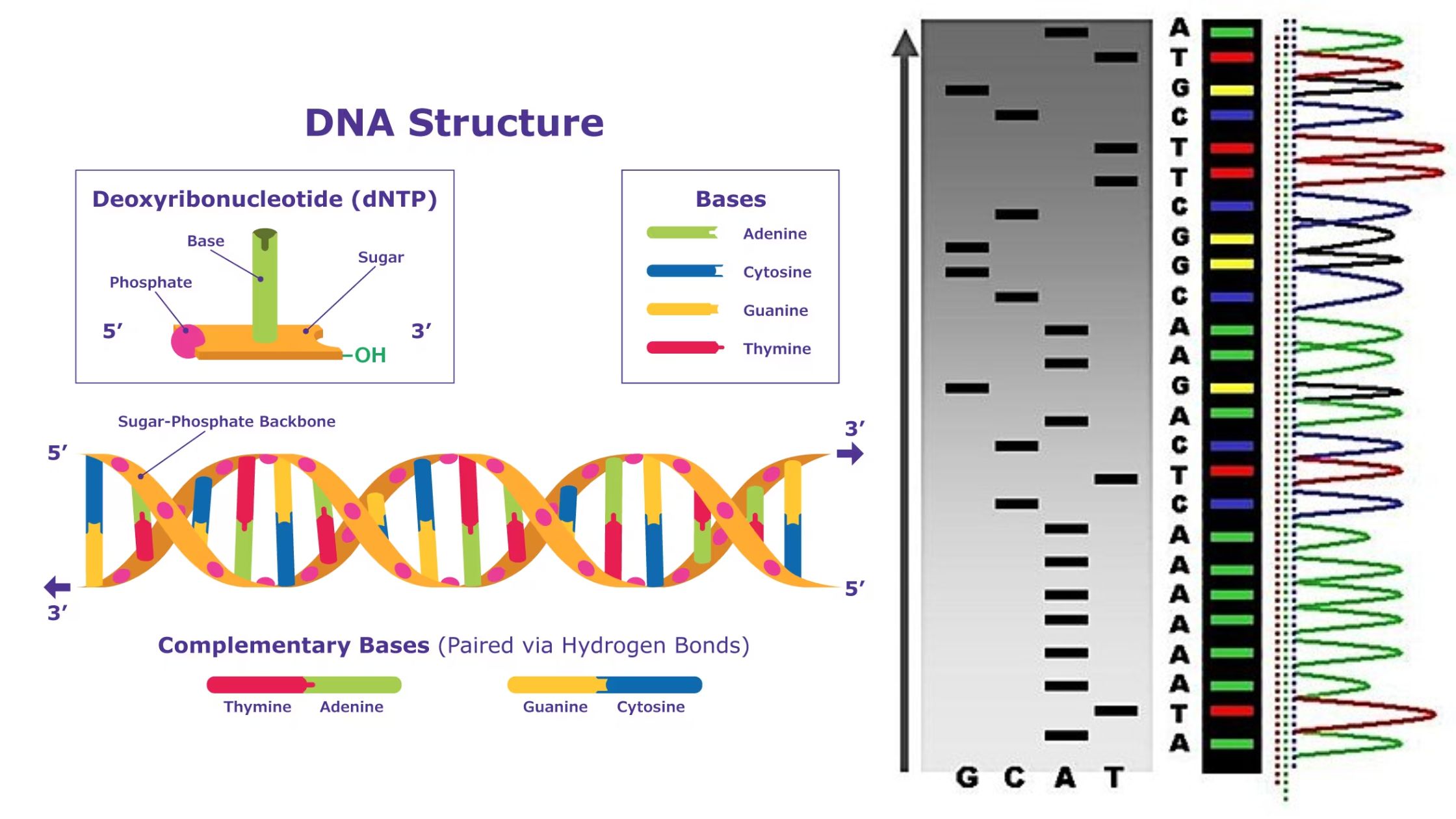
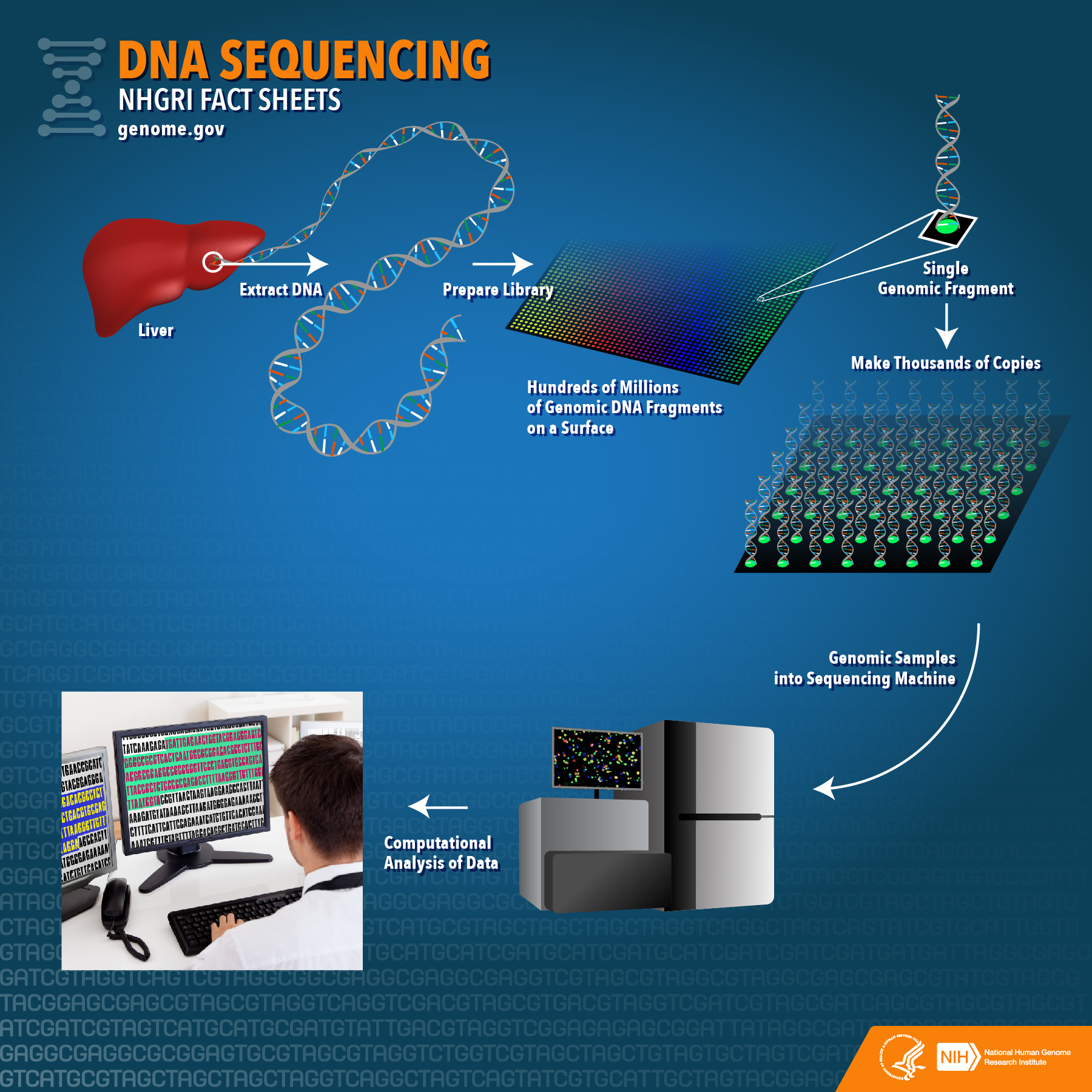
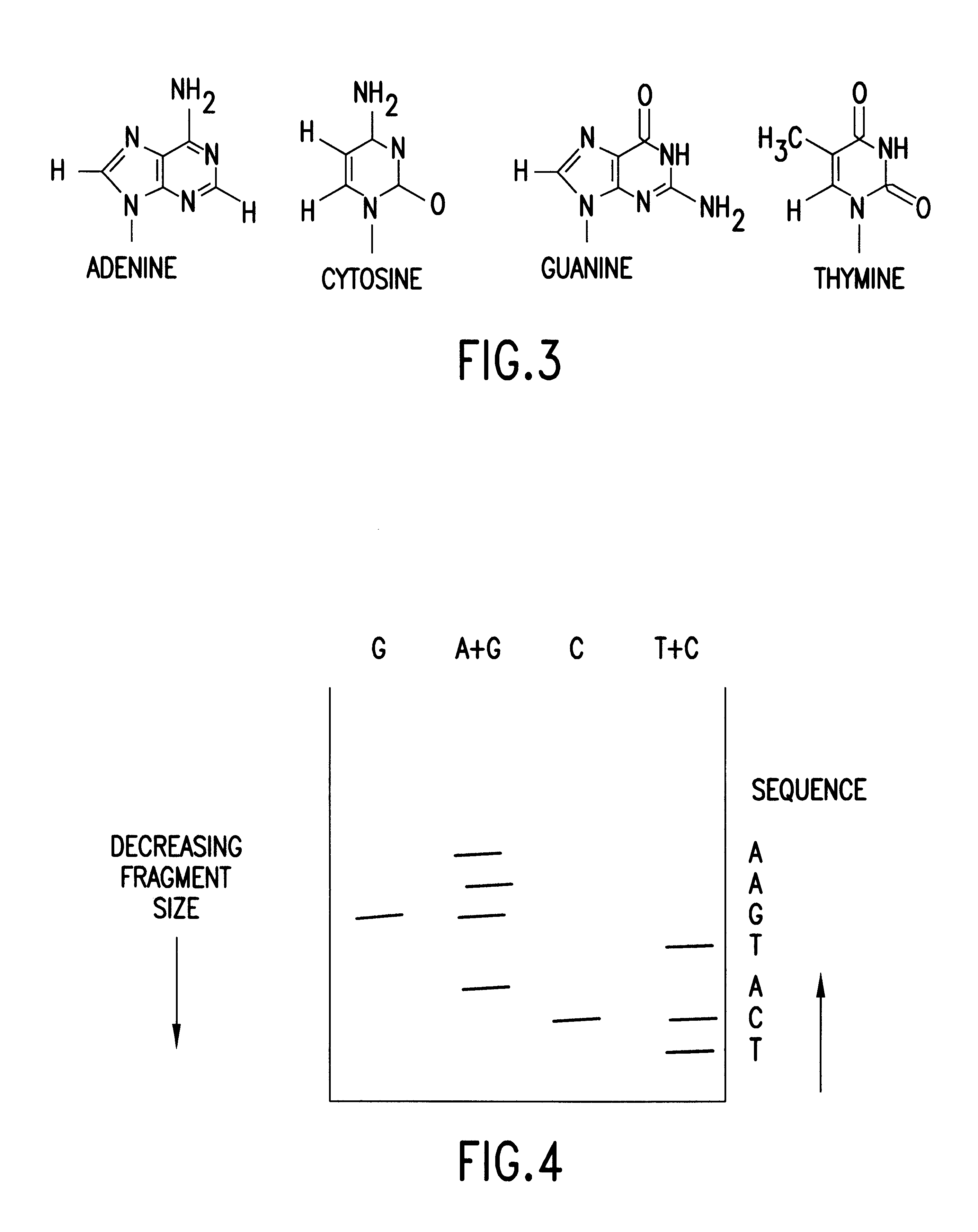
Before diving into practical applications, let's establish a fundamental understanding. DNA sequencing determines the precise order of nucleotide bases (Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine – A, G, C, T) in a DNA molecule. Traditional methods can be time-consuming and expensive. Ionic semiconductor sequencing, in contrast, relies on detecting changes in pH or ion concentrations as DNA polymerase incorporates nucleotides during sequencing. When a nucleotide is incorporated, a hydrogen ion (H+) is released, which is detected by an array of ion sensors built on a semiconductor chip.
US patent applications in this field provide valuable insights into the latest innovations, potential future products, and competitive landscape. Analyzing these patents can help you understand the technological advancements and identify potential opportunities.
Practical Applications in Daily Life
Personalized Medicine
Knowledge of DNA sequencing and related patents can empower you to engage more effectively with your healthcare provider. Here's how:
Understanding Genetic Reports: Many companies offer direct-to-consumer genetic testing. With some knowledge of DNA sequencing technologies and patents, you can better understand the underlying technology used to generate the reports and assess their accuracy and limitations. Look for patents citing specific ionic semiconductor technologies – this can indicate the testing platform used. Pay attention to the stated accuracy and error rates, which should be clearly documented and supported by scientific validation studies. For example, if a patent describes a specific method for error correction used by the testing company, it can provide more assurance.
Informed Discussions with Doctors: When discussing genetic predispositions or potential drug responses with your doctor, you can ask informed questions about the sequencing technology used in the relevant tests. Understanding the limitations of the technology can help you make better-informed decisions about treatment options. For instance, knowing whether a test uses ionic semiconductor sequencing versus another method can provide insights into its sensitivity and specificity for detecting specific genetic variants. Request information about the test's validation data and its ability to detect rare or novel mutations.
Actionable Tips:
- Research the genetic testing companies and their sequencing technologies. Look for published scientific papers or independent evaluations of their performance.
- Inquire about the specific patents associated with the sequencing technology used in your genetic test.
- Consult with a genetic counselor to interpret the results and understand their implications.
Ancestry Tracing
Ancestry tracing companies use DNA sequencing to estimate your ethnic origins and connect you with distant relatives. Here's how you can benefit from understanding the underlying technology:
Comparing Different Platforms: Different ancestry tracing companies use different sequencing platforms and algorithms. Understanding the differences can help you choose the platform that is most suitable for your needs. Look into the size of their reference databases, as a larger database can lead to more accurate ethnicity estimates and more potential matches. For example, one company might use a microarray-based approach, while another uses ionic semiconductor sequencing. Ionic semiconductor sequencing can often provide higher resolution and more detailed information, particularly in regions of the genome that are difficult to sequence with other methods.
Interpreting Ethnicity Estimates: Ethnicity estimates are based on comparing your DNA to reference populations. Understanding the limitations of these comparisons can help you interpret the results with caution. Remember that ethnicity estimates are not absolute and can vary depending on the reference populations used. Consider exploring multiple platforms and comparing the results to get a more comprehensive picture of your ancestry.
Actionable Tips:
- Read reviews and compare the features and services offered by different ancestry tracing companies.
- Investigate the sequencing technology used by each company and its accuracy.
- Consider uploading your raw DNA data to multiple platforms to maximize your chances of finding relatives and gaining insights into your ancestry.
Practical Applications in Your Work
Research and Development
If you are involved in research and development, understanding DNA sequencing and ionic semiconductor technology is crucial. Here's how you can apply this knowledge:
Identifying New Research Directions: By monitoring US patent applications, you can identify emerging trends and unmet needs in the field of DNA sequencing. This can help you develop new research projects or improve existing technologies. For example, you might identify a patent describing a novel method for reducing sequencing errors or improving the throughput of ionic semiconductor sequencing. This could inspire you to develop your own version of the technology or to build upon the existing patent.
Avoiding Patent Infringement: Before commercializing a new DNA sequencing technology, it is essential to conduct a thorough patent search to ensure that you are not infringing on existing patents. Understanding the scope of existing patents can help you design your technology in a way that avoids infringement. Consult with a patent attorney to assess the patent landscape and determine the freedom to operate.
Developing New Applications: Ionic semiconductor sequencing is finding applications in various fields, including diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and agriculture. By understanding the technology and its limitations, you can develop new applications that address specific needs in these fields. For example, you might develop a portable DNA sequencing device for detecting pathogens in water samples or for identifying crop diseases in the field.
Actionable Tips:
- Regularly search the US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) database for new patent applications related to DNA sequencing and ionic semiconductor technology.
- Attend conferences and workshops to learn about the latest advances in the field.
- Collaborate with experts in different fields to develop new applications for DNA sequencing technology.
Investment and Business Development
If you are involved in investment or business development, understanding DNA sequencing and ionic semiconductor technology can help you identify promising investment opportunities. Here's how:
Evaluating Investment Opportunities: When evaluating investment opportunities in DNA sequencing companies, it is crucial to understand the underlying technology and its competitive advantages. Look for companies with strong patent portfolios and innovative technologies. Assess the market potential for the company's products and services, and consider the regulatory landscape. For example, if a company has a patent on a highly accurate and cost-effective ionic semiconductor sequencing platform, it may be a promising investment opportunity.
Identifying Potential Partners: Understanding the patent landscape can help you identify potential partners for collaborations or acquisitions. Look for companies with complementary technologies or expertise. A company with a strong patent position in a specific area of DNA sequencing could be an attractive acquisition target. Consider the strategic fit of potential partners and the potential synergies that could be realized.
Actionable Tips:
- Conduct due diligence on companies involved in DNA sequencing and ionic semiconductor technology.
- Consult with experts in the field to assess the technical and commercial viability of investment opportunities.
- Monitor the competitive landscape and identify emerging trends.
Checklist/Guideline
- Stay Informed: Regularly check the USPTO website for new patent applications related to DNA sequencing and ionic semiconductors.
- Research Companies: When considering genetic testing or ancestry tracing, research the companies' sequencing technologies and their limitations.
- Seek Expert Advice: Consult with genetic counselors, patent attorneys, or other experts to gain a deeper understanding of the technology and its implications.
- Consider Multiple Sources: Don't rely on a single source of information. Compare results from different platforms and consult with multiple experts.
- Evaluate Accuracy: Always assess the accuracy and limitations of any DNA sequencing technology before making decisions based on its results.