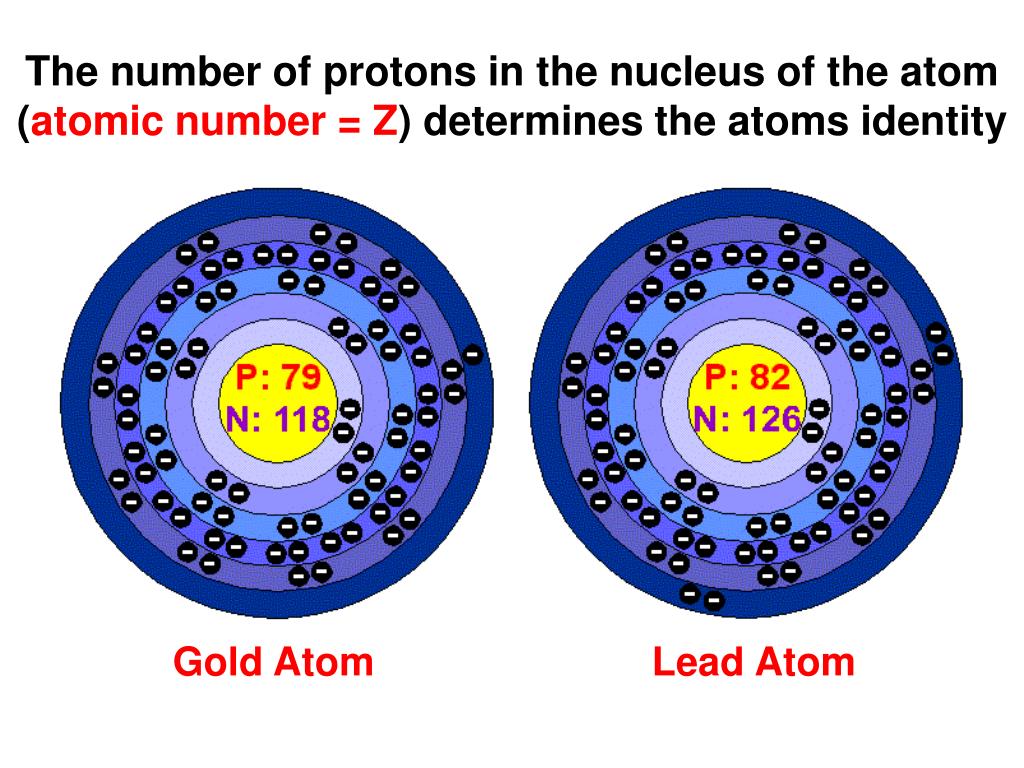
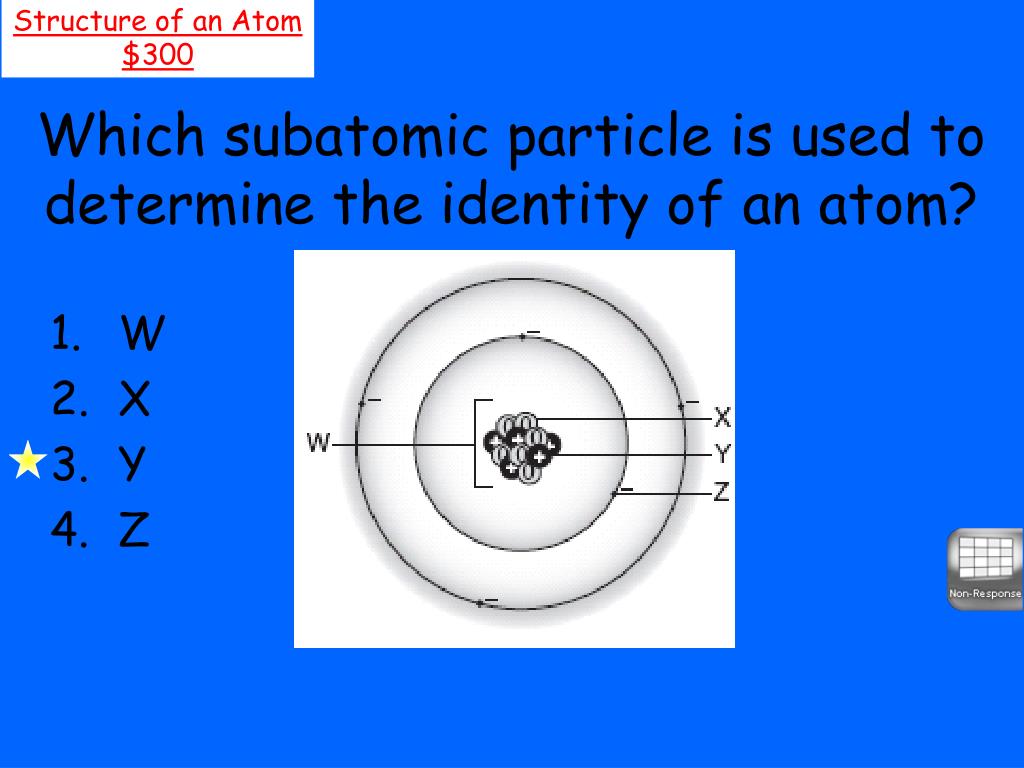
Hey there, science enthusiast! Ever wonder what makes a gold ring golden? Or why helium floats balloons? It all boils down to the fascinating world of atoms. But what gives each atom its unique identity? Let's dive in!
The Atomic ID Card: It's All About the Protons!
Imagine atoms as tiny, invisible Lego bricks. Each type of brick can only be combined with specific other types, resulting in countless unique structures. What makes each “brick” different? The number of protons!
Yep, protons are your atomic ID card. Think of it like this: a social security number for atoms. That number? It's the atomic number.
Protons: The Positive Power Players
Protons live in the nucleus, the atom's central core. They carry a positive charge. They're like the responsible citizens of the atom. They define what element it is.
Got one proton? You're hydrogen, the simplest element. Six protons? Hello, carbon, the backbone of life! Eight protons? Oxygen, essential for breathing. Each element has its own unique proton "signature."
Change the number of protons, and you change the entire element! It’s like changing your name and becoming a whole new person…atomically speaking.
Seriously, messing with the number of protons is nuclear alchemy! That's how you turn lead into gold... in theory! (Don’t try this at home, folks).
Neutrons: The Neutral Buddies
Now, let's meet the neutrons. These guys also hang out in the nucleus. They're neutral, meaning they have no electrical charge.
They're like the peacekeepers of the nucleus. They add to the atom's mass and contribute to nuclear stability. They're crucial, but don't define the element itself.
Atoms of the same element can have different numbers of neutrons. These are called isotopes.
Think of it like this: two apples are still apples, even if one is slightly bigger than the other. The number of protons defines that these are apples. The extra neutrons (the size difference) is what defines the isotope.
Carbon-12 and carbon-14 are isotopes of carbon. Carbon-12 is the most common. Carbon-14 is radioactive and used for dating ancient artifacts. Pretty cool, huh?
Electrons: The Energetic Orbiters
Finally, we have the electrons. These tiny particles whiz around the nucleus in orbits (or, more accurately, complex probability clouds). They carry a negative charge.
Electrons are the social butterflies of the atom. They interact with other atoms, forming chemical bonds. This is how molecules are made!
The number of electrons usually equals the number of protons. This makes the atom electrically neutral. But atoms can gain or lose electrons, becoming ions.
Ions are atoms with an electrical charge. If an atom loses electrons, it becomes positively charged (a cation). If it gains electrons, it becomes negatively charged (an anion).
Think of it like this: sodium chloride (table salt) is made of sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-). Opposites attract, forming the ionic bond that holds the salt crystal together.
The Magic Formula: Protons + Neutrons + Electrons = Atomic Awesome!
So, to recap, the identity of an atom is primarily determined by the number of protons. This is its atomic number. Neutrons contribute to its mass and isotope variations. Electrons govern its interactions with other atoms.
It's a beautiful dance of positive, negative, and neutral charges. These three particles combine to create the incredible diversity of elements that make up our universe.
Why Should You Care?
Okay, so maybe you're not planning on becoming a nuclear physicist. But understanding atomic structure is crucial for understanding… well, everything!
From the food you eat to the air you breathe, from the phone in your hand to the stars in the sky, it's all made of atoms. Understanding how these tiny particles work unlocks the secrets of the universe.
Plus, it's just plain cool! Think about it: everything you see and touch is made of these incredibly small, fundamental building blocks. It's mind-blowing!
Quirky Atomic Facts to Impress Your Friends
- Hydrogen is the most abundant element in the universe. It makes up about 75% of all normal matter.
- Helium was first discovered on the Sun before it was found on Earth. That's why it's named after the Greek word for Sun, "helios."
- Gold is so unreactive that it can be found in its pure form in nature. That's why it's been valued for centuries.
- The heaviest naturally occurring element is uranium. It's radioactive and used in nuclear power plants.
- The number of atoms in a grain of sand is more than the number of stars we can see in the night sky. Woah!
So, there you have it! A whirlwind tour of atomic identity. Hopefully, this has sparked your curiosity and inspired you to learn more about the amazing world of atoms.
Keep exploring, keep questioning, and keep having fun with science! After all, understanding the universe is the ultimate adventure.
And remember, it all starts with those tiny little building blocks: the atoms!