Understanding "Shorted" in the Context of Cart Batteries
The term "shorted" when applied to cart batteries, primarily those used in vaping devices, signifies a critical malfunction within the electrical circuit. Specifically, it indicates an unintended and often uncontrolled path for electricity to flow, bypassing the intended resistance and components of the device.
This is a serious condition that can lead to various negative consequences, ranging from device failure to potential safety hazards. It is crucial to accurately identify and address a short circuit to ensure the safe and efficient operation of a cart battery.
Defining a Short Circuit
In standard electrical circuits, current flows from the power source (the battery) through various components (such as the heating element in a vape cart) that offer resistance. This resistance controls the flow of current, ensuring that the circuit functions as designed. A short circuit occurs when this normal path is circumvented, creating a low-resistance pathway directly across the power source.
This bypass allows a significantly higher current to flow than intended. This excessive current flow can generate substantial heat, potentially damaging components, draining the battery rapidly, and posing a fire risk.
How a Short Circuit Occurs in Cart Batteries
Several factors can contribute to a short circuit in cart batteries, especially considering their compact and sometimes delicate construction:
- Physical Damage: Dropping the device or subjecting it to excessive pressure can damage internal wiring or components, causing them to come into contact inappropriately. This physical breach establishes a direct path for current.
- Liquid Ingress: E-liquid leaking from the cartridge can seep into the battery compartment and create a conductive path between terminals, especially if the liquid contains metallic particles.
- Manufacturing Defects: In rare cases, manufacturing flaws such as poorly insulated wires or improperly assembled components can predispose the device to short circuits.
- Overcharging: While less common with modern batteries that have overcharge protection, prolonged charging beyond the recommended time can damage the battery's internal structure and increase the risk of short circuits.
- Contamination: Debris, dust, or metallic particles entering the battery compartment or connecting points can also bridge the gap between circuits, creating a short.
Identifying a Shorted Cart Battery
Recognizing the signs of a shorted cart battery is vital for preventing further damage or potential hazards. Key indicators include:
- Rapid Battery Drain: The battery depletes much faster than usual, even without frequent use. This is a prime indicator of uncontrolled current flow.
- Overheating: The battery or the surrounding area becomes excessively hot to the touch, signaling significant energy dissipation due to the short circuit. Note: Some warming during normal use is expected, but excessive heat is a warning sign.
- No Activation: The device fails to power on or activate the heating element, despite being fully charged. The short circuit can prevent the battery from delivering power to the intended components.
- Burning Smell: A distinct burning odor emanating from the device is a clear indication of overheating and potential damage to internal components.
- Visible Damage: Physical damage, such as cracks, dents, or melted plastic, around the battery or connector, strongly suggests a possible short circuit event.
Troubleshooting a Suspected Short Circuit
If you suspect your cart battery is shorted, proceed with caution. The following steps outline a safe troubleshooting approach:
- Disconnect the Cartridge: Immediately detach the cartridge from the battery. This isolates the battery and prevents further damage from the cartridge (if the cartridge is the source of the short).
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine the battery and the cartridge connector for any signs of damage, liquid leakage, or debris. Use a magnifying glass if necessary.
- Clean Contacts: Gently clean the battery and cartridge connector with a dry cotton swab to remove any potential contaminants. Ensure the device is powered off or disconnected from the charger during cleaning.
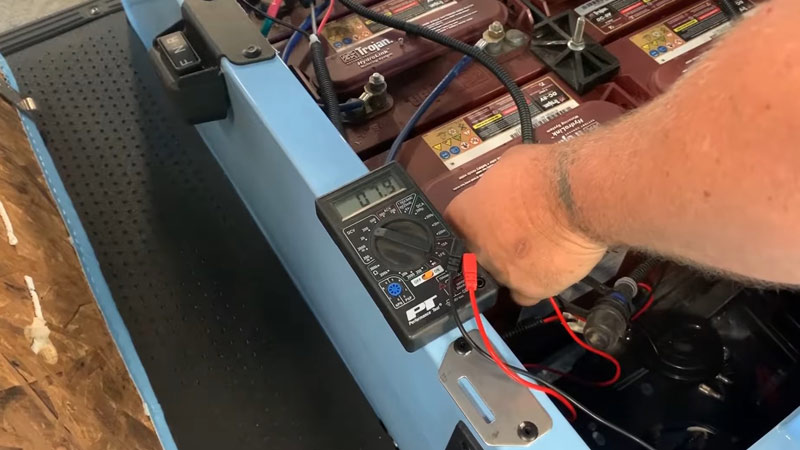
- Test with a Different Cartridge: If possible, try using the battery with a known working cartridge. If the issue persists, the problem likely lies within the battery itself.
- Charging Test: Attempt to charge the battery. If it fails to charge or heats up excessively during charging, it is almost certainly shorted and should not be used.
Safety Precautions
Dealing with a potentially shorted cart battery requires adherence to safety protocols:
- Do not attempt to disassemble the battery: Cart batteries contain lithium-ion cells, which can be dangerous if punctured, crushed, or exposed to air. Disassembly can lead to fire or explosion.
- Avoid contact with bare skin: If there is any visible damage or leakage, avoid direct contact with the battery's contents. If contact occurs, wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and water.
- Do not continue using the device: Continuing to use a suspected shorted battery is highly dangerous and can result in serious injury or property damage.
- Dispose of properly: Damaged or shorted lithium-ion batteries should be disposed of at a designated battery recycling facility or electronic waste collection point. Do not dispose of them in regular trash, as they pose a fire hazard.
The Role of Battery Management Systems (BMS)
Modern cart batteries often incorporate a Battery Management System (BMS), which is a small electronic circuit designed to protect the battery from overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits. While a BMS can provide a level of protection, it is not foolproof. In some cases, a severe short circuit can overwhelm the BMS, rendering it ineffective.
It is crucial to understand that a BMS is a safety feature, not a guarantee against all possible battery malfunctions.
Preventative Measures
While short circuits can sometimes be unavoidable, the following practices can minimize the risk:
- Use Reputable Brands: Opt for cart batteries from reputable manufacturers known for their quality control and adherence to safety standards.
- Handle with Care: Avoid dropping or subjecting the device to excessive force.
- Proper Storage: Store the battery in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures.
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the battery and cartridge connector regularly with a dry cotton swab to remove any potential contaminants.
- Avoid Overcharging: Follow the manufacturer's instructions regarding charging time and voltage. Do not leave the battery charging unattended for extended periods.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways
Recognizing and addressing a shorted cart battery promptly is essential for safety and device longevity. Remember these key points:
- A "shorted" cart battery indicates an unintended and uncontrolled path for electricity, bypassing normal resistance.
- Common causes include physical damage, liquid ingress, and manufacturing defects.
- Key signs include rapid battery drain, overheating, and failure to activate.
- Safety precautions are paramount: do not disassemble, avoid contact with bare skin, and dispose of properly.
- Preventative measures, such as using reputable brands and handling with care, can minimize the risk.
If you suspect a short circuit, immediately cease use and follow the troubleshooting steps outlined above. When in doubt, it is always best to err on the side of caution and replace the battery with a new one from a trusted source.