The CA 27-29 test measures the level of the CA 27-29 protein in your blood. This protein is a tumor marker, meaning it's often elevated in individuals with certain types of cancer, particularly breast cancer. However, it's crucial to understand that a high CA 27-29 level doesn't automatically mean you have cancer. It's just one piece of the puzzle that your doctor uses to assess your overall health.
Understanding "High" CA 27-29
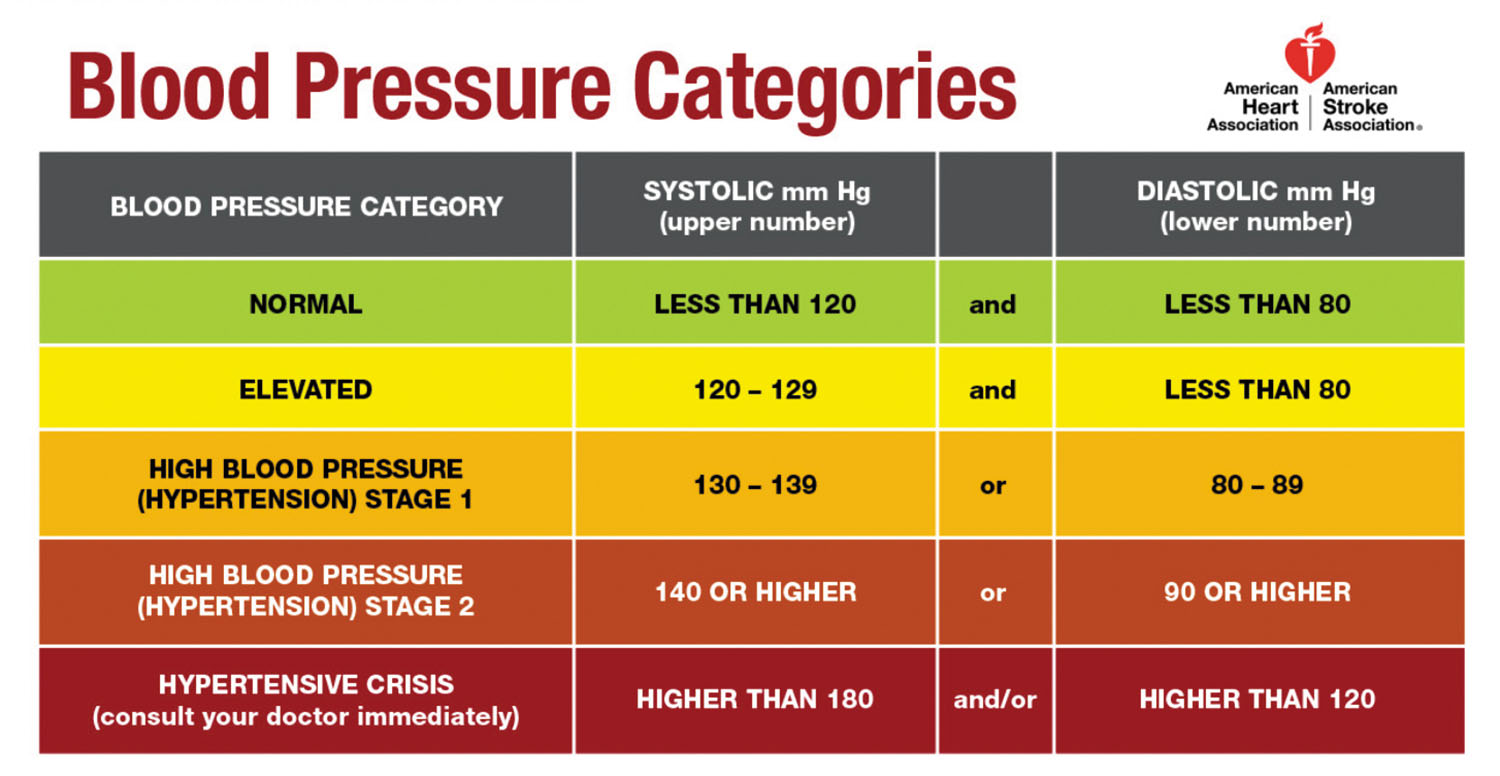
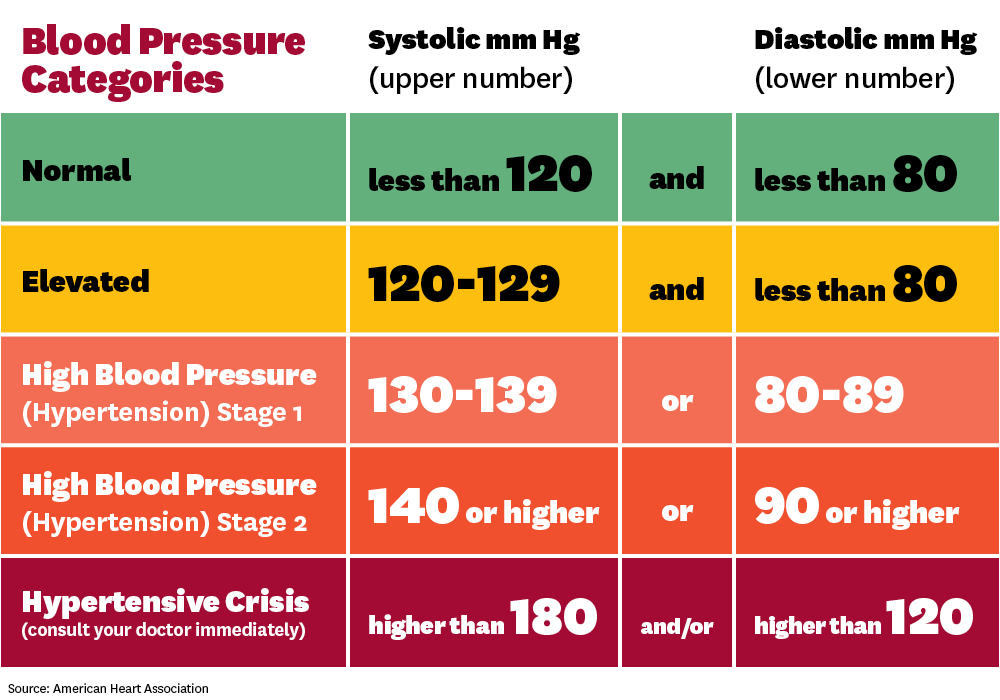
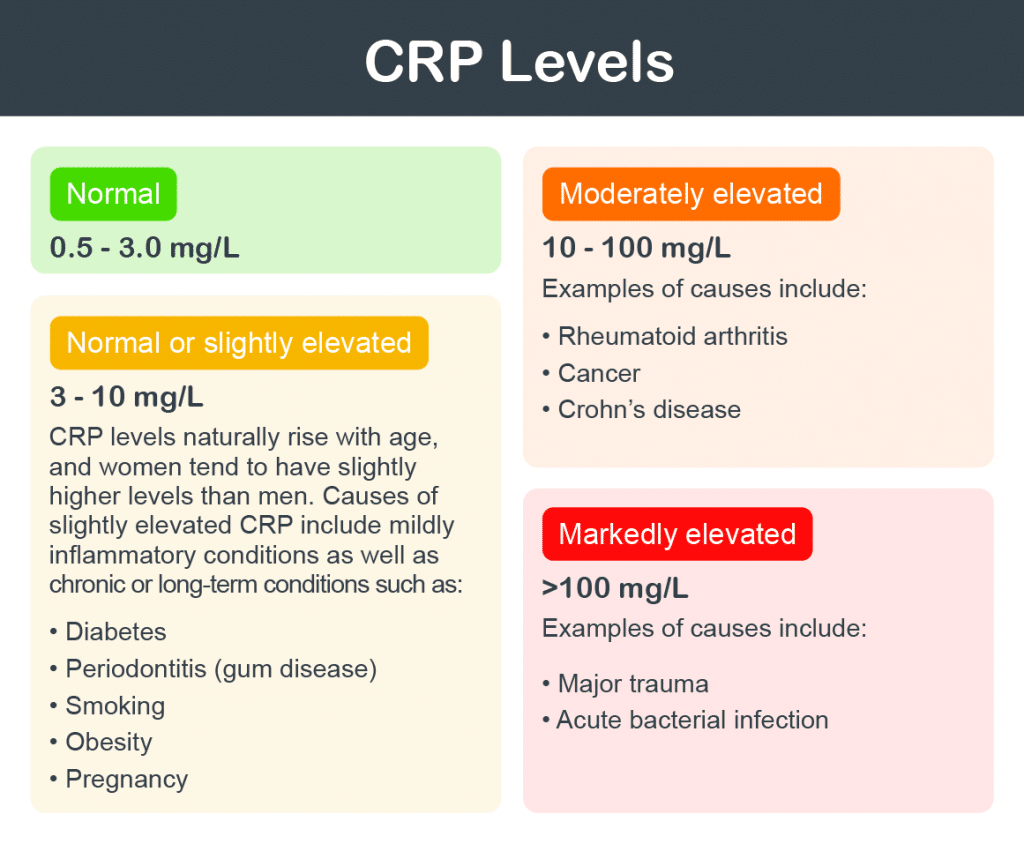
Laboratories establish their own reference ranges for CA 27-29, so what's considered "high" can vary slightly between labs. Generally, a CA 27-29 level above 38-40 U/mL (units per milliliter) is often considered elevated. Always refer to the specific reference range provided on your lab report. This reference range is specific to the testing methods and equipment used by that particular lab. Levels that fall outside of this reference range will be flagged on your report.
It's important to remember that a single high CA 27-29 reading is not a diagnosis. Several factors can influence CA 27-29 levels, including:
- Benign (non-cancerous) conditions: Liver disease, kidney disease, ovarian cysts, endometriosis, and benign breast conditions can sometimes elevate CA 27-29.
- Cancer (other than breast cancer): In rare cases, other cancers like lung, colon, or ovarian cancer may also raise CA 27-29 levels.
- Individual variations: Some perfectly healthy individuals may naturally have slightly higher CA 27-29 levels than others.
Practical Implications for Daily Life
If you've received a report indicating a high CA 27-29 level, here's how you can practically approach the situation:
1. Don't Panic, Consult Your Doctor:
This is the most crucial step. Your doctor is best equipped to interpret your results in the context of your medical history, physical examination, and other diagnostic tests. Avoid self-diagnosing or jumping to conclusions based solely on the CA 27-29 number.
2. Provide Complete Medical History:
Be prepared to share your comprehensive medical history with your doctor, including any past or present medical conditions, medications (prescription and over-the-counter), supplements, and family history of cancer. This information helps your doctor determine the potential cause of the elevated CA 27-29.
3. Understand the Purpose of the Test:
If you are currently undergoing treatment for breast cancer, understanding the purpose of the test is crucial. Is it to monitor treatment response? To detect recurrence? The context matters. If you are unsure, ask your doctor to clearly explain why the test was ordered.
4. Discuss Further Testing:
Your doctor may recommend further testing to investigate the cause of the elevated CA 27-29. This may include:
- Imaging tests: Mammograms, ultrasounds, MRIs, CT scans, or PET scans can help visualize the breasts and other organs to detect any abnormalities.
- Biopsy: If a suspicious area is found on imaging, a biopsy may be necessary to determine if it's cancerous.
- Other blood tests: Additional blood tests can help assess liver and kidney function, rule out other potential causes of elevated CA 27-29, and evaluate for other tumor markers.
5. Monitor CA 27-29 Trends (If Applicable):
If you've been diagnosed with breast cancer, serial CA 27-29 testing can be used to monitor treatment response. Rather than focusing on a single data point, it is the trend of the results that is most meaningful. A rising CA 27-29 level over time may indicate that the cancer is progressing or recurring, while a decreasing level may suggest that treatment is effective. Always discuss trends with your doctor.
6. Lifestyle Considerations:
While CA 27-29 levels themselves may not be directly influenced by lifestyle choices, maintaining a healthy lifestyle is generally beneficial for overall health and well-being, especially if you have a history of breast cancer.
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, red meat, and sugary drinks.
- Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity is linked to an increased risk of several cancers.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of breast cancer.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a known risk factor for many cancers.
7. Manage Stress:
Stress can impact your overall health. Explore stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature.
8. Be Proactive About Screening:
Follow your doctor's recommendations for breast cancer screening, including mammograms and clinical breast exams. Early detection is key to successful treatment.
9. Second Opinion:
If you are uncomfortable with your doctor's recommendations, consider seeking a second opinion from another oncologist.
Practical Tips for Those in Healthcare
For healthcare professionals, especially nurses, medical assistants, and physicians:
- Educate patients clearly: Explain what the CA 27-29 test is, what it measures, and what elevated levels *might* indicate. Emphasize that it's not a definitive cancer diagnosis and further investigation is usually needed.
- Be empathetic: Receiving news of an elevated tumor marker can be anxiety-provoking for patients. Approach the conversation with sensitivity and understanding.
- Accurate documentation: Ensure accurate and thorough documentation of patient history, medications, and relevant findings to aid in interpretation of results.
- Collaborate with other specialists: Work closely with oncologists, radiologists, and other specialists to provide comprehensive patient care.
- Stay updated: Continuously update your knowledge on cancer screening guidelines, tumor markers, and advancements in cancer treatment.
Checklist/Guideline After Receiving High CA 27-29 Results:
Here's a quick checklist to guide you:
- Schedule a follow-up appointment with your doctor. Don't delay.
- Gather your complete medical history, including medications and family history.
- Prepare a list of questions for your doctor.
- Undergo any recommended further testing, such as imaging or biopsy.
- Discuss the results of all tests with your doctor.
- Follow your doctor's recommendations for treatment or monitoring.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: diet, exercise, weight management, stress reduction.
- If you have a history of breast cancer, adhere to your follow-up schedule and screening recommendations.
- Communicate openly with your healthcare team.
Remember, a high CA 27-29 level warrants investigation, but it doesn't necessarily mean you have cancer. Working closely with your doctor and following their recommendations is crucial to determine the cause of the elevation and receive appropriate care.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cancer-antigen-2729-430607-Final-b8a7e5951fbc46c6ac049816b15f9d0e.jpg)



+is+secreted+if+Ca%2B2+levels+fall..jpg)