Ever been stuck behind a super slow driver in the fast lane? Or waited in line for what felt like an eternity at the grocery store, only to see the cashier painstakingly scan each item like they're deciphering ancient hieroglyphics? That, my friend, is a real-world demonstration of low throughput. And trust me, we've all been there. The opposite, smooth sailing on the highway or a speedy checkout, that’s high throughput in action.
What's Throughput Anyway? The "How Much Stuff Gets Done" Meter
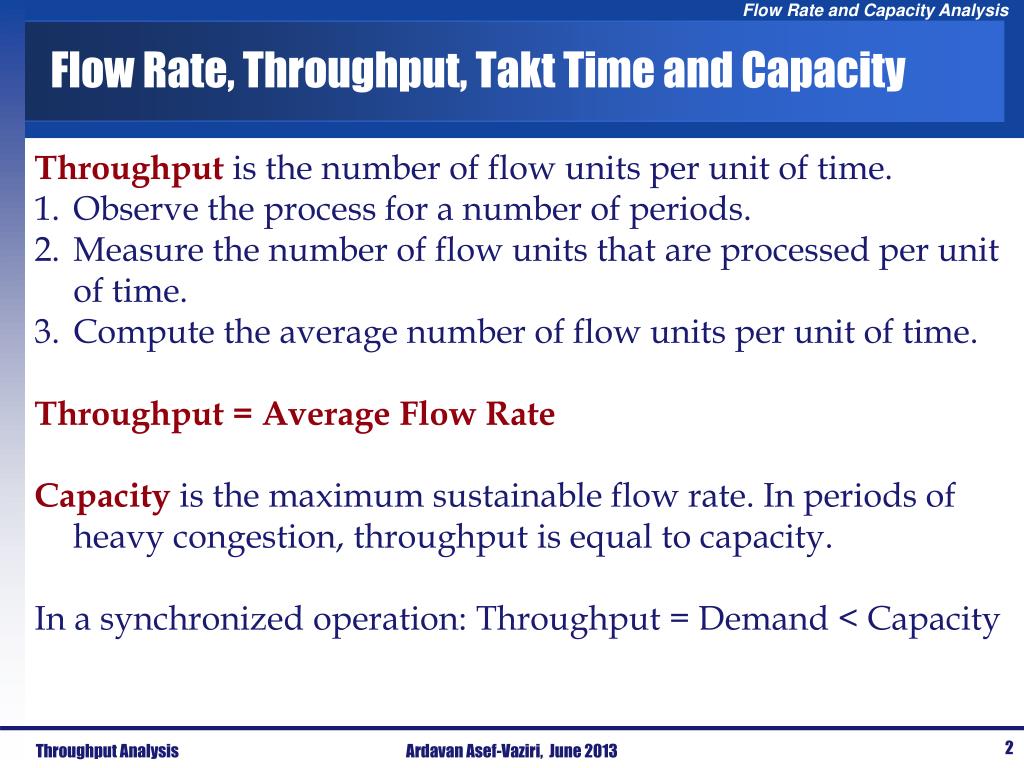
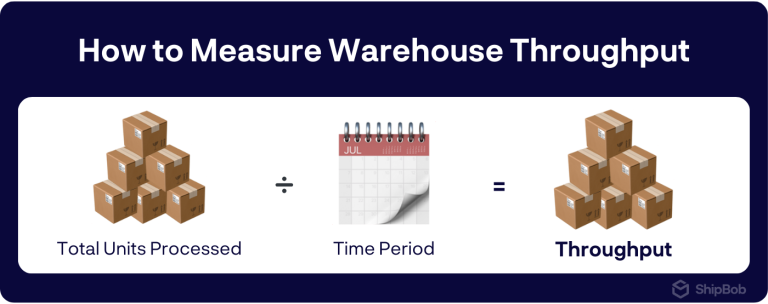
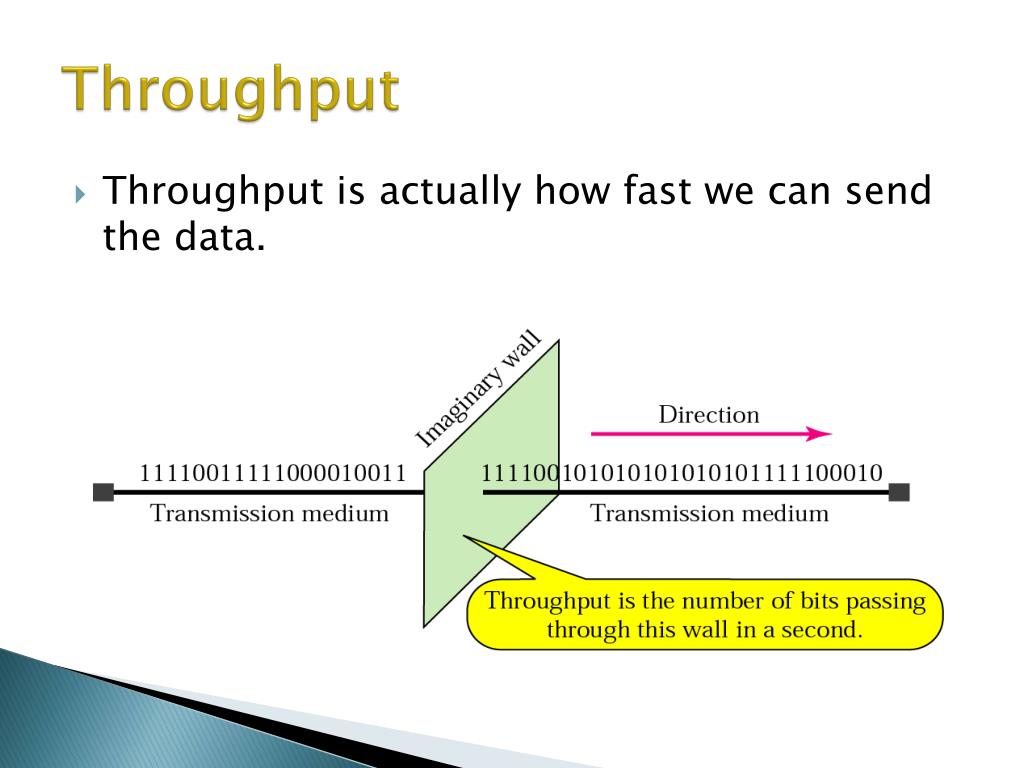
Okay, let’s break it down. Throughput, in its simplest form, is a measure of how much work gets done in a specific amount of time. Think of it like this: if you're baking cookies, throughput is how many cookies you can successfully churn out per hour. If you only manage 5 cookies an hour because your oven is ancient and you keep burning them, your throughput is pretty low. If you're cranking out 50 perfectly golden-brown cookies per hour, you’re rocking a high throughput.
It’s used *everywhere*, not just in baking. We're talking about computers, networks, manufacturing, call centers… basically, any system where things are processed. It’s a crucial metric for understanding efficiency and identifying bottlenecks. If throughput is low, something’s slowing things down. It's like having a clogged drain – the water's gotta go somewhere, but it's struggling to get through!
Beyond Cookies: Real-World Throughput Examples
Let's get a little more specific. Here are some examples of throughput in action, and why it matters:
- Computer Networks: Imagine you're streaming your favorite cat videos (who doesn't, right?). The throughput of your internet connection determines how smoothly that video plays. High throughput means no buffering, crystal-clear picture. Low throughput? Prepare for pixelation and frustrating pauses. We've all been there, staring blankly at the spinning wheel of doom, questioning our life choices. That's throughput slapping you in the face.
- Manufacturing: A factory producing widgets needs to maximize its throughput. How many widgets can they produce per day? High throughput equals more profit. Low throughput? Lost revenue and potential disgruntled customers. Picture a tiny hamster wheel powering a giant machine. That's your low-throughput factory. Now picture a well-oiled robot arm assembling widgets at lightning speed – that's high throughput!
- Call Centers: Call centers live and die by throughput. How many calls can an agent handle per hour? High throughput means shorter wait times for customers and a happier workforce. Low throughput? Angry customers on hold, and stressed-out employees. Imagine being stuck on hold, listening to that same awful elevator music for what feels like an eternity. That’s a throughput problem.
- Data Processing: Think about processing millions of credit card transactions after a big sale. The throughput of the data processing system determines how quickly those transactions can be authorized and processed. High throughput means minimal delays. Low throughput? Customers might abandon their carts, and the company loses money. Nobody wants to wait forever for a payment to go through, especially when that perfect pair of shoes is at stake!
Measuring Throughput: It's Not Rocket Science (But It Can Be Complex)
So, how do you actually measure throughput? Well, it depends on what you're measuring! The units of measurement will vary depending on the system:
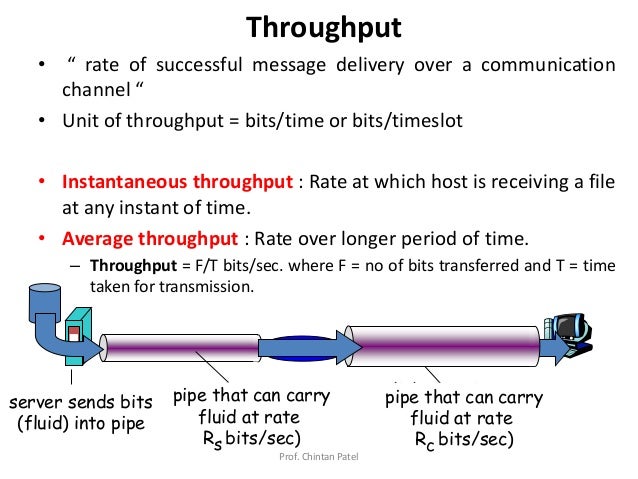
- Network Throughput: Often measured in bits per second (bps), kilobits per second (kbps), megabits per second (Mbps), or gigabits per second (Gbps). The higher the number, the faster the data is being transferred.
- Manufacturing Throughput: Measured in units per hour, units per day, etc.
- Call Center Throughput: Measured in calls per hour, calls per day, etc.
- Data Processing Throughput: Might be measured in transactions per second (TPS).
The *actual* calculation of throughput can be tricky. It's not just about theoretical maximums. You have to consider all sorts of real-world factors, like errors, delays, and overhead. Imagine a water pipe that can theoretically carry 100 gallons per minute. That's its capacity. But if the pipe is partially clogged with gunk, it might only actually carry 70 gallons per minute. That 70 gallons per minute is its *actual* throughput.
Factors That Impact Throughput: The Culprits Behind the Slowdown
So, what can cause low throughput? There are a whole bunch of potential culprits:
- Bottlenecks: A bottleneck is the slowest part of the system. It's like that one slow cashier holding up the entire grocery store line. Identifying and removing bottlenecks is crucial for improving throughput. Think of it as unclogging that drain!
- Resource Constraints: Not enough memory, processing power, bandwidth, etc. It's like trying to bake a hundred cookies with only one oven. You simply don't have the resources to handle the load.
- Inefficient Processes: Poorly designed workflows, unnecessary steps, or outdated technology can all slow things down. It's like using a horse-drawn carriage to deliver packages in the age of airplanes.
- Errors: Errors require retransmissions, reprocessing, or manual intervention, all of which reduce throughput. Think of it like baking a cake and realizing you forgot the sugar. Now you have to start all over again.
- Overhead: Every system has some overhead, which is the resources used for things other than the actual work. It's like the administrative tasks in a factory. Too much overhead can eat into your throughput.
Boosting Throughput: Speeding Things Up
Fortunately, there are ways to increase throughput! Here are a few common strategies:
- Identify and Eliminate Bottlenecks: This is the *most important* step. Find the slowest part of the system and fix it! Is your internet slow? Upgrade your plan or replace your router. Is your computer sluggish? Add more RAM or get a faster processor. Fix the clog!
- Increase Resources: Add more memory, processing power, bandwidth, etc. Give the system the resources it needs to handle the load. Buy another oven!
- Optimize Processes: Streamline workflows, automate tasks, and use more efficient technology. Upgrade from that horse-drawn carriage to an airplane!
- Reduce Errors: Implement error-checking mechanisms and improve quality control. Double-check your ingredients before baking that cake!
- Reduce Overhead: Streamline administrative tasks and eliminate unnecessary processes. Make sure your administrative processes aren't slowing down widget production.
- Load Balancing: Distribute the workload across multiple resources. It's like opening multiple checkout lanes at the grocery store.
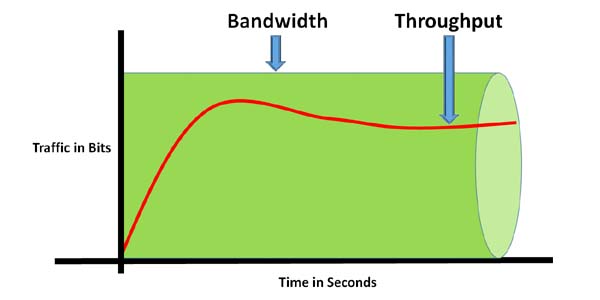
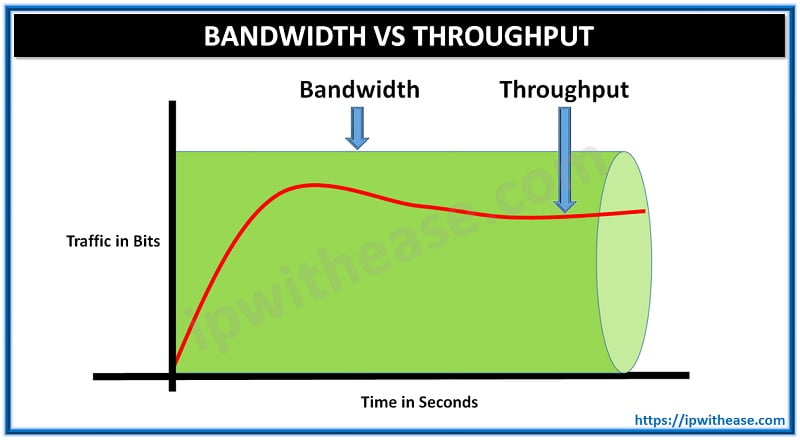
Throughput vs. Latency: They're Not the Same!
It's easy to confuse throughput with latency, but they're different things. Throughput is about how much gets done, while latency is about how long it takes to get something done. Imagine a highway. High throughput means lots of cars are passing through per hour. Low latency means each car can get from point A to point B quickly. You can have a highway with high throughput but also high latency if there are lots of cars but they're all stuck in traffic.
Think of it this way: throughput is like how many packages a delivery truck can carry, while latency is how long it takes the truck to deliver a single package. You could have a truck that carries a huge number of packages (high throughput), but it takes a long time to deliver each one because of traffic (high latency). Or you could have a smaller truck that delivers packages quickly (low latency), but it can't carry as many at once (low throughput).
Why Should You Care About Throughput? (It Affects Your Life!)
Okay, so you know what throughput is. But why should you actually care? Well, because it affects your daily life in countless ways, whether you realize it or not. A good understanding of throughput can help you make informed decisions, like:
- Choosing an Internet Provider: Look for an ISP that offers high throughput. You want to be able to stream videos, download files, and browse the web without frustrating delays.
- Upgrading Your Computer: If your computer is slow, upgrading components like the RAM or processor can improve throughput.
- Optimizing Your Home Network: A properly configured home network can improve throughput for all your connected devices.
- Understanding Website Performance: If a website is slow to load, it could be due to low throughput on the server.
- Making Business Decisions: Understanding throughput is crucial for optimizing business processes and improving efficiency.
In short, throughput is a key indicator of performance in many systems. By understanding what it is, how it's measured, and what factors affect it, you can make better decisions and improve your overall experience in a variety of areas. So, the next time you're waiting in a long line or struggling with a slow internet connection, remember the concept of throughput. Maybe, just maybe, understanding the *why* behind the delay will make it just a little bit less annoying. Or at least give you something to think about while you’re stuck on hold with that terrible elevator music. Happy throughput optimizing!



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/throughput.asp-final-00a8cf7eab8f40079ce8d5afcd355fa6.png)