Getting a good night's sleep is crucial for overall health, productivity, and well-being. While factors like stress and sleep environment play significant roles, your diet can also profoundly impact your sleep quality. Certain foods and beverages can disrupt your sleep cycle, making it harder to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. Understanding which foods to avoid, especially close to bedtime, can lead to more restful nights and improved daytime performance.
Caffeine-Rich Foods and Beverages
Caffeine is a stimulant that many people rely on to stay alert. It blocks adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and sleepiness. While coffee is the most well-known source of caffeine, it's also found in various other foods and drinks.
- Coffee: Avoid coffee for at least 6 hours before bedtime. The effects of caffeine can linger, making it difficult to fall asleep.
- Tea: Black and green teas also contain caffeine, although usually less than coffee. Be mindful of your tea consumption in the evening. Herbal teas are a caffeine-free alternative.
- Chocolate: Dark chocolate, in particular, contains caffeine and theobromine, another stimulant. Even milk chocolate has some caffeine, so it's best to avoid it before bed.
- Energy Drinks: These drinks are packed with caffeine and other stimulants. They are a definite no-no before bed.
- Soda: Many sodas contain caffeine. Check the labels and opt for caffeine-free versions in the evening.
- Certain Medications: Some over-the-counter pain relievers and cold medications contain caffeine. Read the labels carefully.
Practical Tip: Keep a caffeine journal to track your intake and its effects on your sleep. Gradually reduce your caffeine consumption, especially in the afternoons and evenings.
Alcohol
While alcohol might initially make you feel sleepy, it can disrupt your sleep cycle later in the night. It interferes with REM sleep, which is crucial for cognitive function and memory consolidation.
Alcohol can also lead to:
- Frequent awakenings: You're more likely to wake up during the night after consuming alcohol.
- Poor sleep quality: Alcohol reduces the restorative effects of sleep.
- Increased snoring: Alcohol relaxes throat muscles, potentially worsening snoring and sleep apnea.
Practical Tip: Avoid alcohol at least 3 hours before bedtime. If you do drink, do so in moderation and drink plenty of water to stay hydrated.
Spicy Foods
Spicy foods can cause heartburn and indigestion, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. The capsaicin in chili peppers can also raise your body temperature, which can disrupt your sleep.
Practical Tip: Limit spicy foods, especially in the evening. If you're prone to heartburn, avoid them altogether before bed.
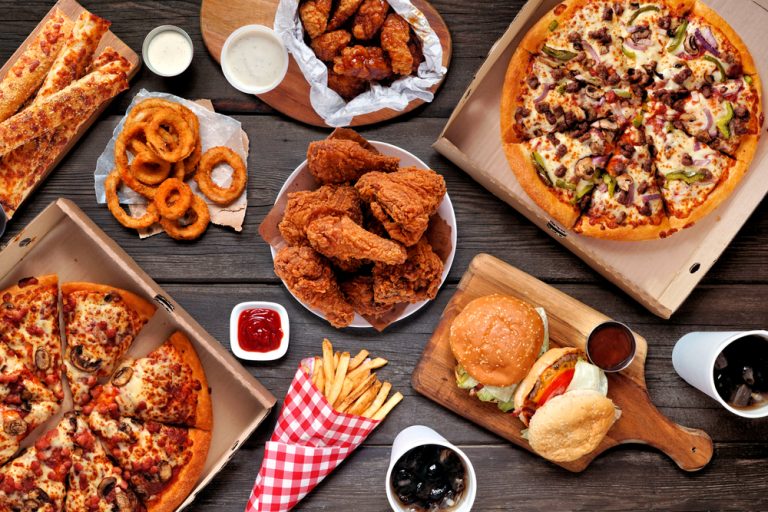
Fatty Foods
High-fat foods take longer to digest, which can lead to discomfort and disrupt your sleep. They can also trigger acid reflux.
Examples include:
- Fried foods
- Fast food
- Processed snacks
- Rich sauces and gravies
Practical Tip: Opt for lighter, easier-to-digest meals in the evening. Choose lean proteins, whole grains, and vegetables.
Sugary Foods
Consuming sugary foods before bed can lead to a rapid spike in blood sugar, followed by a crash. This can disrupt your sleep and cause awakenings during the night. Sugary foods also affect hormones that regulate sleep.
Examples include:
- Candy
- Cookies
- Cakes
- Sugary cereals
- Ice cream
Practical Tip: Avoid sugary snacks and desserts before bed. If you need a snack, choose something with protein and healthy fats, like a handful of almonds or a small piece of fruit with peanut butter.
Large Meals
Eating a large meal close to bedtime can put a strain on your digestive system and make it difficult to fall asleep. Your body will be focused on digesting the food instead of relaxing and preparing for sleep.
Practical Tip: Eat your last meal at least 2-3 hours before bed. Keep it light and easy to digest.
Foods High in Tyramine
Tyramine is an amino acid that stimulates the brain and can interfere with sleep. Certain foods are naturally high in tyramine.
Examples include:
- Aged cheeses (cheddar, parmesan, blue cheese)
- Cured meats (salami, pepperoni)
- Fermented foods (sauerkraut, kimchi)
- Smoked fish
Practical Tip: Be mindful of your intake of tyramine-rich foods, especially in the evening. Consider alternatives or eat them earlier in the day.
Hydration Habits
While staying hydrated is important, drinking too much fluid before bed can lead to frequent trips to the bathroom during the night, disrupting your sleep.
Practical Tip: Reduce your fluid intake in the 1-2 hours before bedtime. Empty your bladder before getting into bed.
Working Around Food Cravings
Sometimes, you get cravings right before bed, but before you reach for something unhealthy, consider these swaps:
- Instead of: Ice cream, Try: Frozen fruit or Greek yogurt with a drizzle of honey
- Instead of: Chips, Try: Air-popped popcorn with a sprinkle of nutritional yeast
- Instead of: Candy, Try: A small handful of mixed nuts and dried fruit
- Instead of: Pizza, Try: A whole-wheat English muffin with tomato sauce, veggies, and a sprinkle of cheese
Mindful substitutions can satisfy cravings without compromising sleep quality.
Applying This Knowledge in Your Daily Life/Work
Incorporating these dietary adjustments into your daily life and work routine can significantly improve your sleep. Here are some practical ways to do so:
- Meal Planning: Plan your meals in advance to ensure you're eating sleep-friendly foods in the evening. Prepare healthy snacks to avoid impulsive, unhealthy choices.
- Workplace Cafeteria: Be mindful of the options available in your workplace cafeteria. Choose healthier alternatives and avoid caffeine and sugary drinks in the afternoon.
- Business Travel: When traveling for work, be extra cautious about your food choices. Avoid late-night meals and alcohol at business dinners.
- Shift Work: If you work shifts, pay close attention to your eating schedule. Try to maintain a consistent meal pattern, even on off-days, to regulate your body clock.
- Stress Management: Stress can trigger cravings for unhealthy foods. Practice stress-reducing techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises to manage cravings and improve sleep.
Example Routine
Imagine you have a crucial presentation tomorrow. Instead of ordering takeout (pizza or fast food), you prepare a light, balanced meal of grilled chicken salad. You skip the afternoon coffee and opt for herbal tea. After dinner, you unwind with a book instead of watching TV and snacking on chips.
Sleep-Friendly Foods To Incorporate
While it's important to avoid sleep-disrupting foods, there are also foods that can promote better sleep:
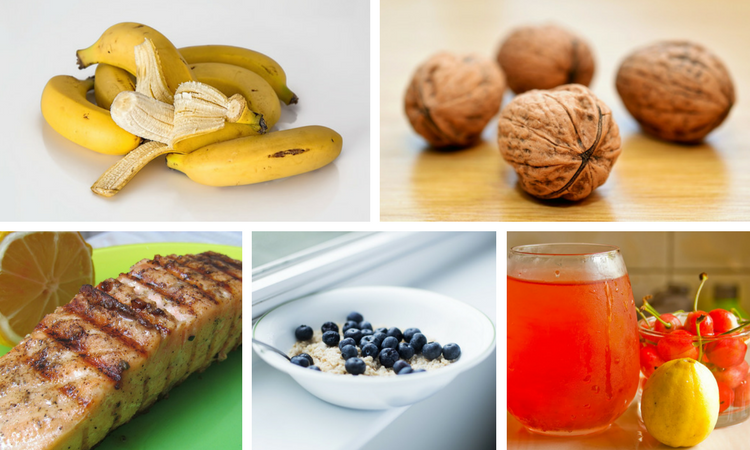
- Tart Cherries: Contain melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep.
- Almonds: A good source of magnesium, which promotes relaxation.
- Warm Milk: Contains tryptophan, an amino acid that can help you sleep.
- Chamomile Tea: Has calming properties.
- Kiwi: Rich in antioxidants and serotonin, which can improve sleep quality.
Incorporating these foods into your diet, especially in the evening, can help you achieve a more restful sleep.
Sleep-Friendly Food Checklist
Use this checklist to help you make better food choices for better sleep:
- [ ] Avoid caffeine for at least 6 hours before bedtime.
- [ ] Limit alcohol consumption, especially close to bedtime.
- [ ] Avoid spicy and fatty foods in the evening.
- [ ] Limit sugary snacks and desserts before bed.
- [ ] Eat your last meal at least 2-3 hours before bedtime.
- [ ] Be mindful of tyramine-rich foods.
- [ ] Reduce fluid intake in the 1-2 hours before bedtime.
- [ ] Incorporate sleep-promoting foods into your diet.