Understanding Equity and its Fluctuations
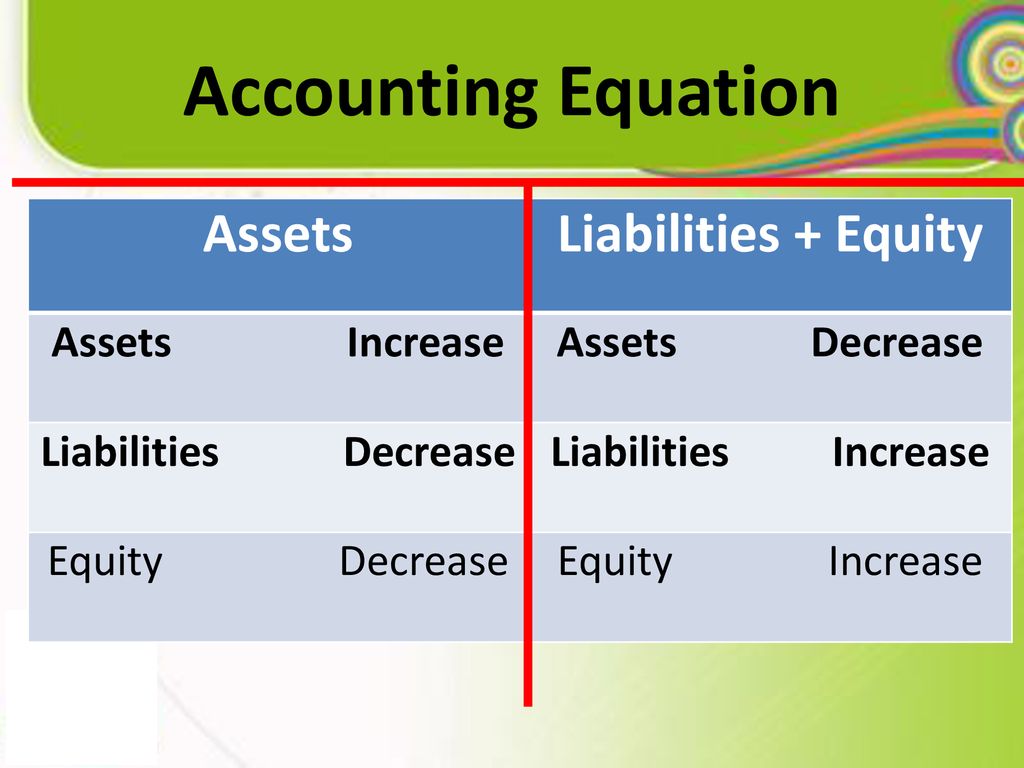
Equity, often referred to as shareholders' equity or owners' equity, represents the residual interest in the assets of an entity after deducting its liabilities. It's essentially the net worth of a business. A healthy equity position is crucial for financial stability and long-term growth. However, various factors can erode or decrease equity, impacting a company's financial health.
Key Factors Decreasing Equity
Several events and accounting entries can lead to a decrease in equity. The most common include:
- Net Losses
- Dividends Paid to Shareholders
- Treasury Stock Purchases
- Distributions to Owners (for non-corporate entities)
- Certain Accounting Adjustments
Let's examine each of these in detail.
Net Losses: A Primary Driver of Equity Reduction
A net loss occurs when a company's total expenses exceed its total revenues over a specific accounting period. This is directly reflected in the retained earnings account, which is a component of equity. When a net loss is incurred, retained earnings decrease, consequently reducing overall equity. A prolonged period of net losses can severely deplete equity, potentially leading to financial distress.
For example, if a company has $1,000,000 in retained earnings at the beginning of the year and experiences a net loss of $200,000 during the year, its retained earnings will decrease to $800,000, directly reducing equity by $200,000.
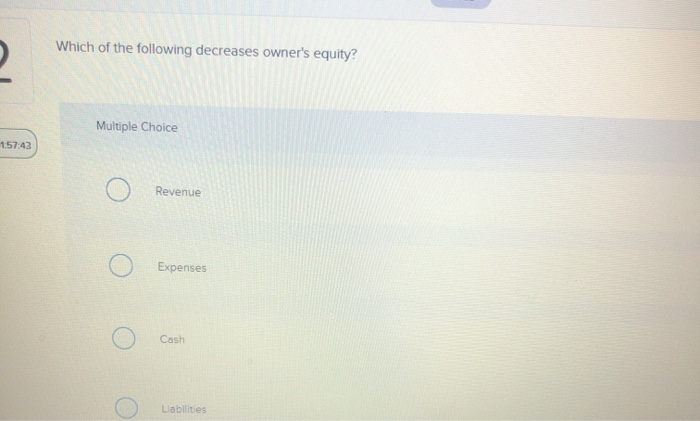
Dividends: Distributing Profits, Reducing Equity
Dividends represent a distribution of a company's accumulated profits to its shareholders. While dividends are attractive to investors, they directly reduce retained earnings, which in turn lowers equity. Paying dividends is a financial decision that companies weigh carefully, balancing shareholder expectations with the need to reinvest profits for future growth.
Consider a company with $5,000,000 in retained earnings that declares a dividend of $500,000. After the dividend is paid, retained earnings will be reduced to $4,500,000, decreasing equity by the same amount. It is crucial to note that declared but unpaid dividends are recognized as a liability, not an immediate reduction in equity. The reduction occurs upon actual payment of the dividend.
Treasury Stock: Repurchasing Shares, Impacting Equity
Treasury stock refers to shares of a company's own stock that it has repurchased from the open market. This reduces the number of outstanding shares and is accounted for as a reduction in equity. The repurchase price is used to reduce the treasury stock account, which is a contra-equity account.
For instance, if a company initially issued 1,000,000 shares and later repurchases 100,000 shares as treasury stock, the equity section of the balance sheet will reflect a reduction equivalent to the cost of repurchasing those shares. The repurchase doesn't 'destroy' the value; it shifts it. The cash is used to buy the shares, so the cash account decreases, and the treasury stock (a contra-equity account) increases. The net effect is a decrease in equity.
Distributions to Owners (Non-Corporate Entities)
For businesses that are not corporations, such as partnerships or sole proprietorships, owners may withdraw funds from the business for personal use. These distributions to owners are similar to dividends in that they represent a return of capital to the owners and reduce the owner's equity in the business.
For example, if a partner withdraws $50,000 from the partnership's capital account, the partnership's equity will decrease by $50,000. This withdrawal is not an expense; it's a direct reduction in the owner's investment in the business.
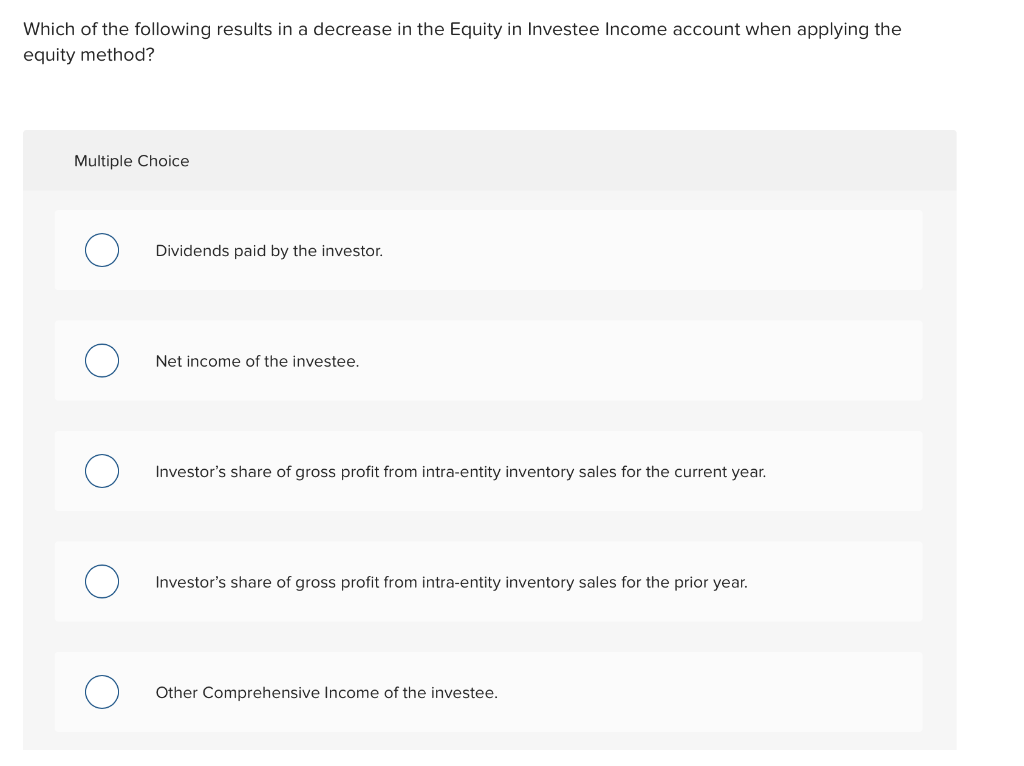
Accounting Adjustments: Other Comprehensive Income (OCI) Impacts
Certain accounting adjustments, specifically those related to Other Comprehensive Income (OCI), can also decrease equity. OCI includes items that are not recognized in net income but are reported separately and accumulate in equity. Examples include:
- Unrealized losses on available-for-sale securities
- Foreign currency translation adjustments
- Certain pension adjustments
When these items result in losses, they reduce accumulated other comprehensive income, which in turn reduces overall equity. Conversely, gains within OCI would increase equity. The impact of OCI can be complex and often requires a deeper understanding of accounting standards.
For example, a company holding available-for-sale securities may experience a decline in their market value. This unrealized loss is not recognized in net income but is recorded in OCI, leading to a decrease in equity until the securities are sold.
Additional Considerations
While the above are the most common causes of equity decrease, other less frequent events can also have a negative impact:
- Write-downs of assets: If an asset's value is deemed to be impaired, a write-down is necessary, which results in an expense on the income statement (leading to a net loss) and a reduction in the asset's carrying value on the balance sheet.
- Settlement of liabilities: While generally a decrease in a liability is positive, if the settlement requires a greater payment than the recorded liability (e.g., due to litigation), the difference is expensed, leading to a net loss.
- Changes in accounting principles: Retrospective application of new accounting standards can sometimes require adjustments to retained earnings, potentially decreasing equity.
It's important to analyze the specific circumstances to fully understand the impact of each event on equity.
The Importance of Monitoring Equity
Tracking changes in equity is crucial for understanding a company's financial performance and solvency. A consistent decline in equity can signal underlying problems, such as poor profitability, excessive dividend payouts, or inefficient capital management. Lenders and investors closely monitor equity to assess the risk associated with lending to or investing in a company.
"Equity is the lifeblood of a company. Managing it effectively is critical for sustainable growth and long-term success."
Conclusion: Key Takeaways Regarding Decreases in Equity
In summary, the following events consistently decrease equity:
- Net Losses: The most direct and significant factor reducing retained earnings and overall equity.
- Dividends Paid: Distributions of accumulated profits to shareholders.
- Treasury Stock Purchases: Repurchasing a company's own shares.
- Distributions to Owners: Withdrawals of capital by owners in non-corporate entities.
- Certain Accounting Adjustments (OCI): Losses recorded in Other Comprehensive Income.
Careful monitoring and analysis of equity trends are essential for maintaining financial stability and ensuring the long-term health of a business. Understanding the factors that can decrease equity allows management to make informed decisions about profitability, capital allocation, and shareholder distributions.
Understanding these decreases in equity requires a close examination of the balance sheet and related financial statements. Analyzing the causes and magnitude of the reductions is crucial for understanding a company's financial health and strategic direction.