Identifying facial bones is a foundational element of anatomy, relevant in fields ranging from medical imaging to forensic science. To accurately determine which option from a list constitutes a facial bone requires a solid understanding of the skeletal structure of the face.
Understanding the Facial Skeleton
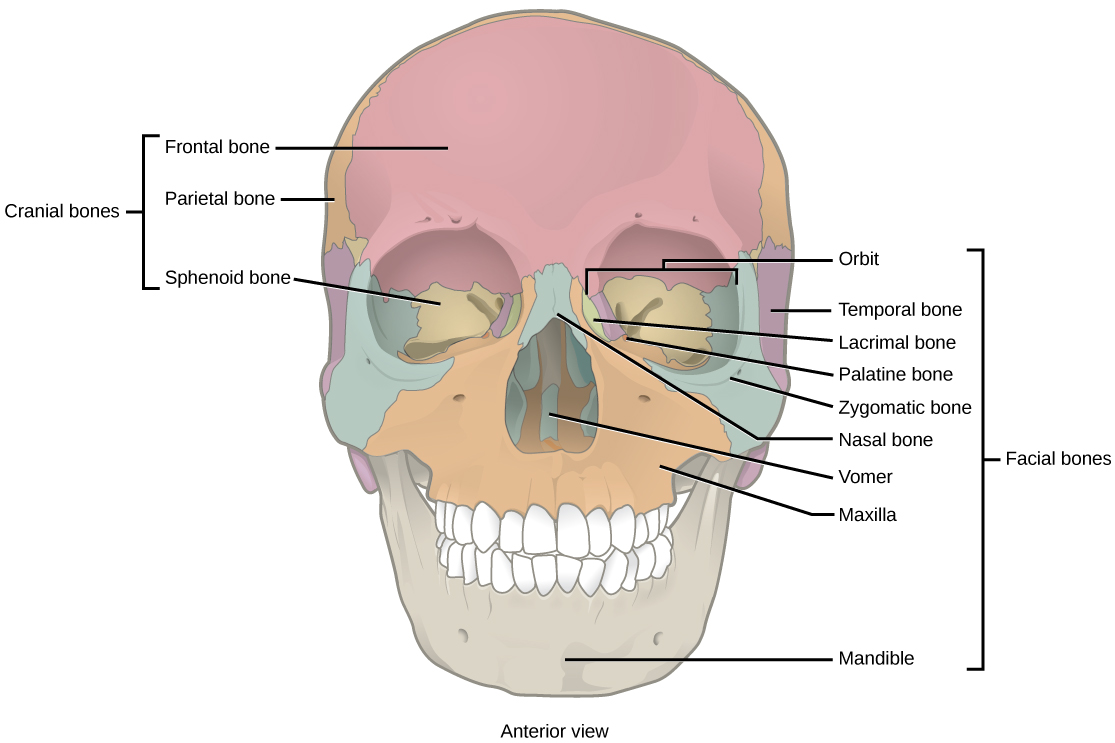
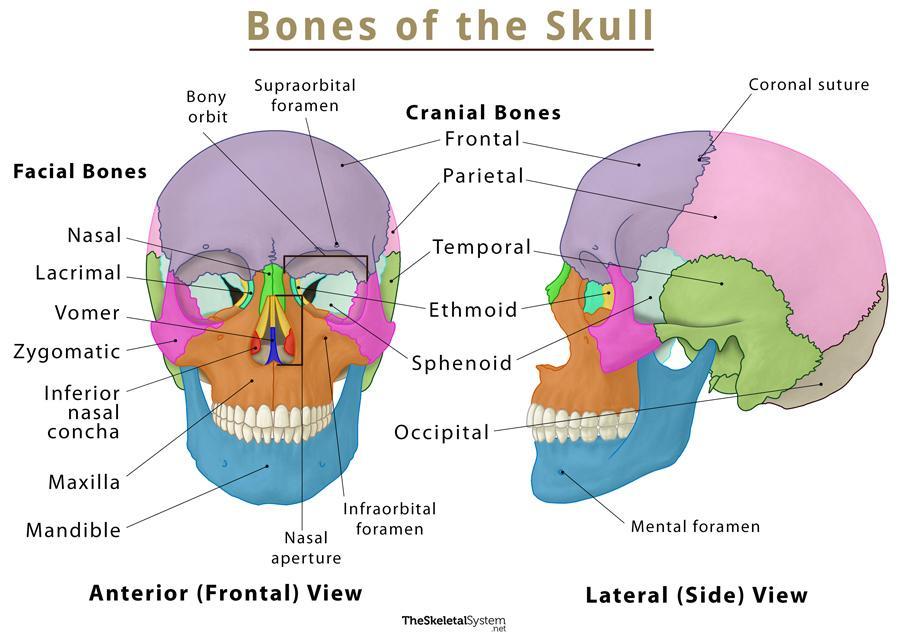
The human skull is comprised of two main parts: the cranium and the facial skeleton. The cranium, or neurocranium, encases and protects the brain. The facial skeleton, or viscerocranium, forms the structure of the face and supports the sensory organs.
Key Components of the Facial Skeleton
The facial skeleton is composed of several bones, each with specific functions and locations. Understanding these individual bones is crucial for accurate identification.
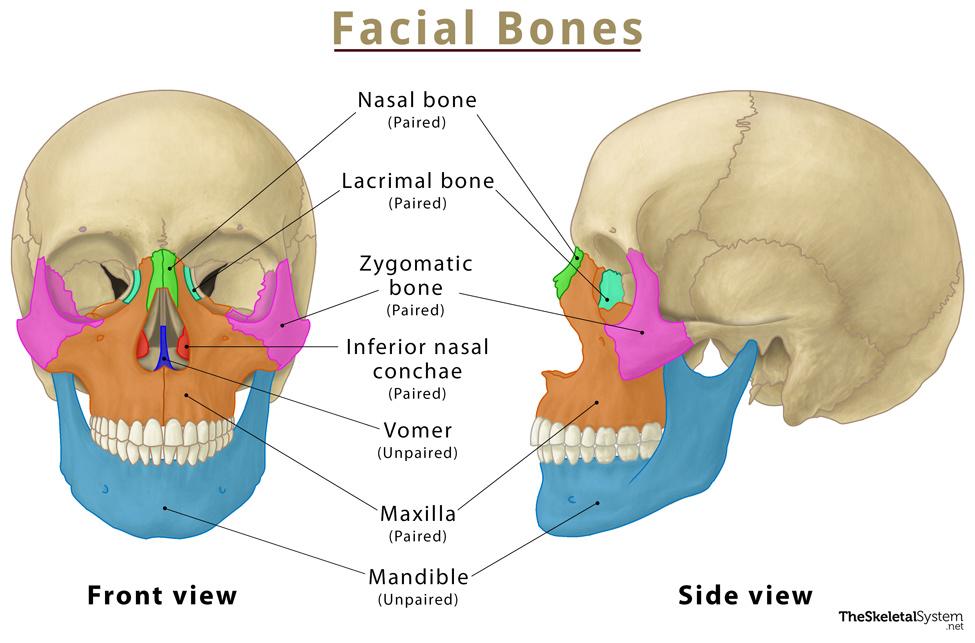
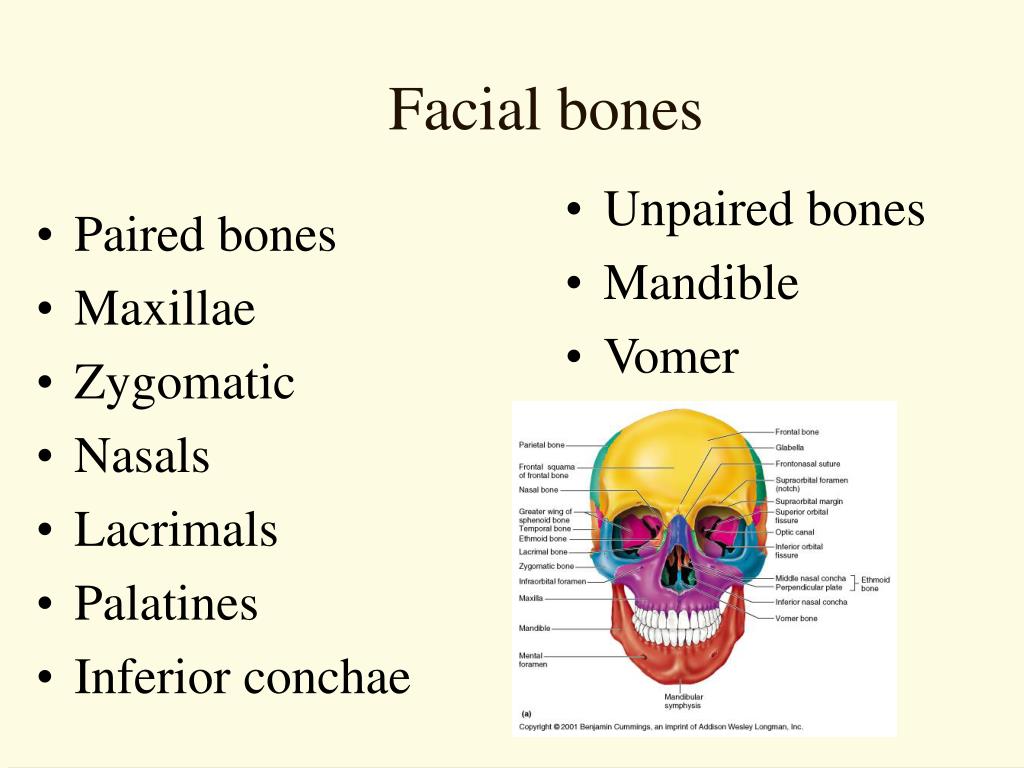
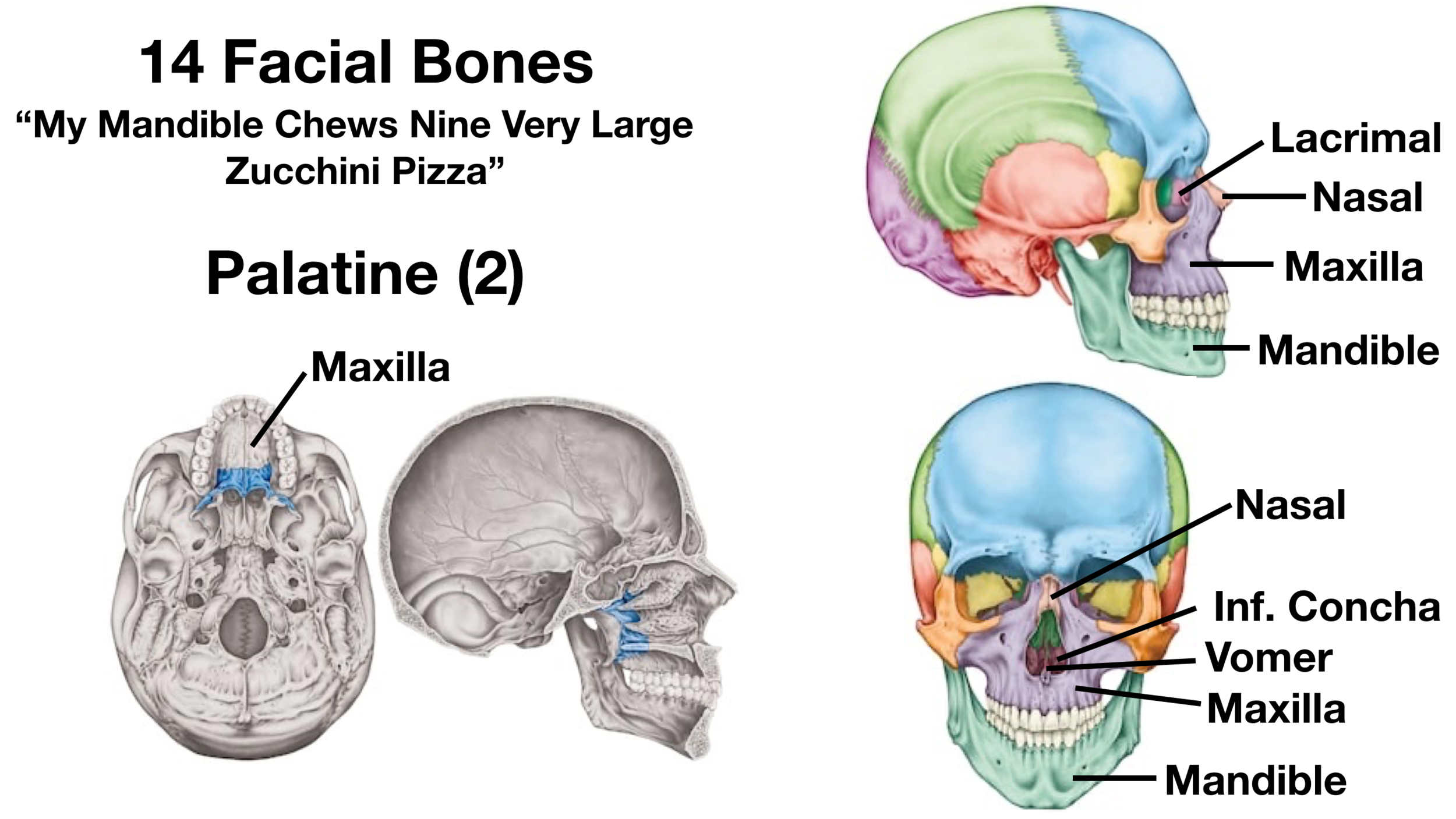
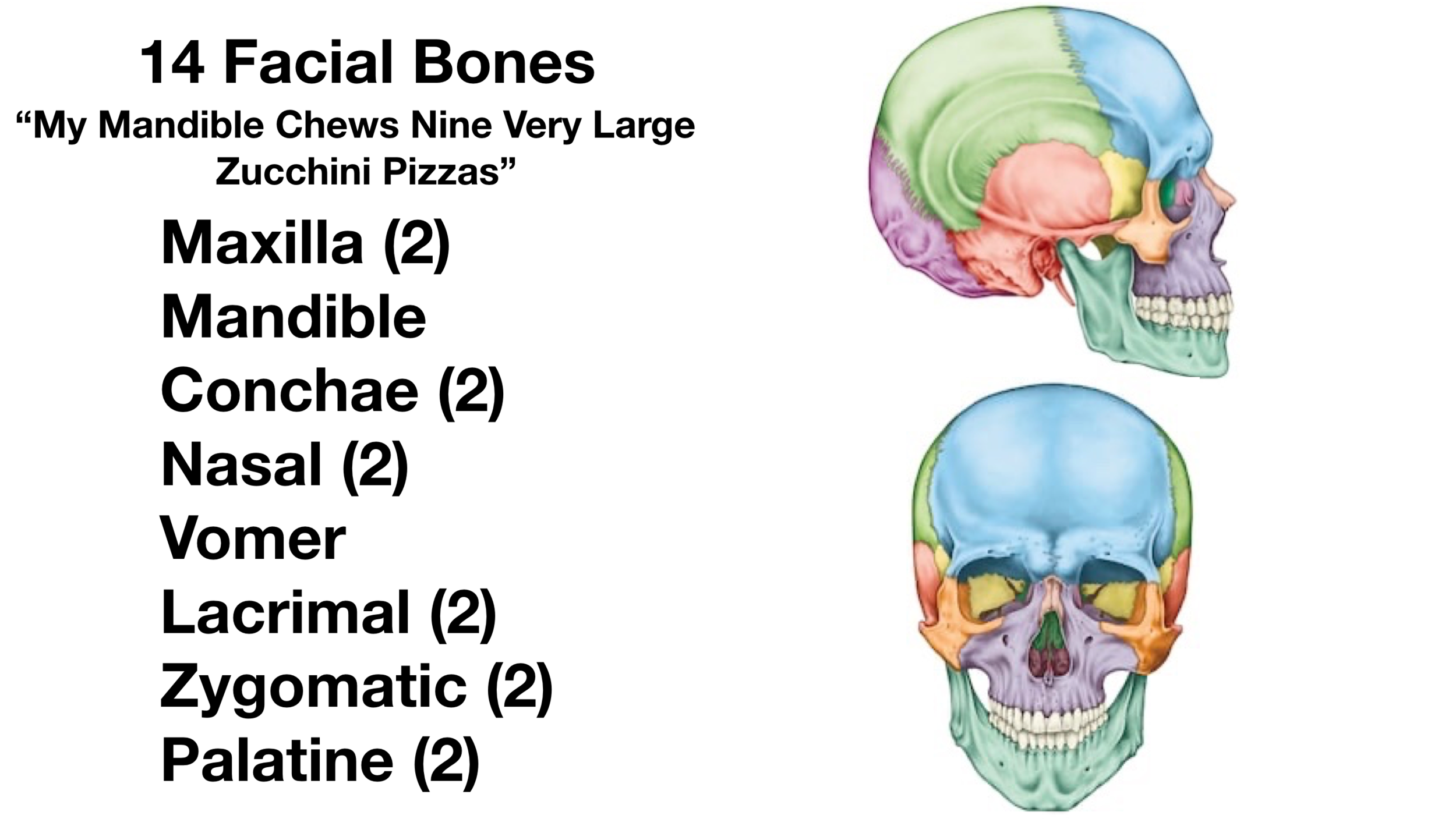
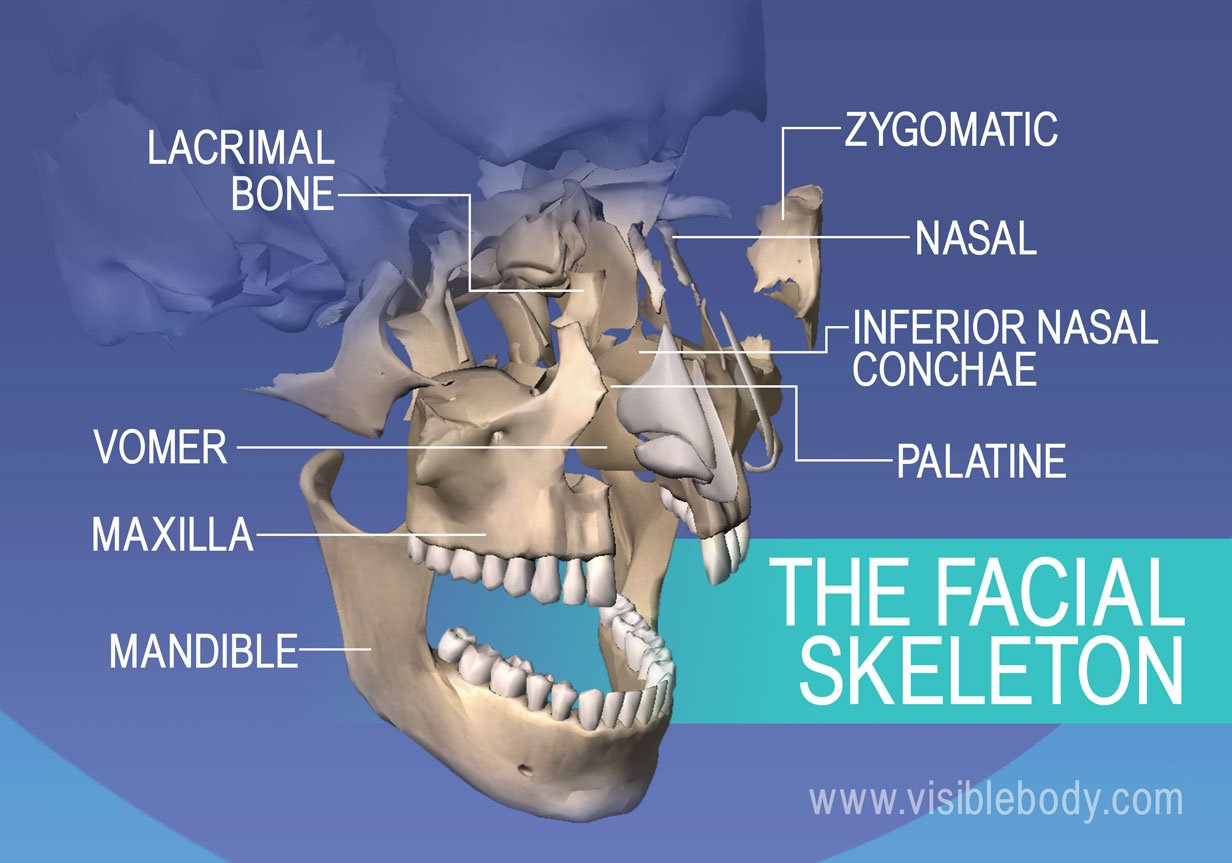
- Maxilla (Maxillae): These paired bones form the upper jaw, contribute to the hard palate, and house the upper teeth. They also form part of the nasal cavity and the orbit of the eye.
- Mandible: The mandible is the only movable bone in the skull and forms the lower jaw. It houses the lower teeth and provides attachment points for muscles involved in chewing and facial expression.
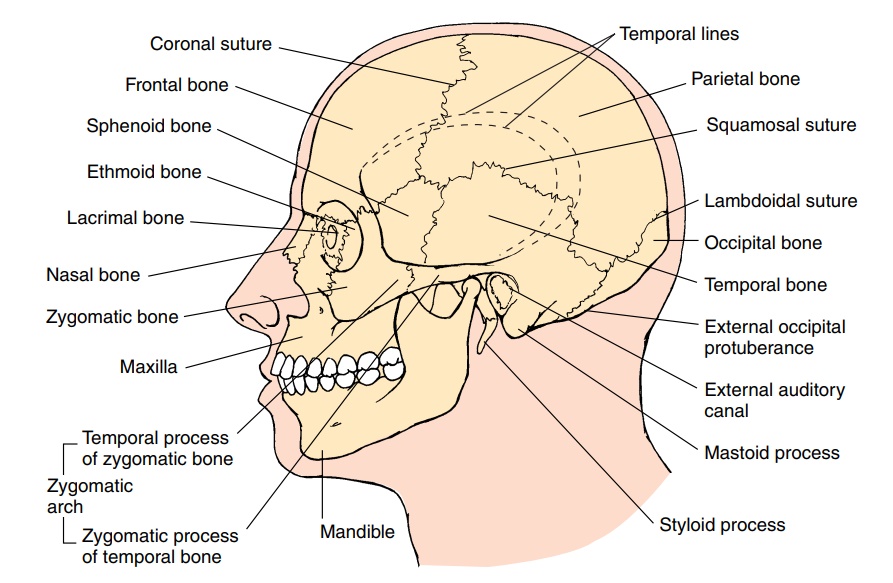
- Nasal Bones: These small paired bones form the bridge of the nose.
- Zygomatic Bones: Commonly known as the cheekbones, these paired bones form the prominence of the cheeks and contribute to the lateral wall of the orbit.
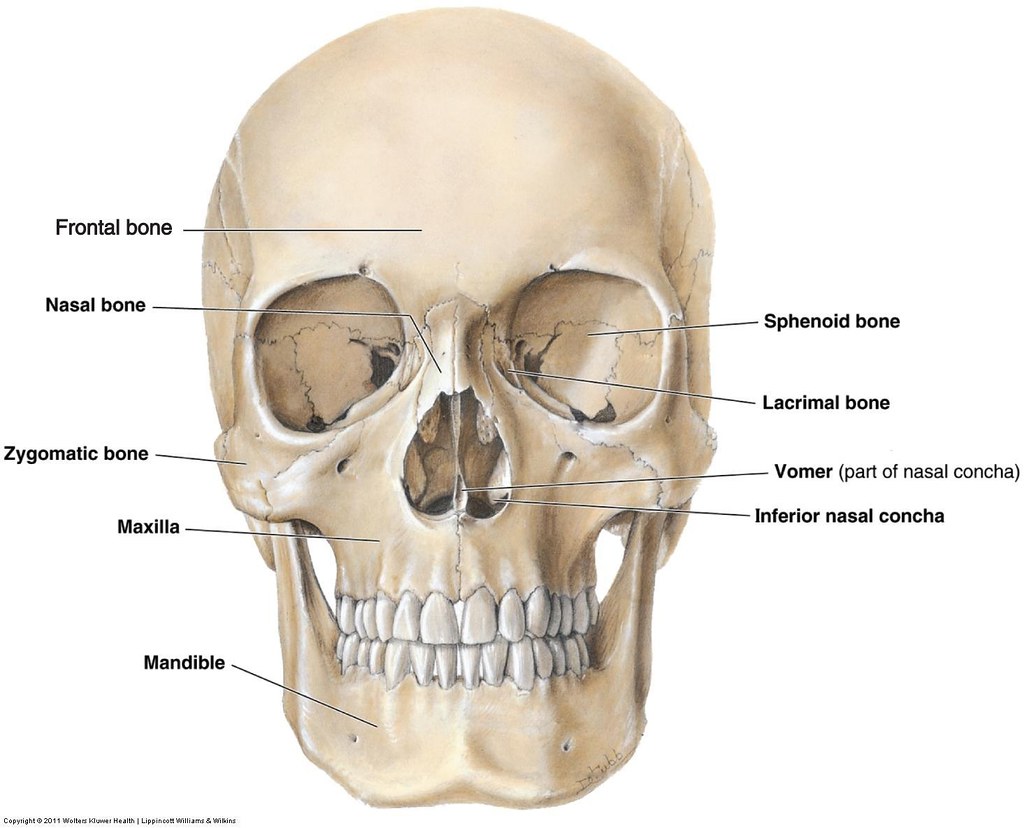
- Lacrimal Bones: These small paired bones are located in the medial wall of the orbit and contain the lacrimal groove, which helps drain tears.
- Palatine Bones: These paired bones contribute to the posterior part of the hard palate, the floor of the nasal cavity, and the orbit.
- Inferior Nasal Conchae: These scroll-shaped bones project into the nasal cavity and help to humidify and filter air.
- Vomer: This single bone forms the inferior and posterior part of the nasal septum, dividing the nasal cavity into two halves.
Distinguishing Facial Bones from Cranial Bones
A common point of confusion is differentiating between facial bones and cranial bones. Cranial bones primarily protect the brain, while facial bones provide structural support for the face and sensory organs.
Cranial Bones
Examples of cranial bones include:
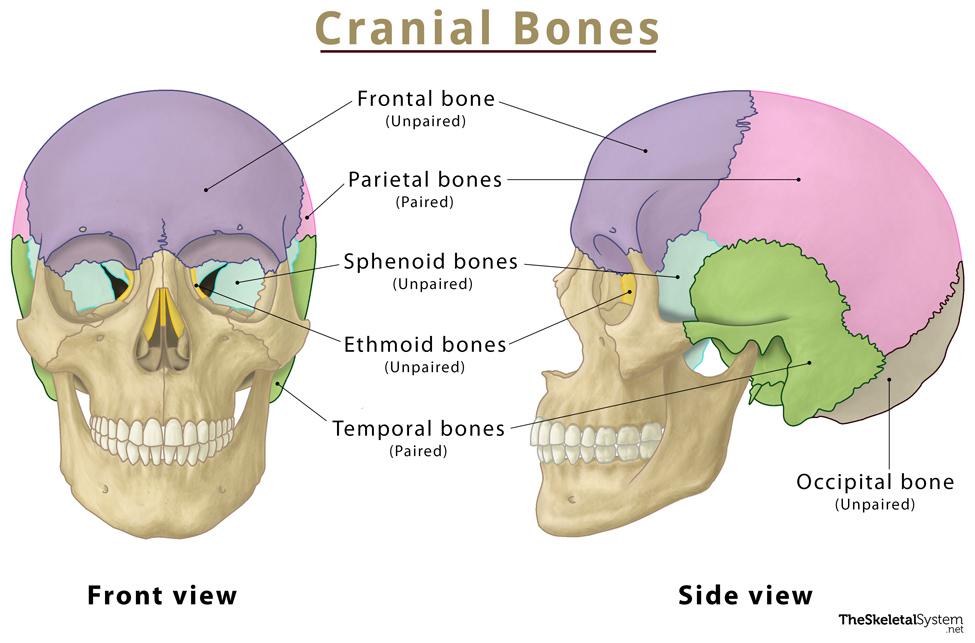
- Frontal Bone: Forms the forehead and the upper part of the eye sockets.
- Parietal Bones: Form the sides and roof of the cranium.
- Temporal Bones: Form the sides and base of the cranium and house the inner ear structures.
- Occipital Bone: Forms the back of the skull and the base of the cranium.
- Sphenoid Bone: A complex bone that forms part of the base of the skull, the orbits, and the sides of the skull.
- Ethmoid Bone: Located between the orbits, it forms part of the nasal cavity and the orbit walls. While the ethmoid bone contributes to the structure around the nasal cavity and orbit, it is generally classified as a cranial bone due to its position and primary function of supporting the braincase.
While some bones, like the ethmoid and sphenoid, contribute to both the cranial cavity and structures related to the face (like the orbits), they are still considered part of the cranium. The key differentiator lies in the bone's primary protective function for the brain.
Examples and Context
Consider these examples to solidify your understanding:
If the question asks: "Which of the following is a facial bone: Frontal, Parietal, Maxilla, Temporal?" The correct answer is Maxilla.
The maxilla directly contributes to the structure of the face, specifically the upper jaw. The other options, frontal, parietal, and temporal, are cranial bones protecting the brain.
Another example: "Which is part of the facial skeleton: Occipital, Zygomatic, Sphenoid, Ethmoid?" The correct answer is Zygomatic.
The zygomatic bone forms the cheekbone and is a clear component of the facial structure. The other bones are primarily associated with the cranium, even though the sphenoid and ethmoid have some orbital involvement.
Potential Pitfalls and Misconceptions
It's crucial to avoid common misconceptions:
- Confusing orbital bones: While the frontal, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones contribute to the orbit, the lacrimal and zygomatic bones are specifically facial bones involved in forming the orbit.
- Overlooking smaller bones: Don't forget the nasal bones, lacrimal bones, inferior nasal conchae, palatine bones and the vomer, which are all critical parts of the facial skeleton.
- Misclassifying jaw components: The mandible (lower jaw) is a facial bone, while the bones that house the inner ear (within the temporal bone) are cranial.
Remembering the distinct functions of cranial versus facial bones helps to avoid these pitfalls.
The Importance of Anatomical Knowledge
Understanding facial bone anatomy is critical in various fields:
- Medicine: Surgeons, radiologists, and dentists require precise knowledge for diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical procedures.
- Forensic Science: Facial reconstruction and identification often rely on accurate skeletal knowledge.
- Anthropology: Studying skull morphology provides insights into human evolution and population history.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers benefit from understanding the underlying skeletal structure to accurately depict facial features.
The implications of inaccurate identification can range from misdiagnosis in a medical setting to flawed reconstruction in forensic anthropology.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways
Accurately identifying facial bones hinges on understanding the fundamental difference between the cranium and the facial skeleton. The facial skeleton provides the structural framework of the face, supports sensory organs, and facilitates functions like chewing and facial expression. Key facial bones include the maxilla, mandible, nasal bones, zygomatic bones, lacrimal bones, palatine bones, inferior nasal conchae, and vomer.
To ensure you can successfully determine which of several options is a facial bone, remember the following:
- Facial bones primarily define the structure of the face.
- Cranial bones primarily protect the brain.
- Some bones contribute to both, but their primary function dictates their classification.
- Pay attention to the specific roles and locations of each bone within the skull.
By grasping these key points, you can confidently identify facial bones in various contexts and appreciate the intricate architecture of the human skull.