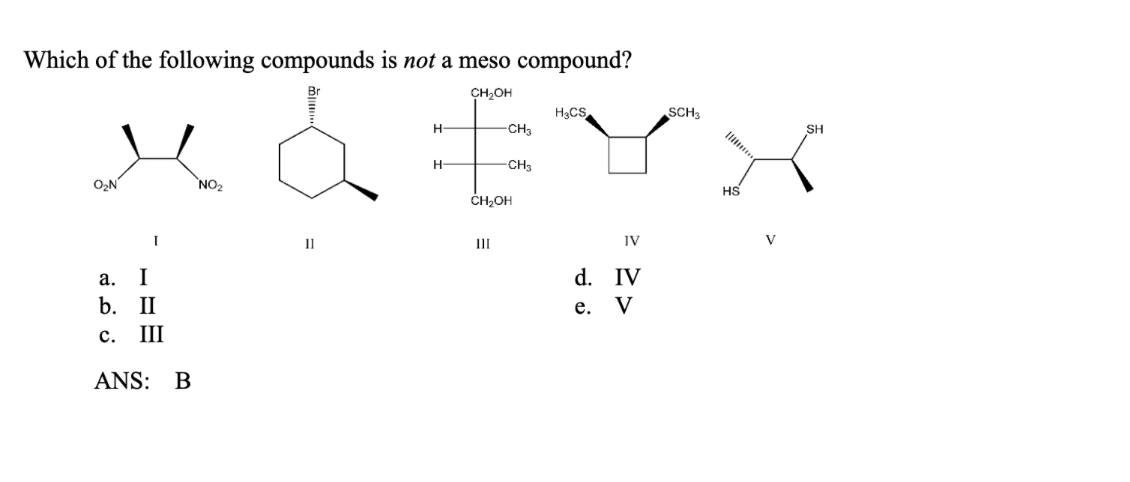
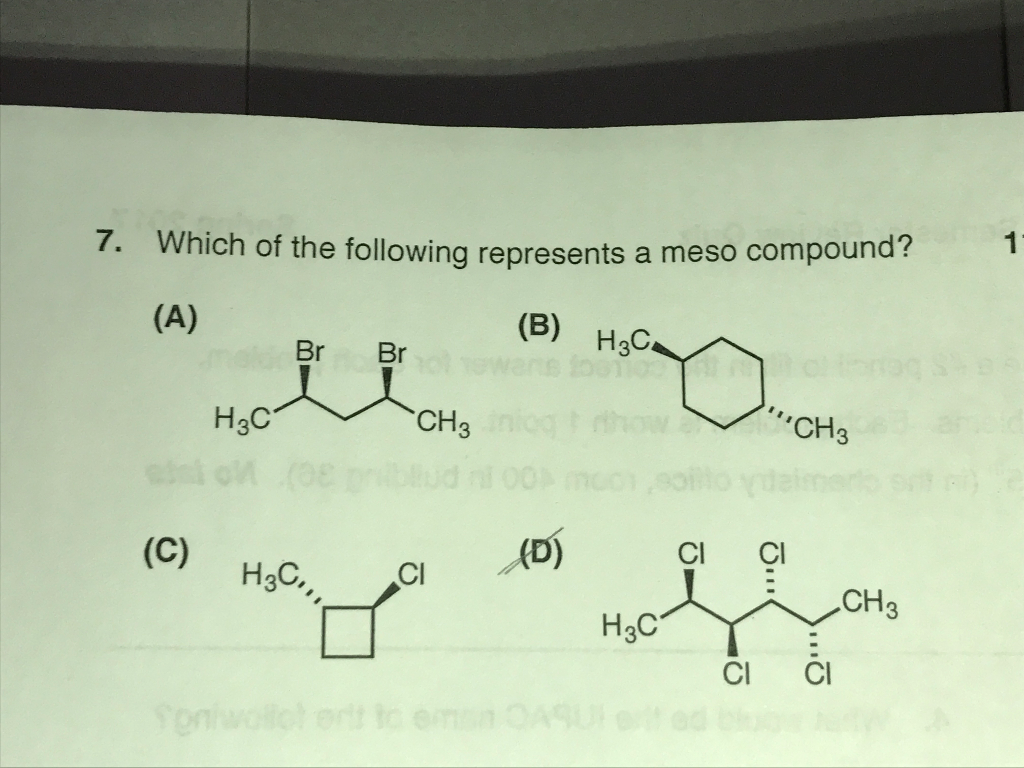
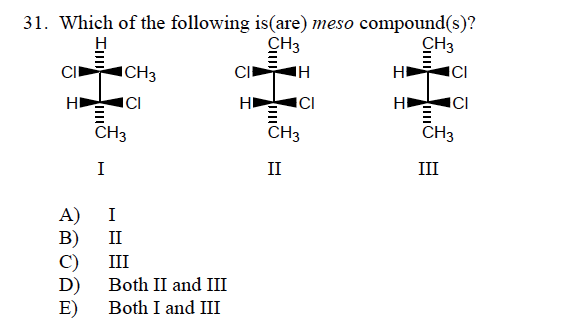
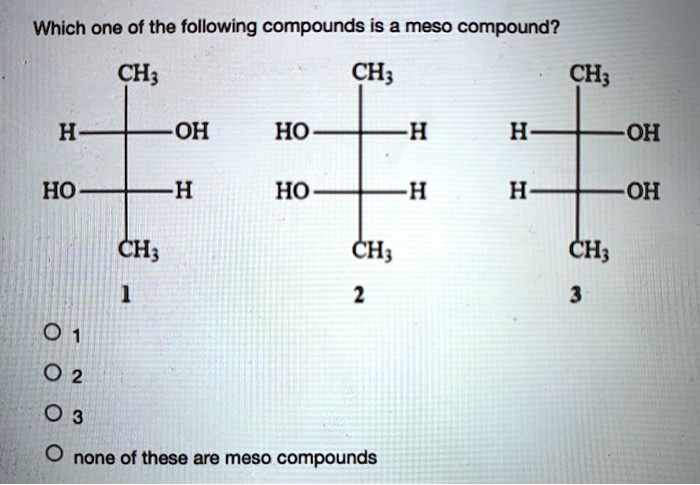
Meso compounds are a fascinating aspect of stereochemistry, and understanding them can be surprisingly useful in various real-world scenarios, even if you're not a chemist by profession. The key lies in recognizing symmetry within molecules.
Identifying Meso Compounds: A Practical Guide
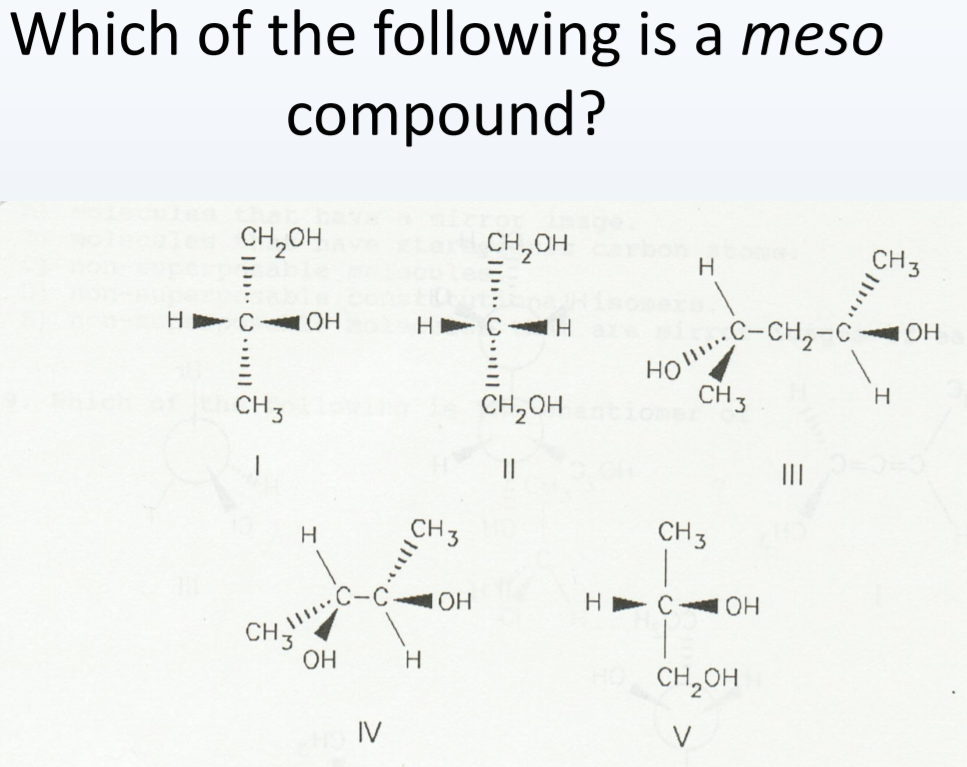
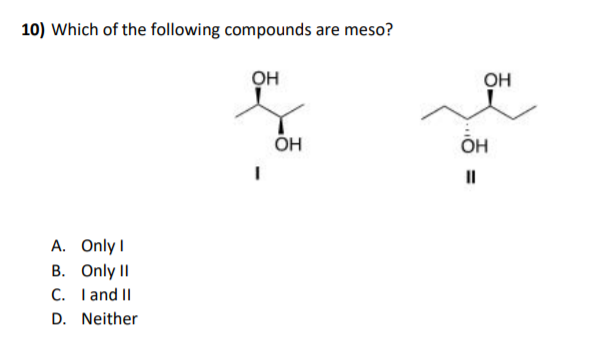
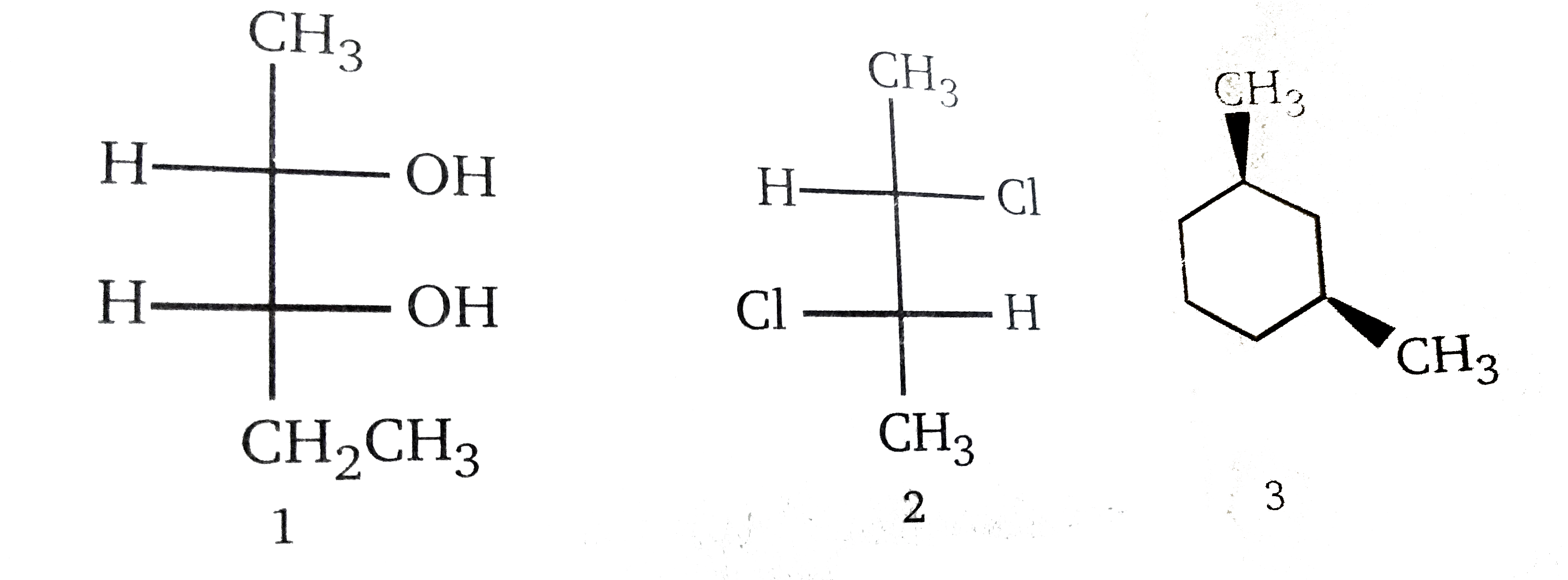
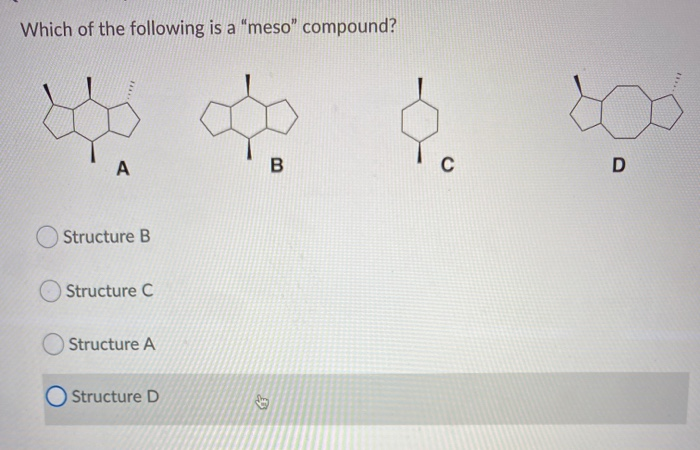
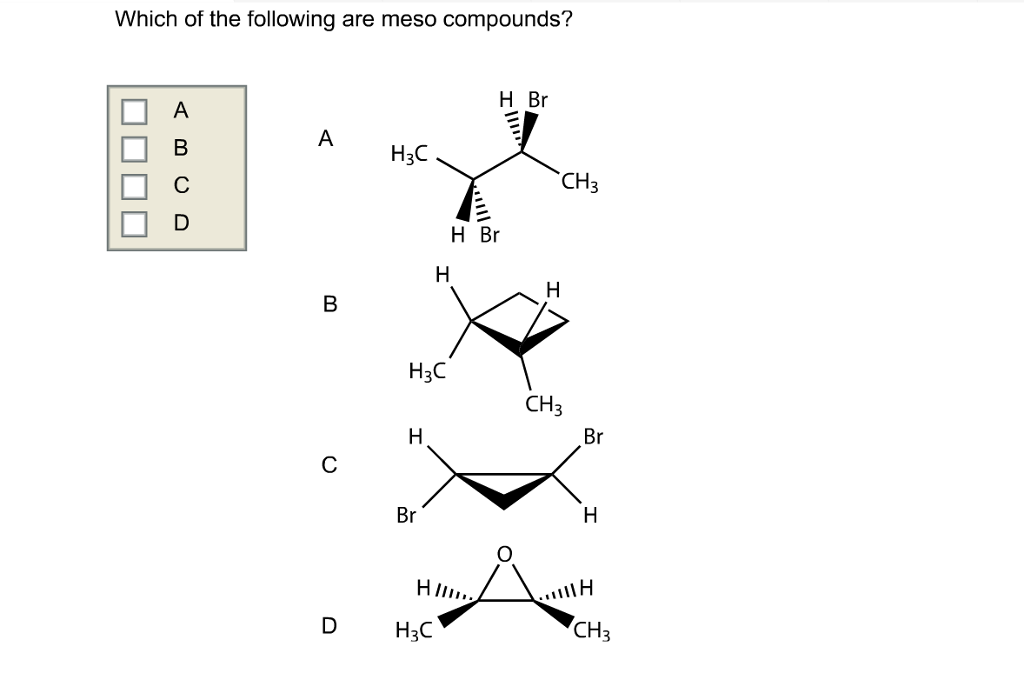
A meso compound is essentially an achiral (non-chiral) molecule that contains chiral centers. This might sound contradictory, but the crucial element is the presence of an internal plane of symmetry or a center of inversion. This symmetry cancels out the chirality of the individual chiral centers, rendering the overall molecule achiral. Here's how to spot them:
Step 1: Identify Chiral Centers
A chiral center (also called a stereocenter) is a carbon atom bonded to four different groups. This is the foundation. To identify it, examine each carbon atom in the molecule. Is it attached to four unique substituents? If so, it's potentially a chiral center. Mark these carbons clearly.
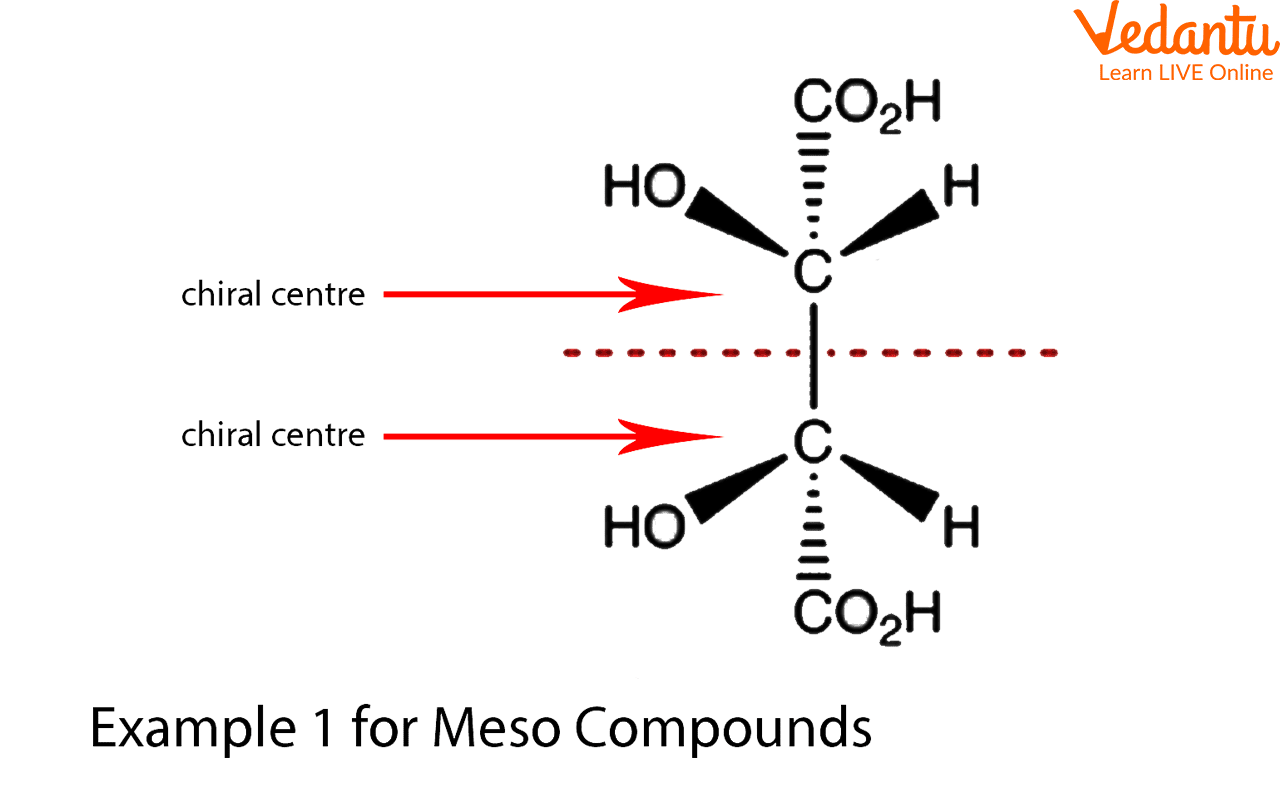
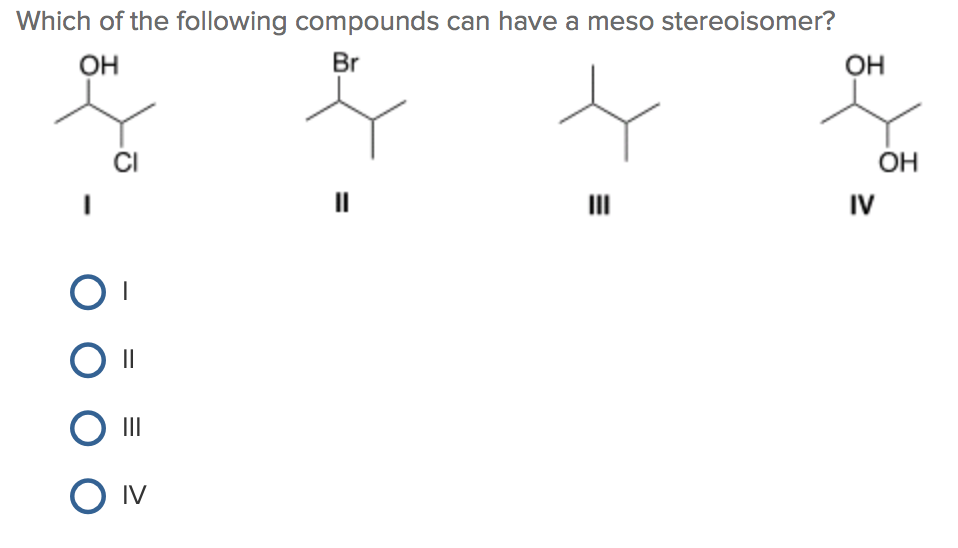
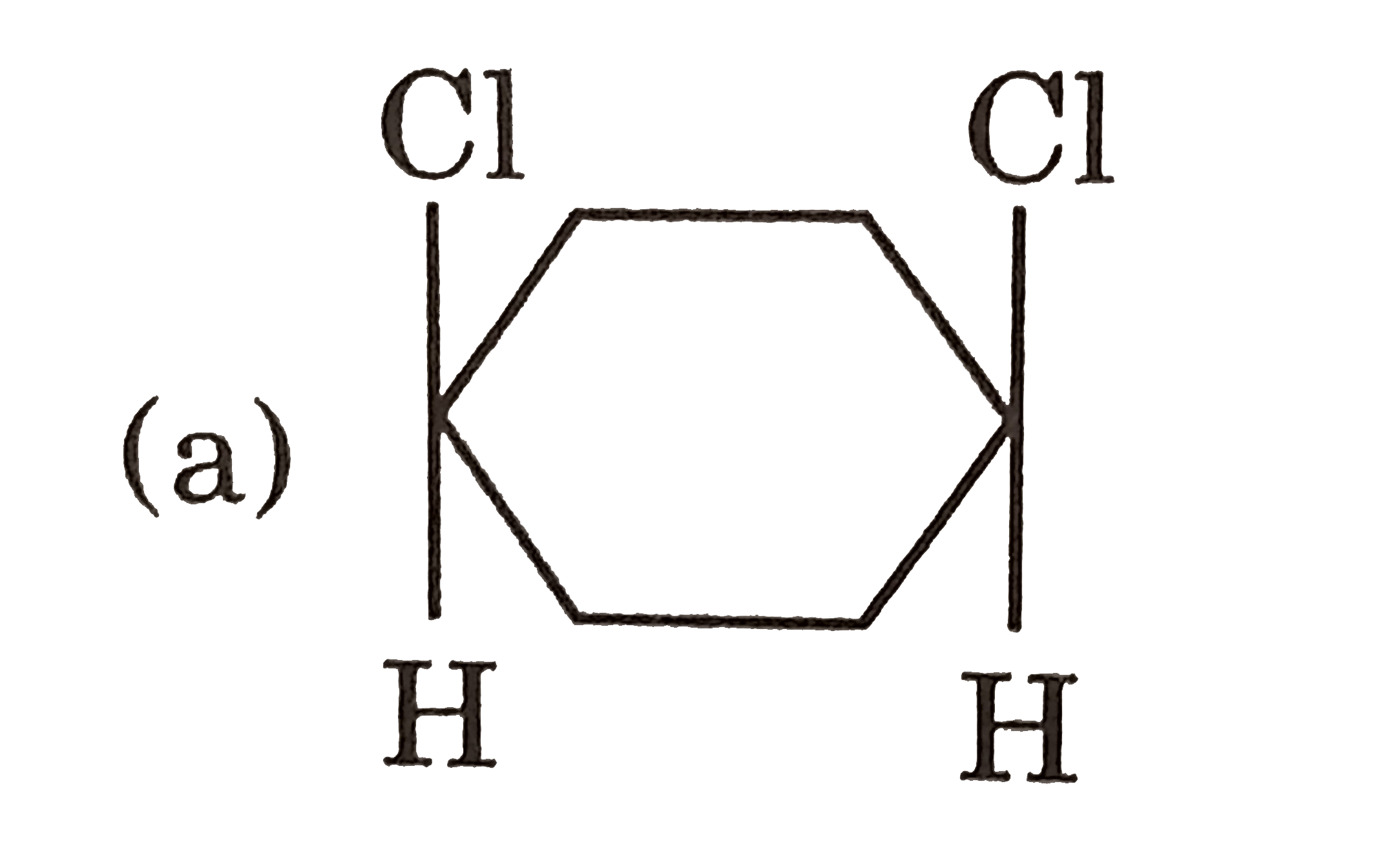
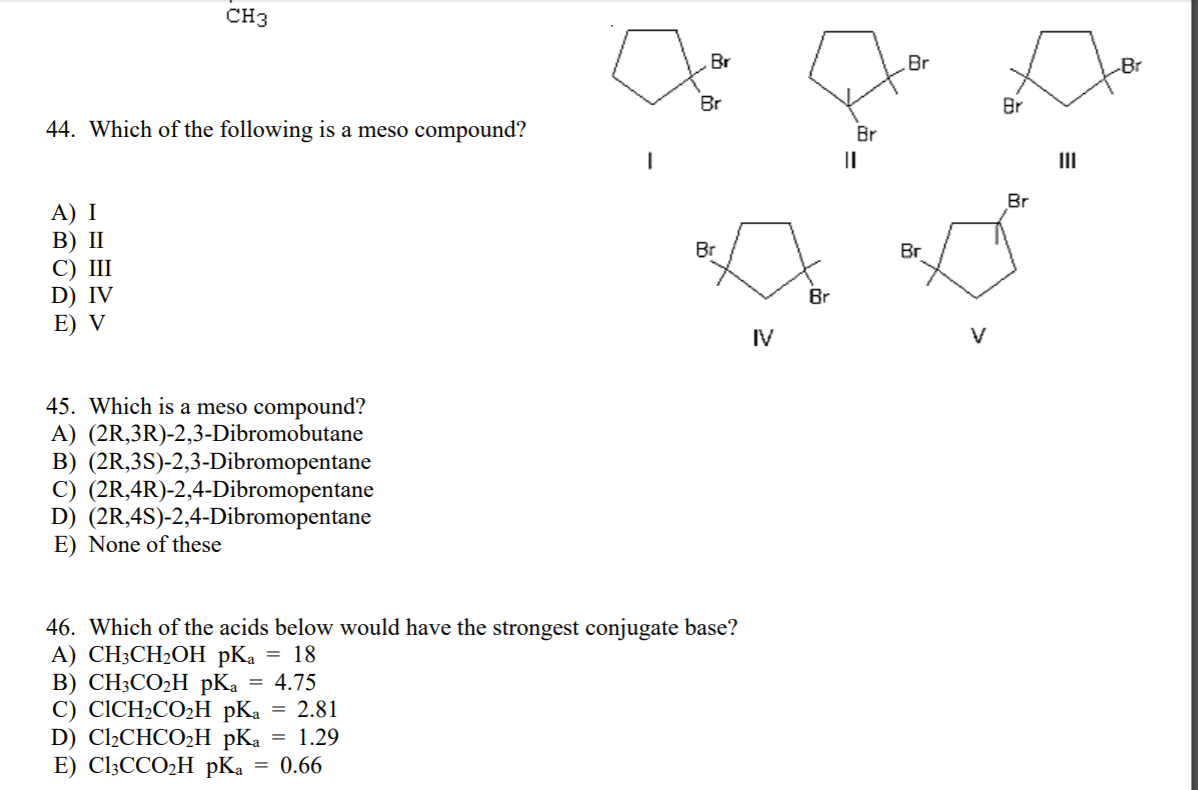
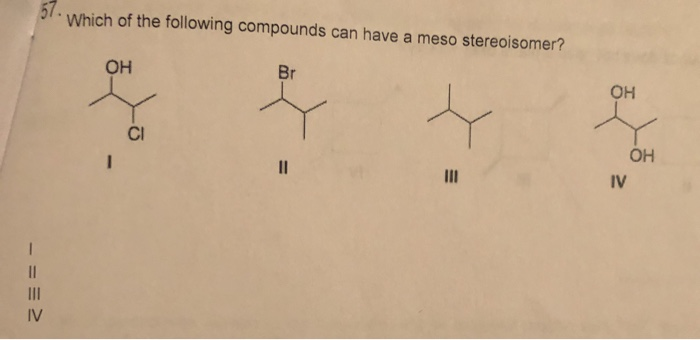
Example: Consider 2,3-dichlorobutane. Carbon 2 is attached to a chlorine atom, a hydrogen atom, a methyl group (CH3), and the rest of the molecule (CHCl-CH3). Similarly, carbon 3 is also attached to four different groups. Therefore, carbons 2 and 3 are chiral centers.
Step 2: Look for Symmetry
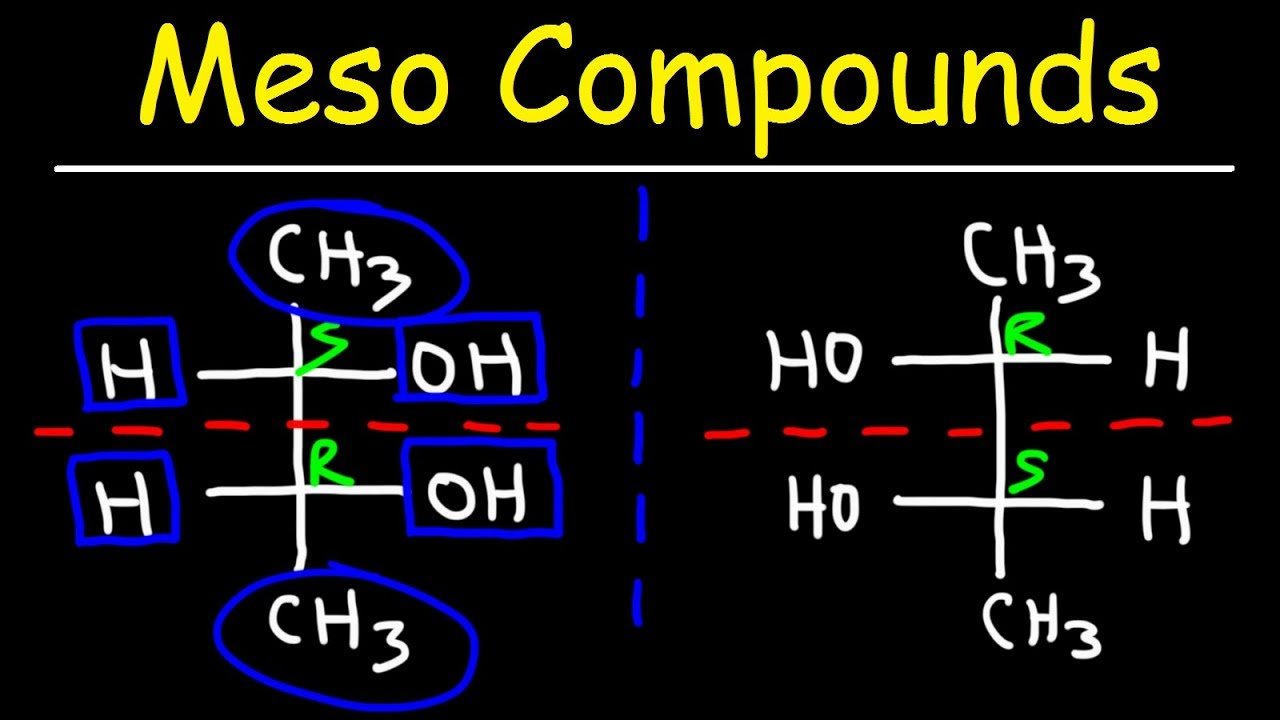
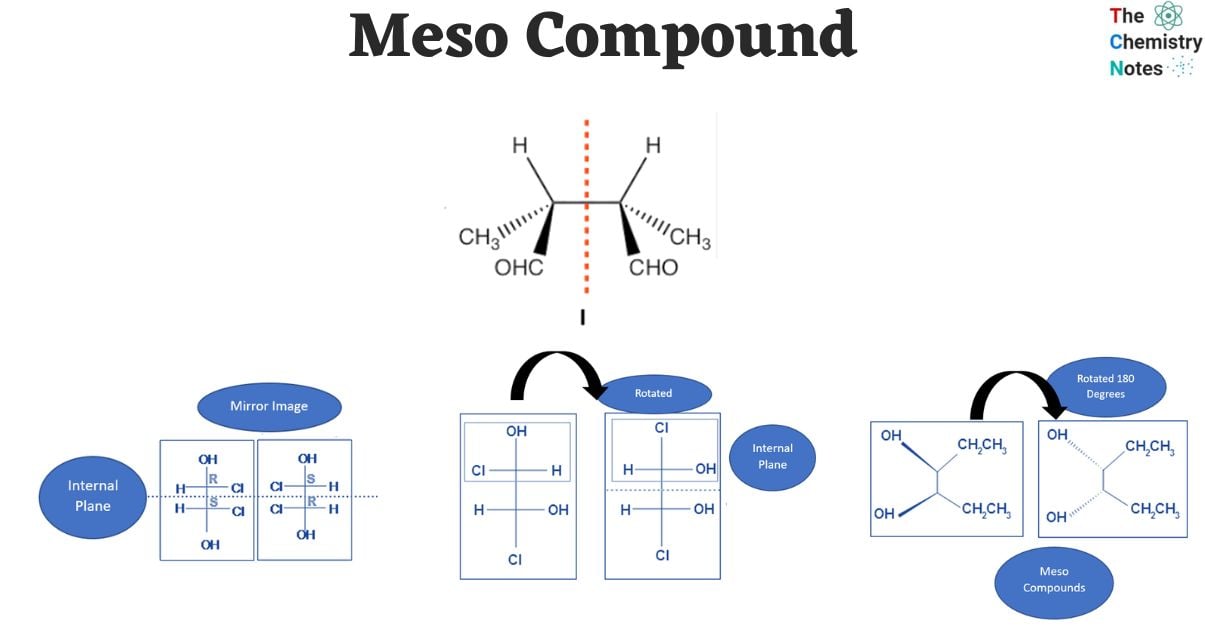
This is the heart of meso compound identification. Once you've identified potential chiral centers, look for an internal plane of symmetry. Imagine slicing the molecule in half. If one half is a mirror image of the other half across that plane, then you have a meso compound. This symmetry essentially "cancels out" the individual chiral centers.
Practical Tip: It's often easier to visualize this with molecular models (even virtual ones). Playing around with rotations can help you see if a plane of symmetry exists. If models aren't available, draw the molecule carefully, paying close attention to the spatial arrangement of atoms. Newman projections can also be incredibly helpful.
Step 3: Confirm Achirality
A meso compound, by definition, is achiral. This means it's superimposable on its mirror image. If you can't find a plane of symmetry, double-check to see if the molecule, as a whole, is superimposable on its mirror image. If it is, then it's not a chiral molecule.
Important Note: Don't confuse a meso compound with a racemic mixture. A racemic mixture is an equimolar mixture of two enantiomers (non-superimposable mirror images). Meso compounds are *single* molecules with internal symmetry. A racemic mixture involves *two different* molecules.
Step 4: Consider Different Representations
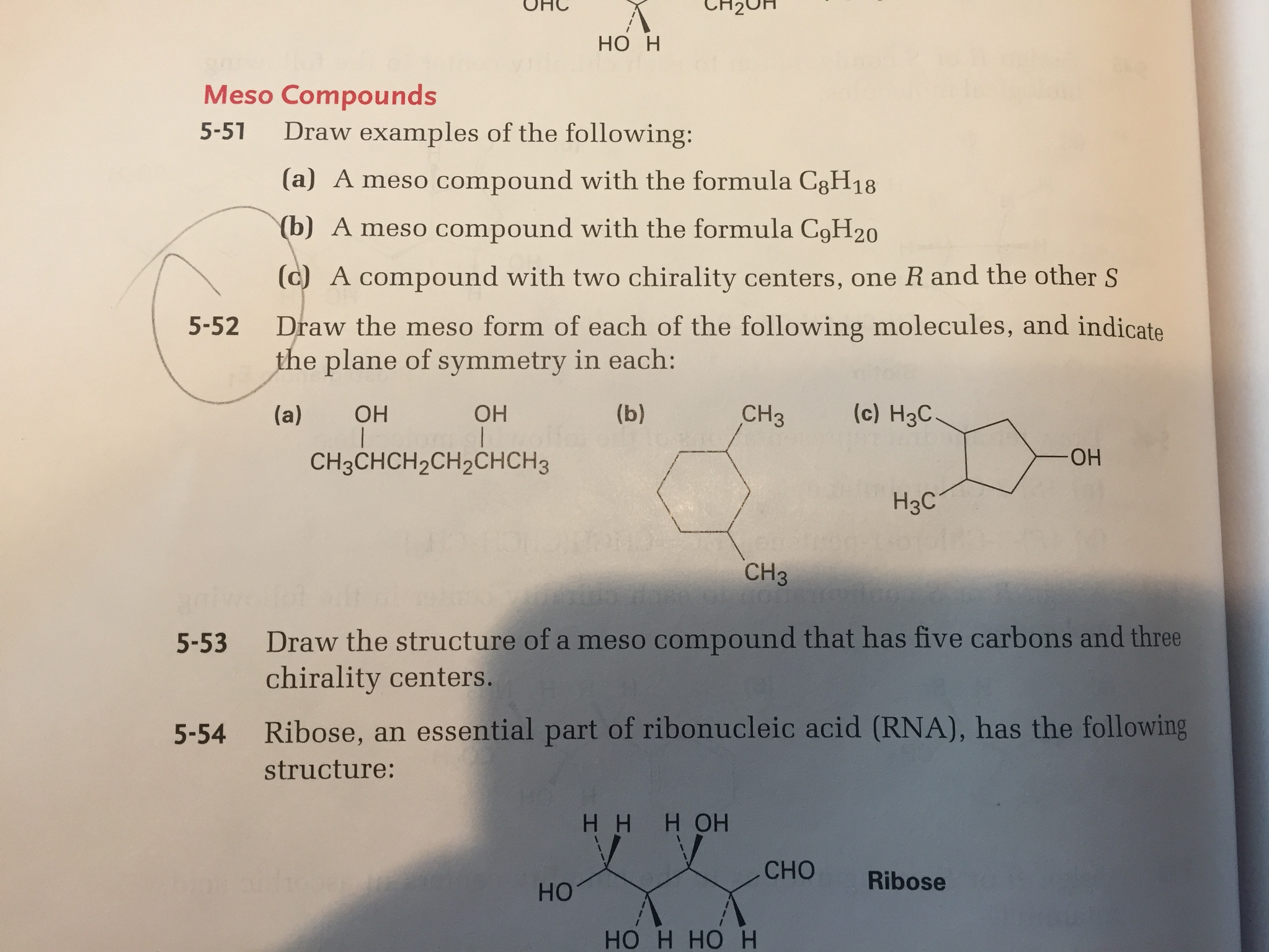
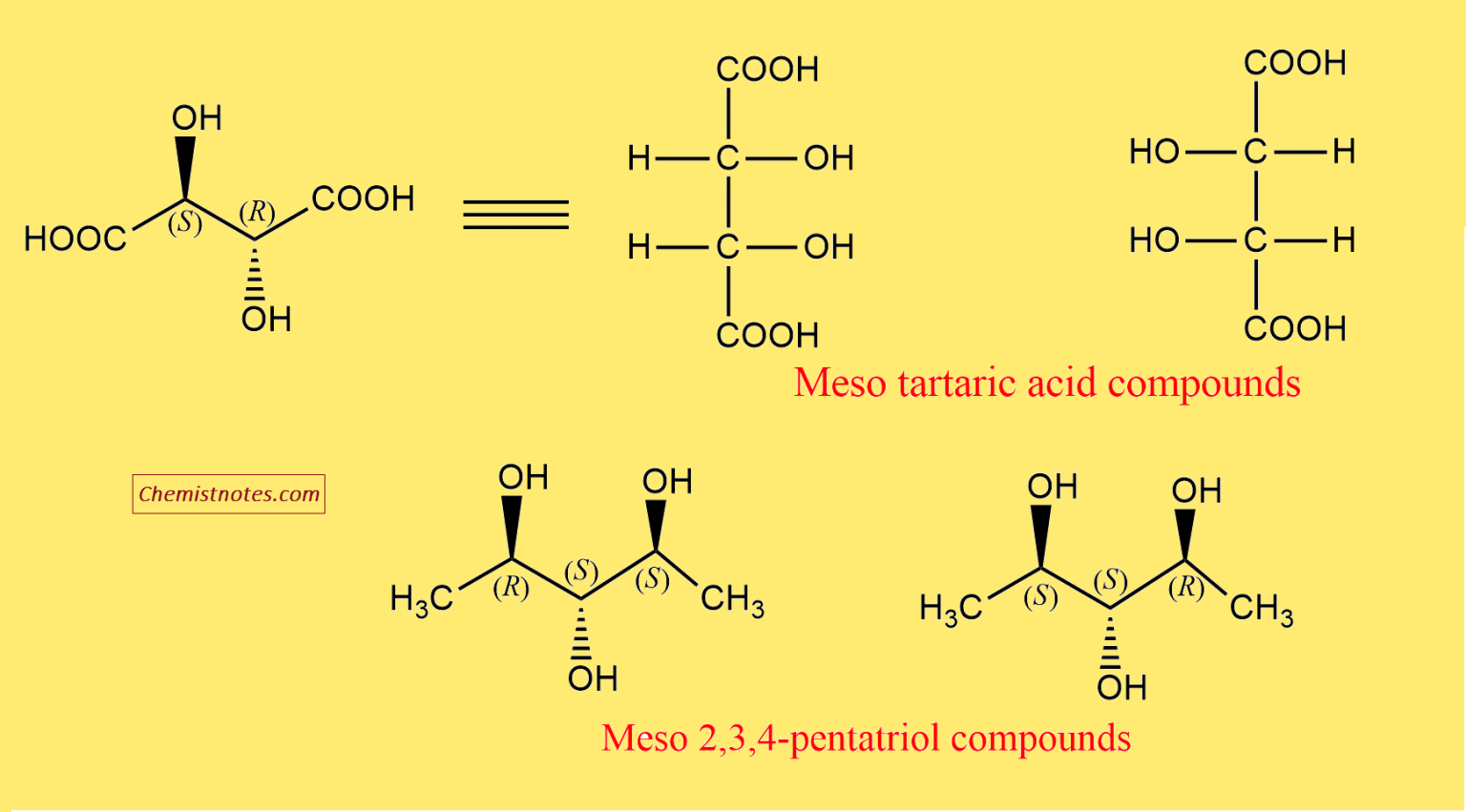
Sometimes, the symmetry of a meso compound is not immediately apparent in a particular drawing. It's often helpful to rotate the molecule or redraw it in a different conformation (e.g., from a sawhorse projection to a Fischer projection) to make the plane of symmetry more obvious. Fischer projections are particularly useful for identifying meso compounds with multiple chiral centers on a chain.
Example: In a Fischer projection, a meso compound will have the same substituents on the top and bottom, and a horizontal plane of symmetry is easy to visualize.
Real-World Applications (Beyond the Chemistry Lab)
While the direct application of identifying meso compounds may seem limited to chemistry labs, the underlying principle – recognizing symmetry and its impact on properties – is incredibly valuable in various fields:
- Pharmaceuticals: The stereochemistry of drug molecules is critical. Different stereoisomers can have vastly different biological activities. Understanding meso compounds and chirality helps in designing and synthesizing drugs with the desired effect and minimizing potential side effects. For example, if a target receptor in the body is chiral, it will interact differently with different stereoisomers of a drug. Recognizing that a compound might exist as a meso form (and thus be achiral) is important for ensuring the correct interaction.
- Materials Science: The properties of polymers and other materials are often influenced by their stereochemistry. The arrangement of monomers in a polymer chain can affect its strength, flexibility, and other characteristics. Understanding symmetry and chirality can help in designing materials with specific properties.
- Food Science: The flavor and aroma of food are often determined by chiral molecules. The ability to distinguish between different stereoisomers is crucial for creating and enhancing flavors. For example, some amino acids exist as stereoisomers, and they contribute differently to the overall taste profile of a food product.
- Forensic Science: Chiral molecules can be used as forensic markers. The ratio of different stereoisomers in a sample can provide clues about its origin and history. For example, the stereochemical analysis of drugs or explosives can help in identifying their source.
- Problem Solving in General: The ability to recognize patterns, symmetry, and asymmetry is a fundamental skill that applies to many areas of life. Whether you're designing a building, organizing a project, or simply trying to understand a complex situation, the principles of stereochemistry can help you to see things from a different perspective.
Even without formal chemistry training, appreciating the concepts of chirality and symmetry can enhance your critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Learning to identify spatial relationships and predict how these relationships influence properties is transferable to countless situations.
Meso Compound Identification Checklist
Use this checklist to confidently identify meso compounds:
- Identify all chiral centers: Look for carbons bonded to four different groups.
- Search for a plane of symmetry: Can you slice the molecule in half so that one half is a mirror image of the other?
- Confirm achirality: Is the molecule superimposable on its mirror image?
- Consider different representations: Rotate the molecule or draw it in a different conformation to reveal symmetry.
- Distinguish from racemic mixtures: Is it a single molecule with internal symmetry or a mixture of two enantiomers?
By consistently applying these steps, you'll be well-equipped to identify meso compounds and appreciate the role of symmetry in determining molecular properties.